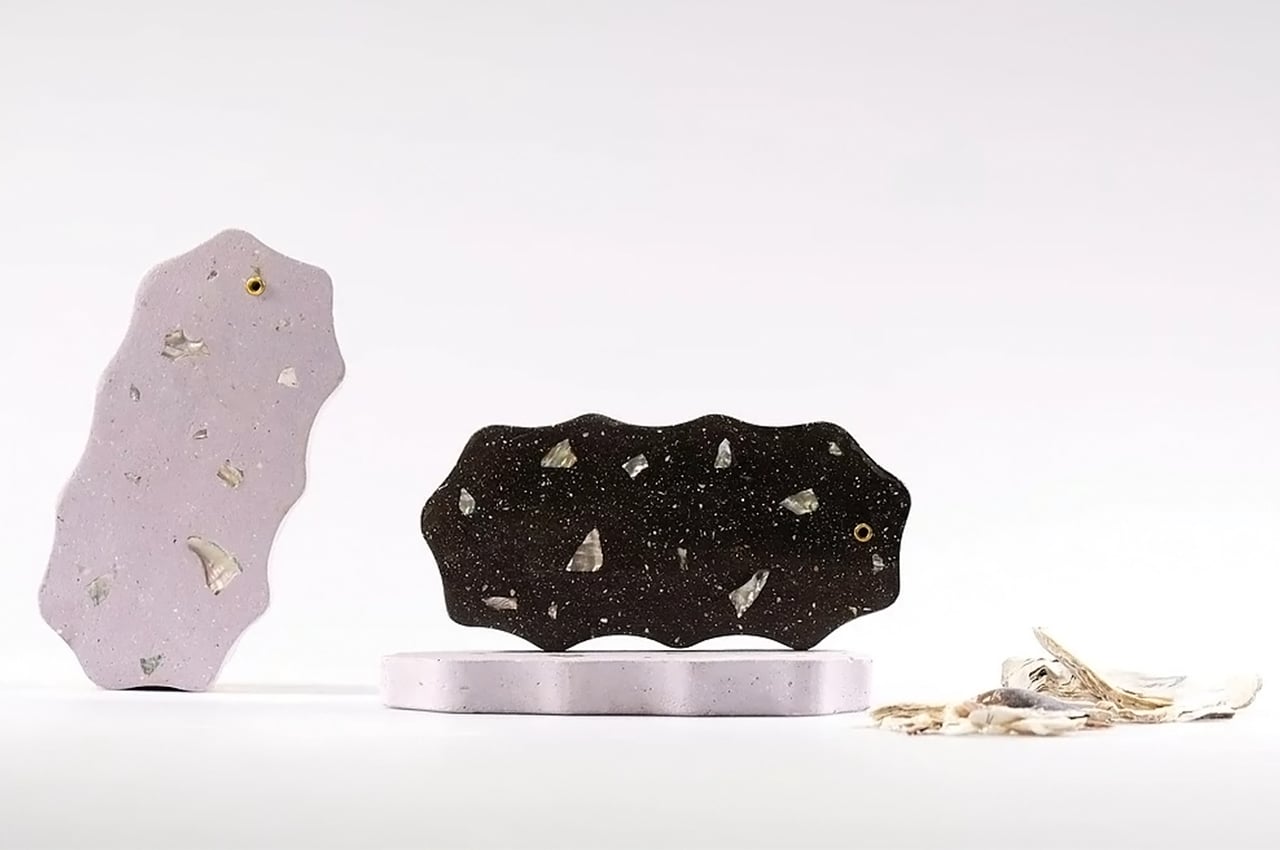
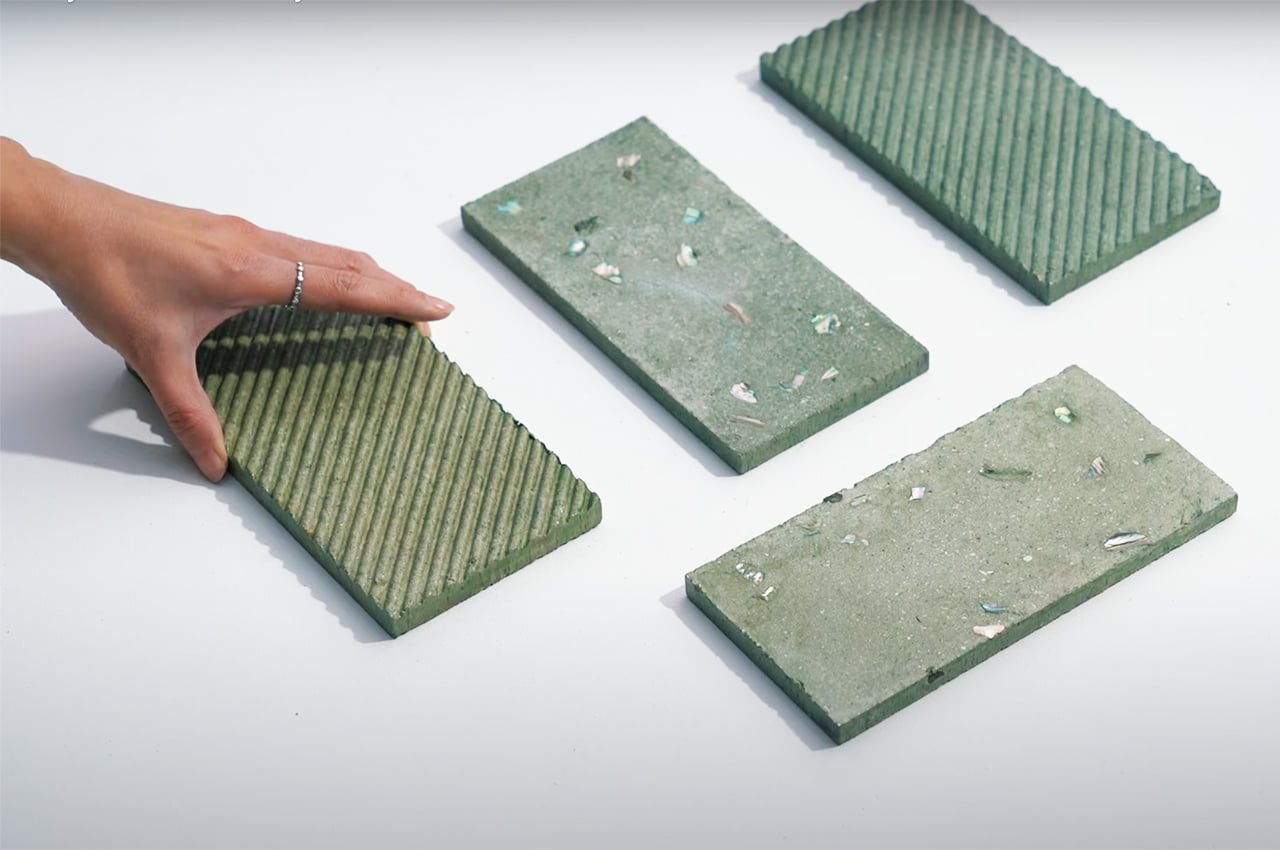
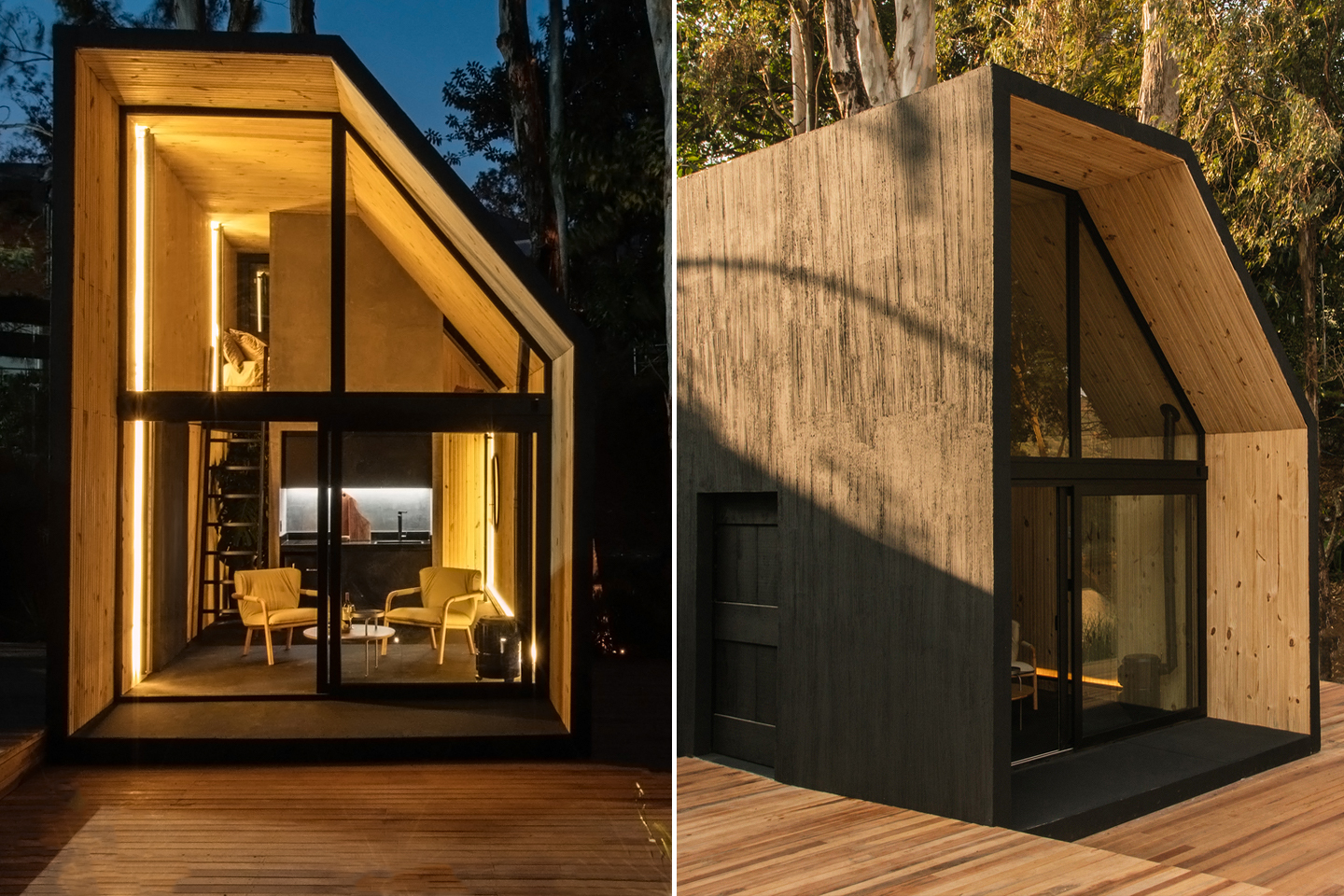
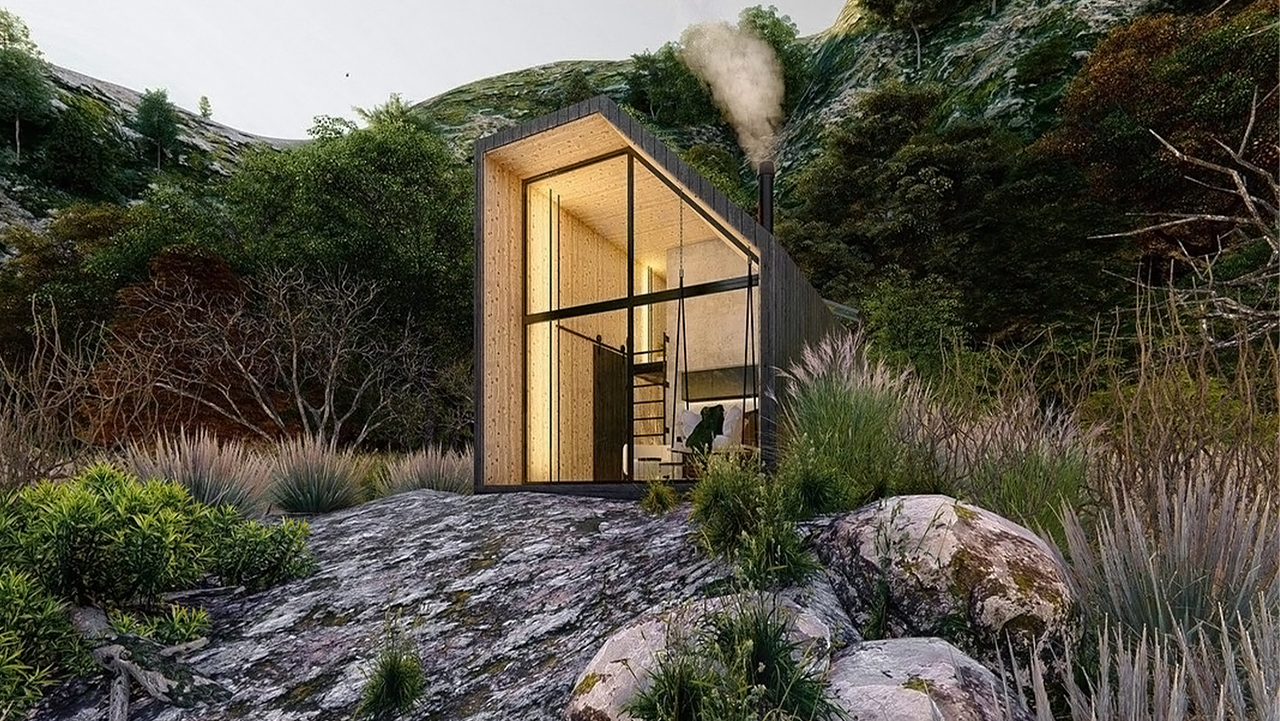
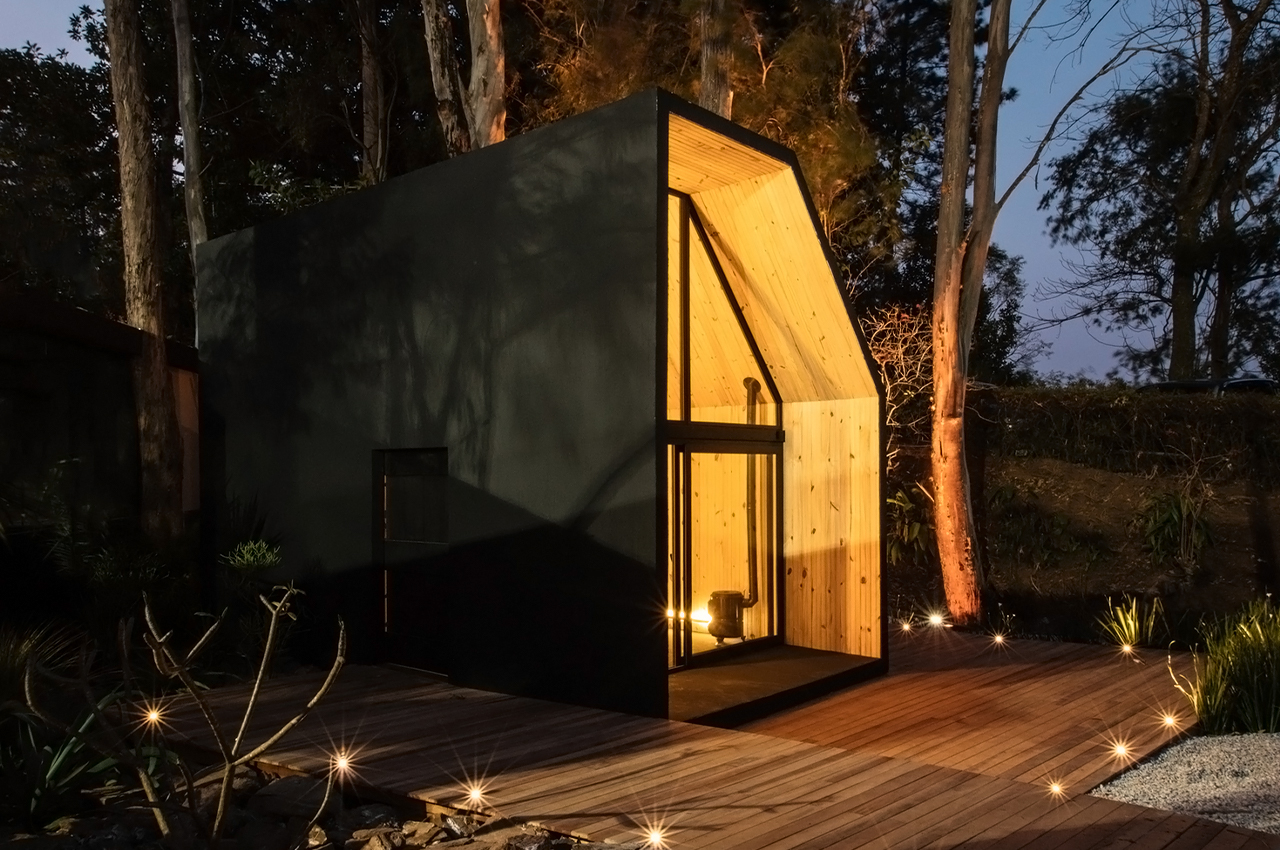
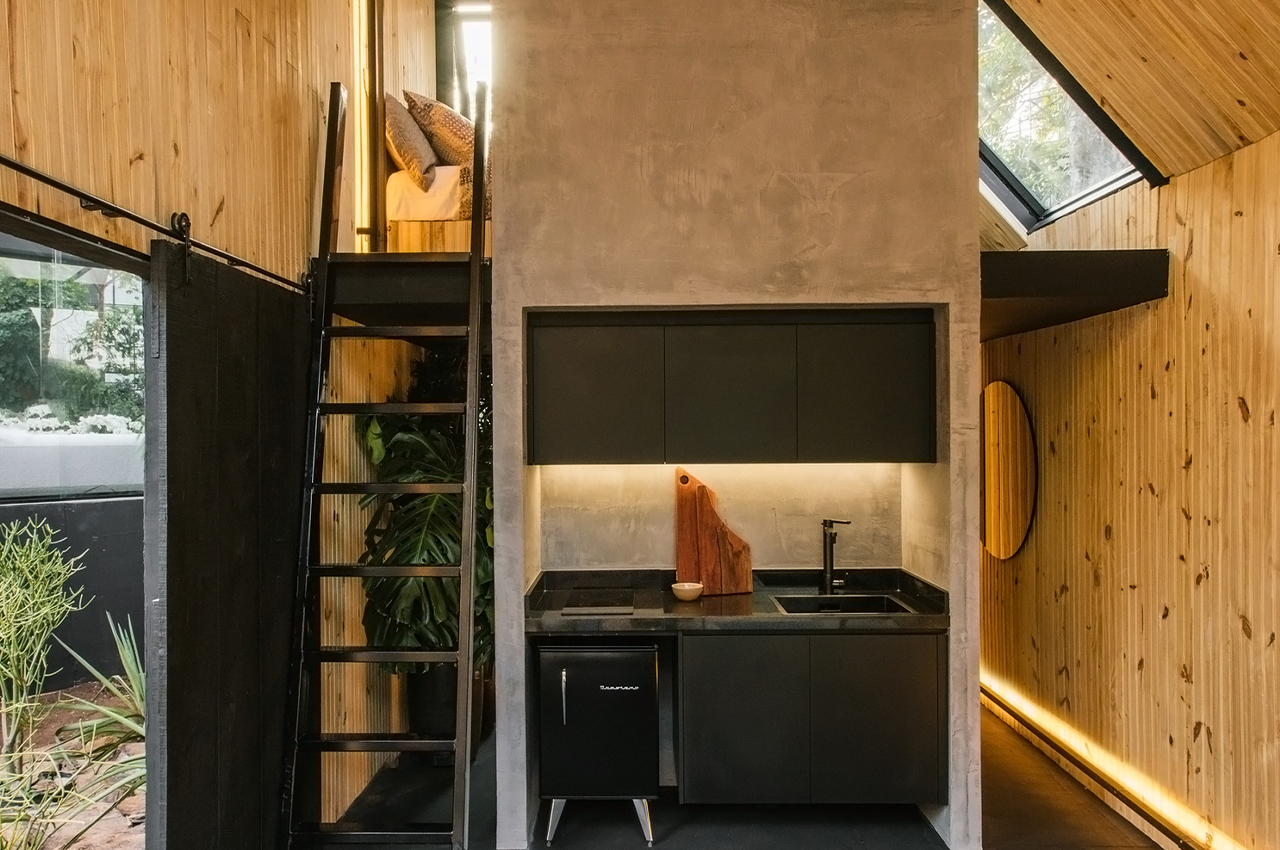
Each year over 7 million tons of seashells are thrown away by the seafood industry into landfills. Shells are not biodegradable and have a very high disposal cost which harms the environment as well as the restaurant owners. So this innovative, women-run, material lab called Newtab-22 created Sea Stone – a natural product made from seashell waste that was salvaged from the seafood and aquaculture industries. It is a sustainable alternative to using concrete – one of the biggest producers of carbon emissions – in the making of smaller products.
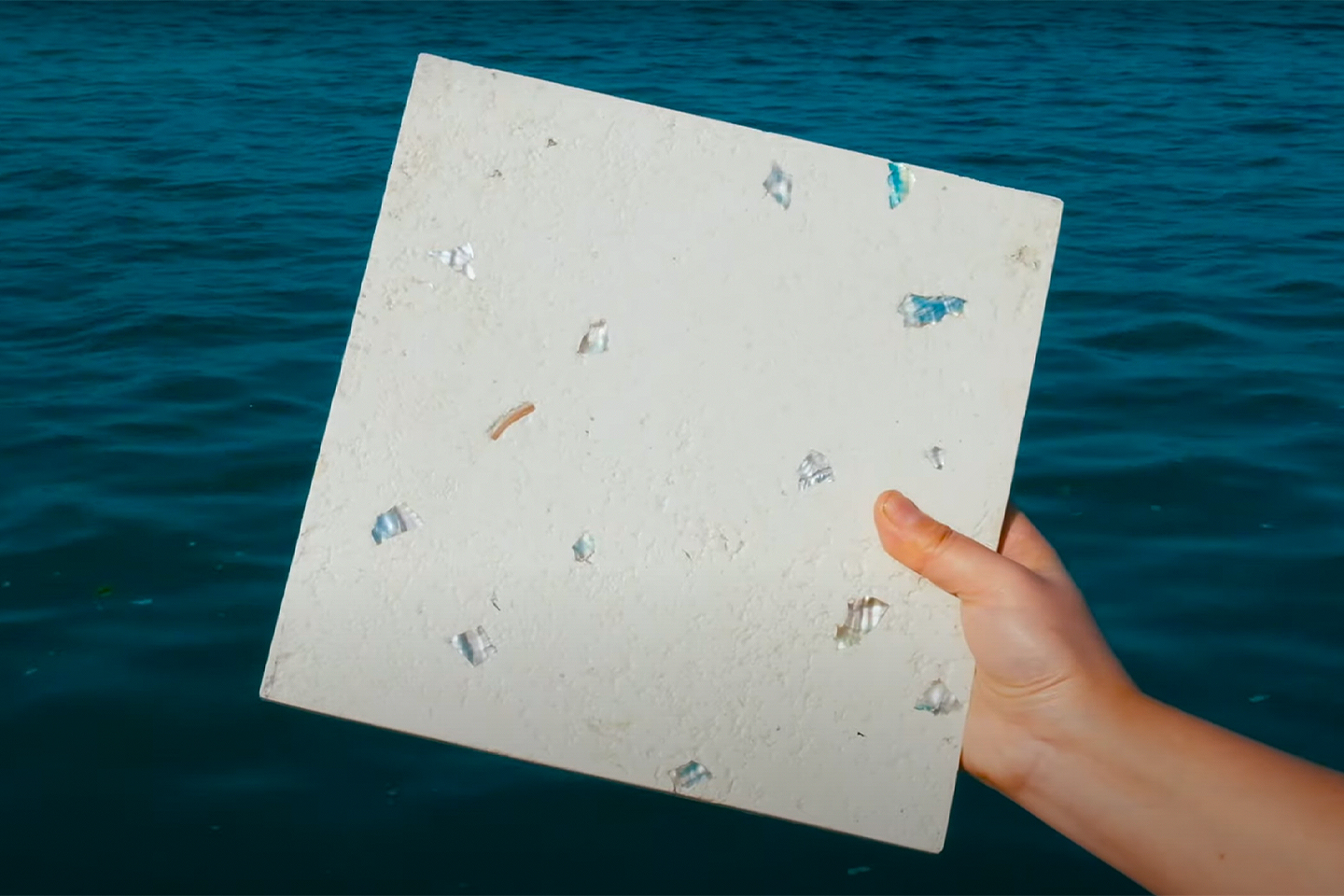

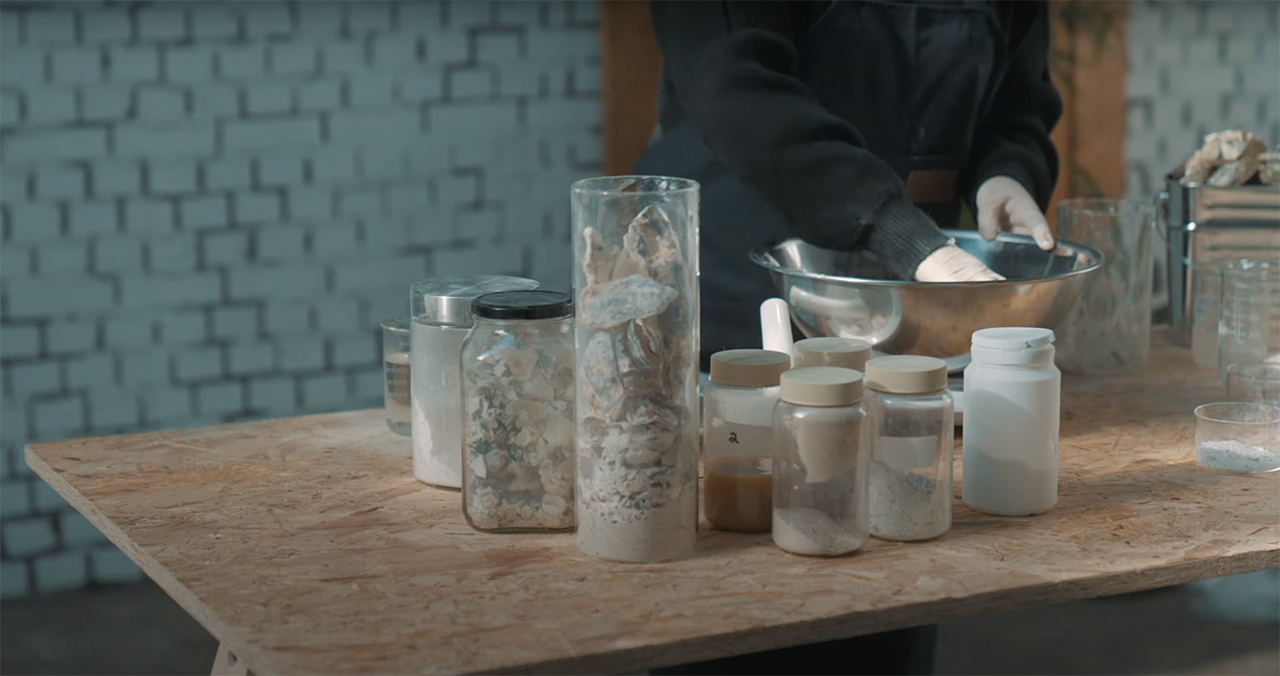
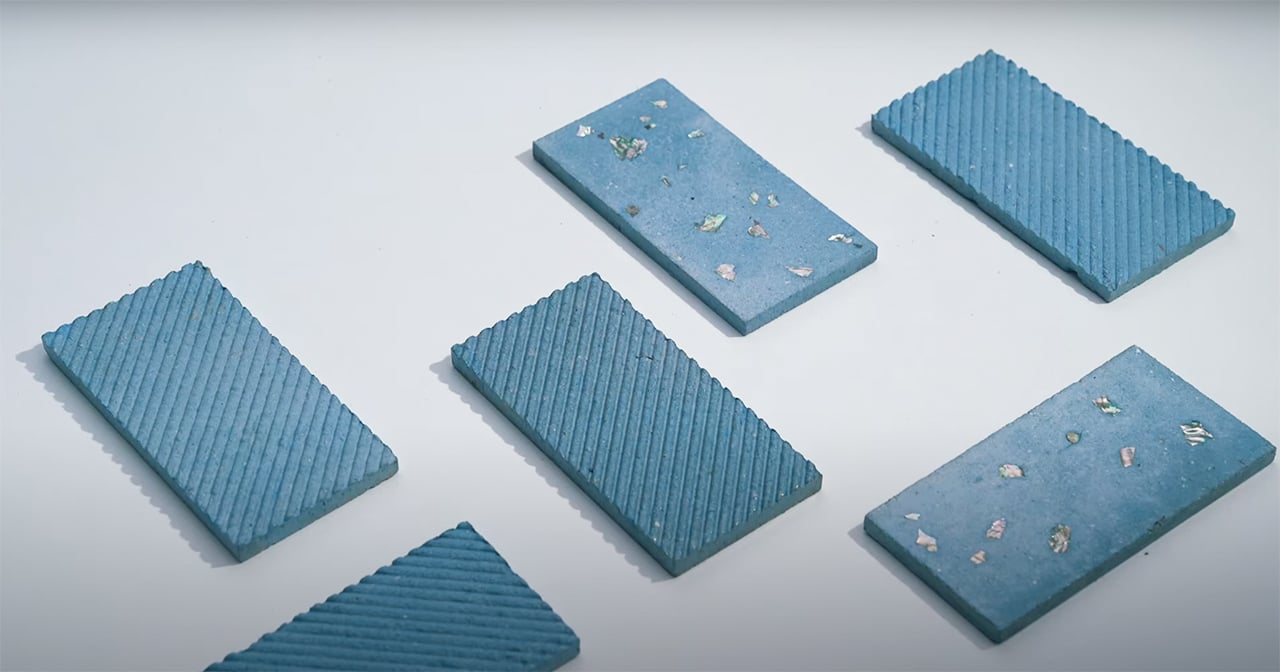
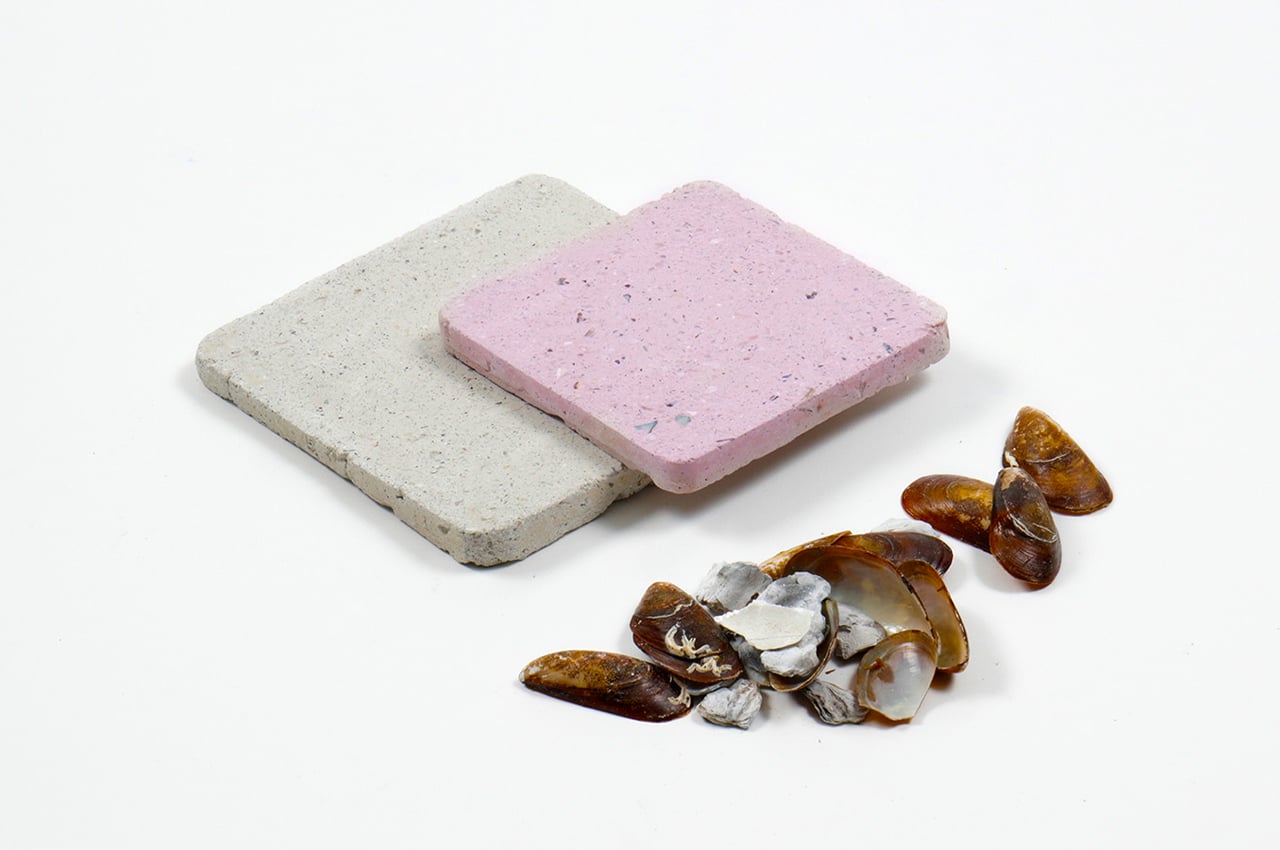
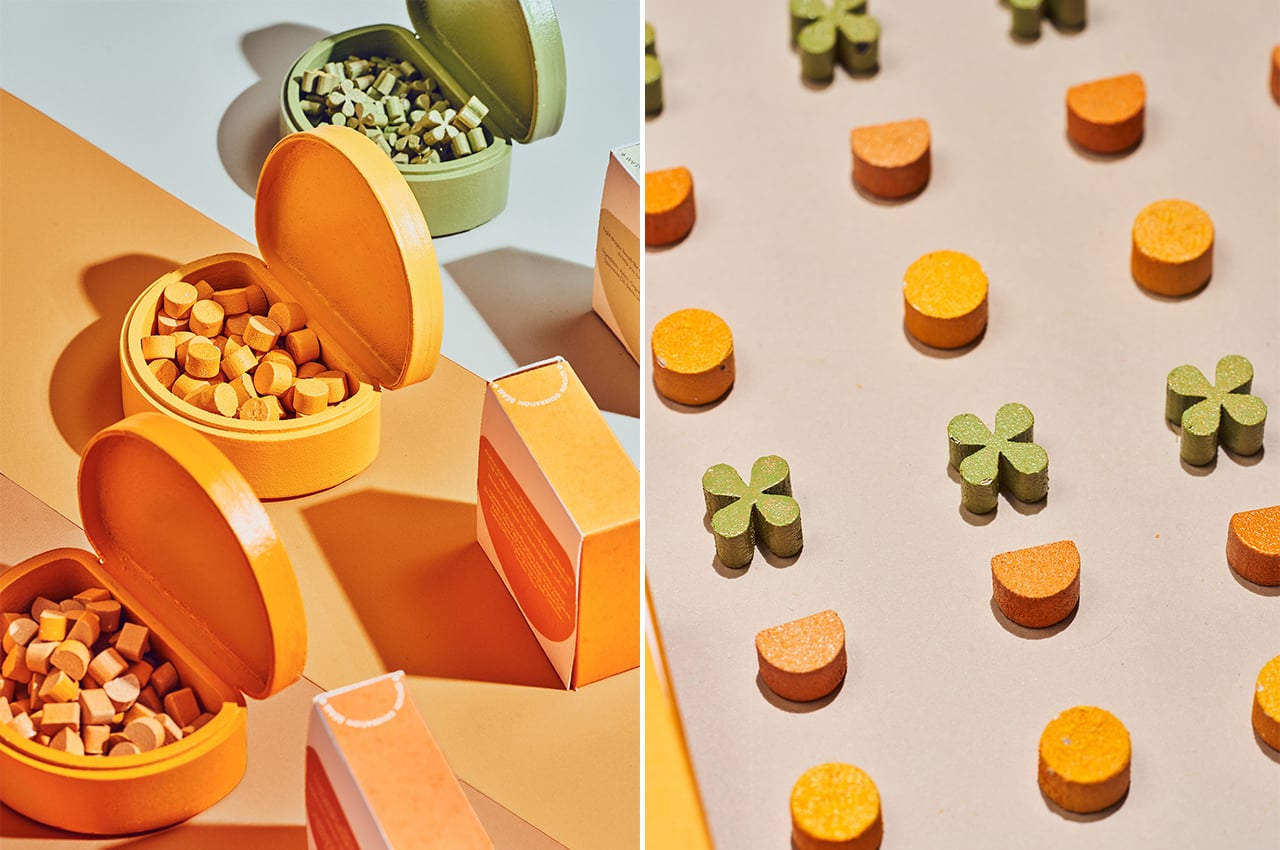
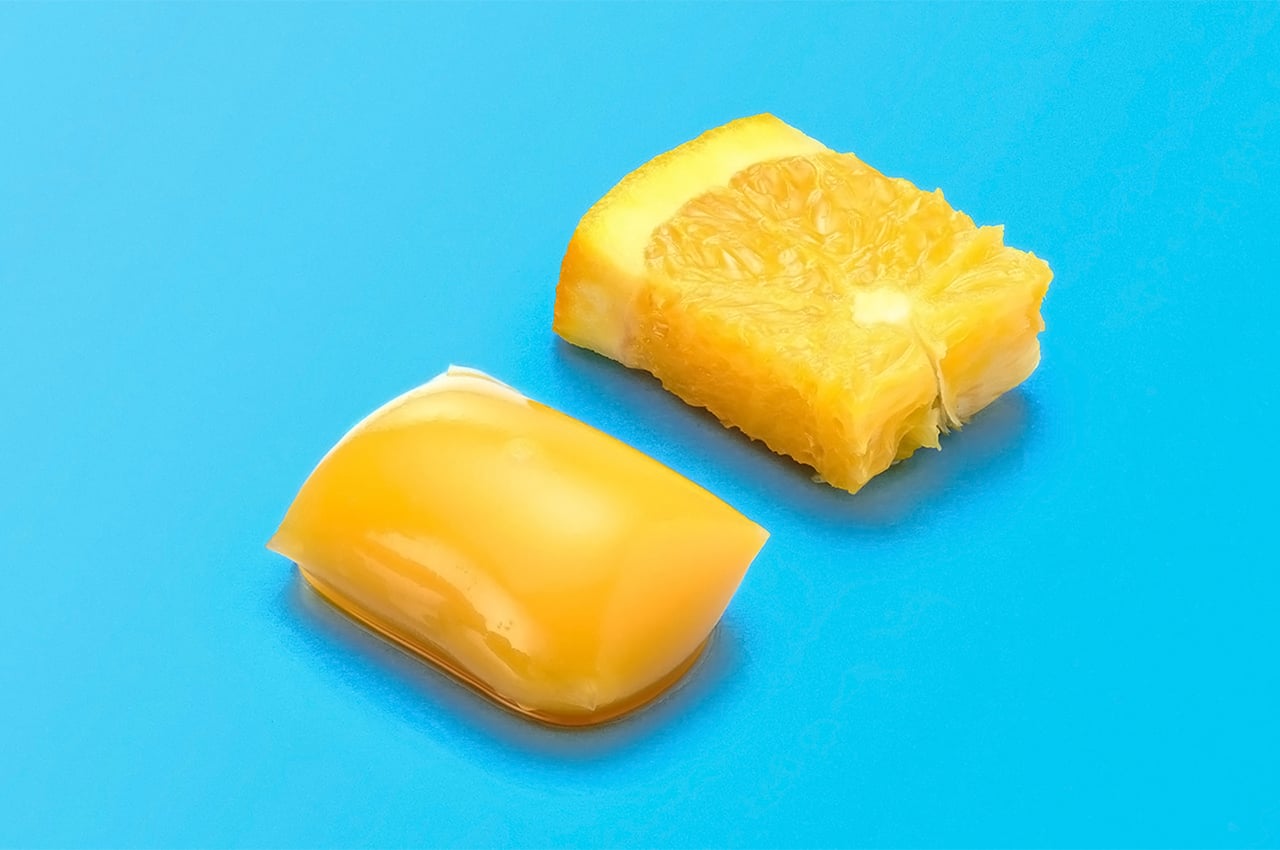
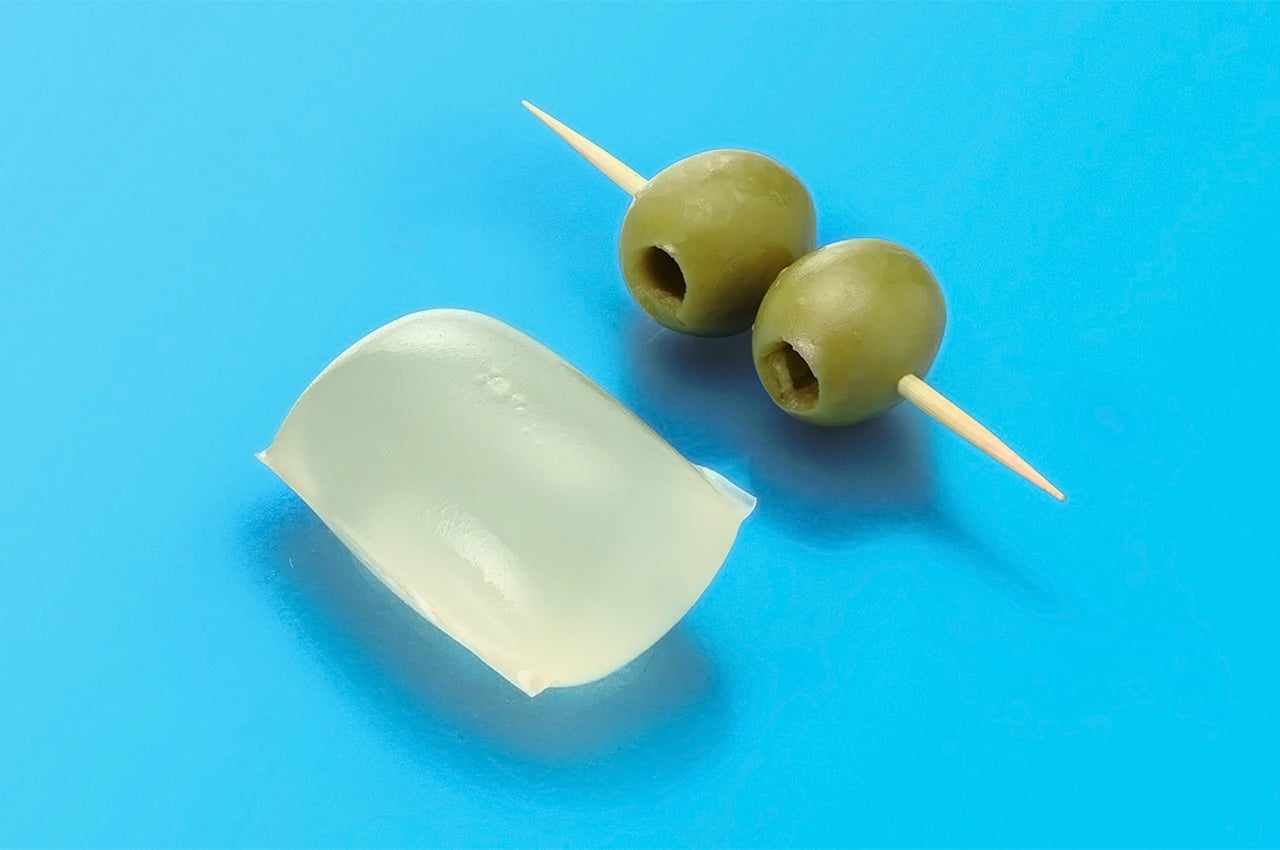
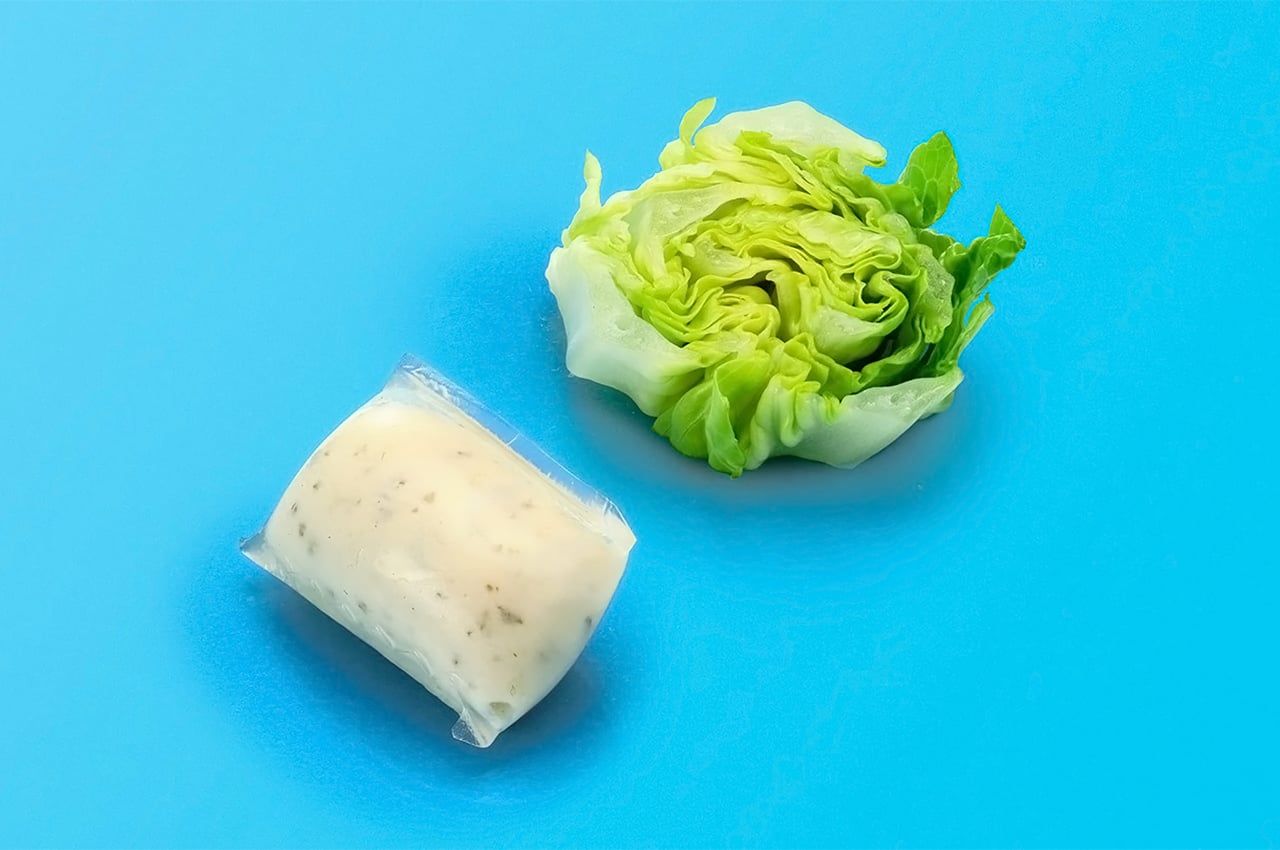
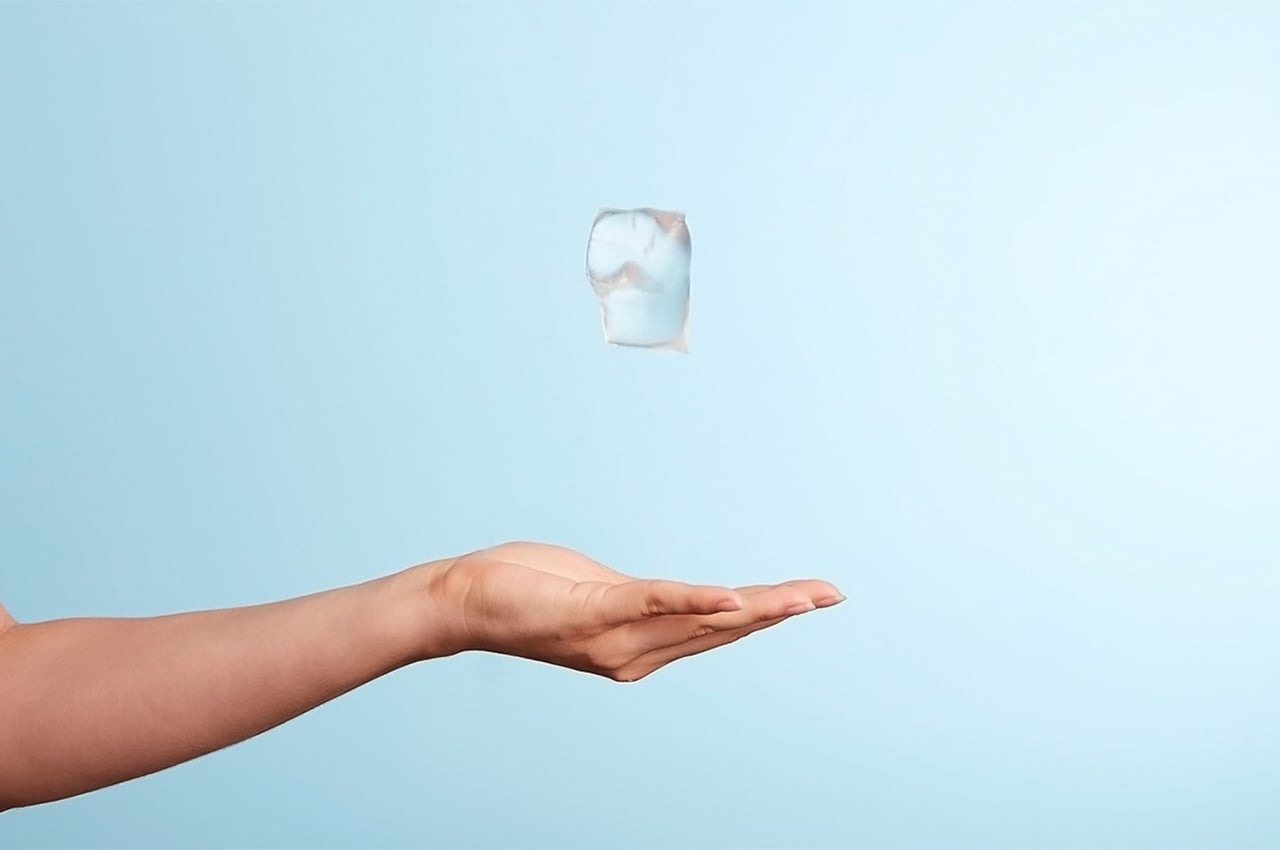
Sea Stone is made by grinding down shells that are destined for landfills before combining them with natural, non-toxic binders. This grants the material a terrazzo-like aesthetic. The aim is to make it a sustainable alternative to concrete in the design of small-scale products, as the two materials share similar properties. Seashells are rich in calcium carbonate aka limestone, which is used to make cement – a key ingredient of concrete.
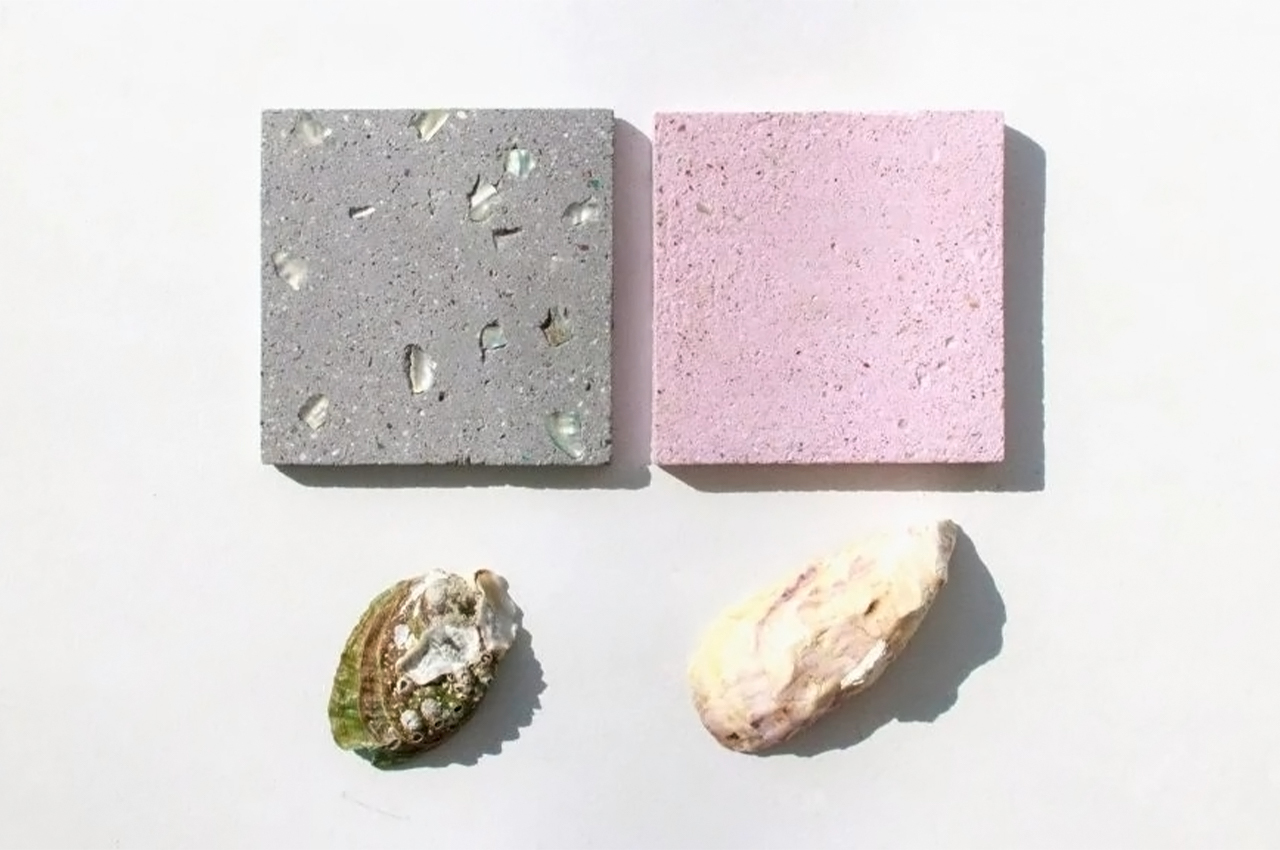

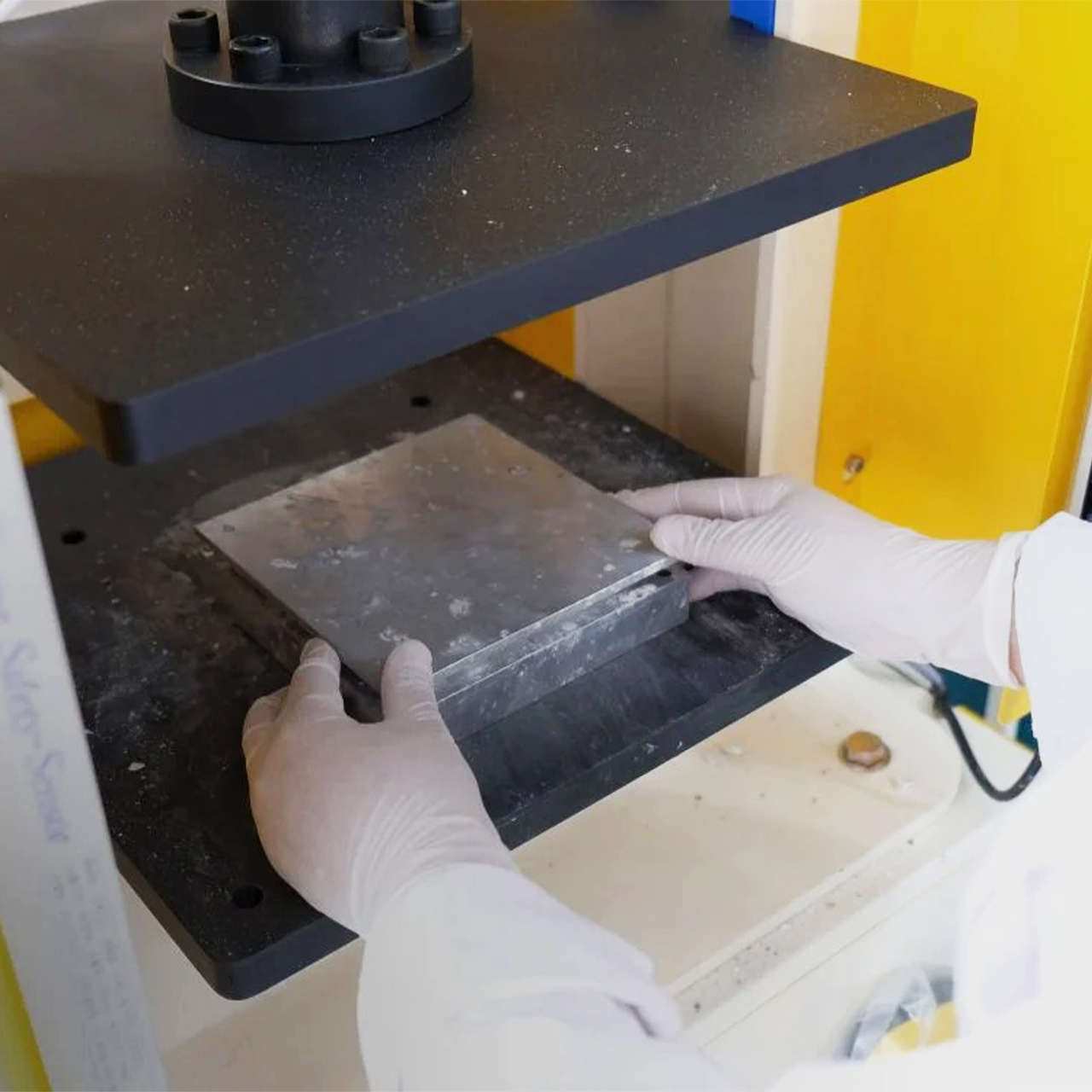
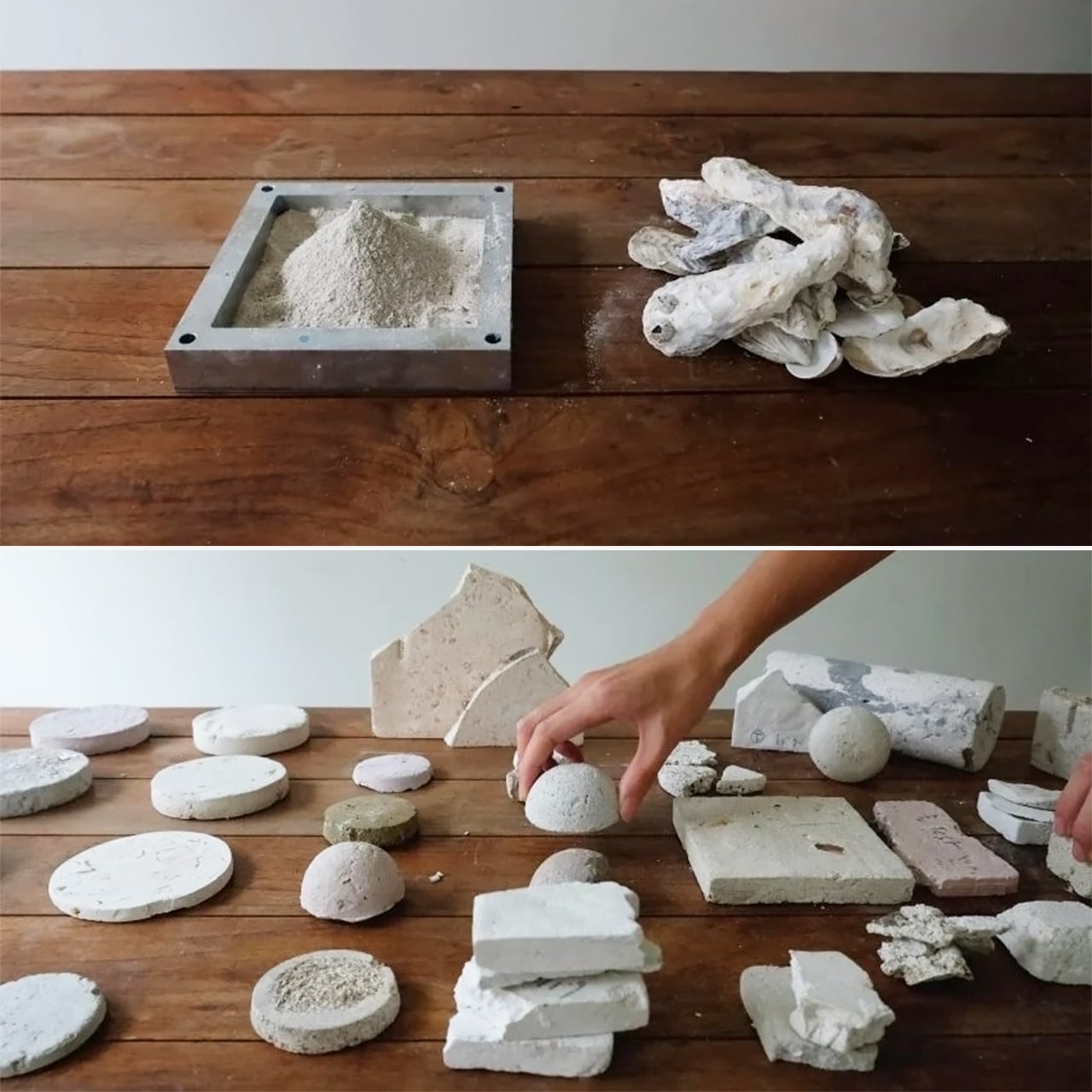
The process involves grinding down the shells and mixing them with natural binders. They are then added to a mould and left to solidify into concrete-like tiles. This method is currently carried out manually to avoid the use of heat, electricity and chemical treatments and ensure the process is as sustainable and affordable as possible. It results in variations in the sizes, textures and colours of the shell fragments and means that each piece of Sea Stone is unique. You can get different textures by altering the number of shells, binders, or adding coloured dyes for aesthetics.
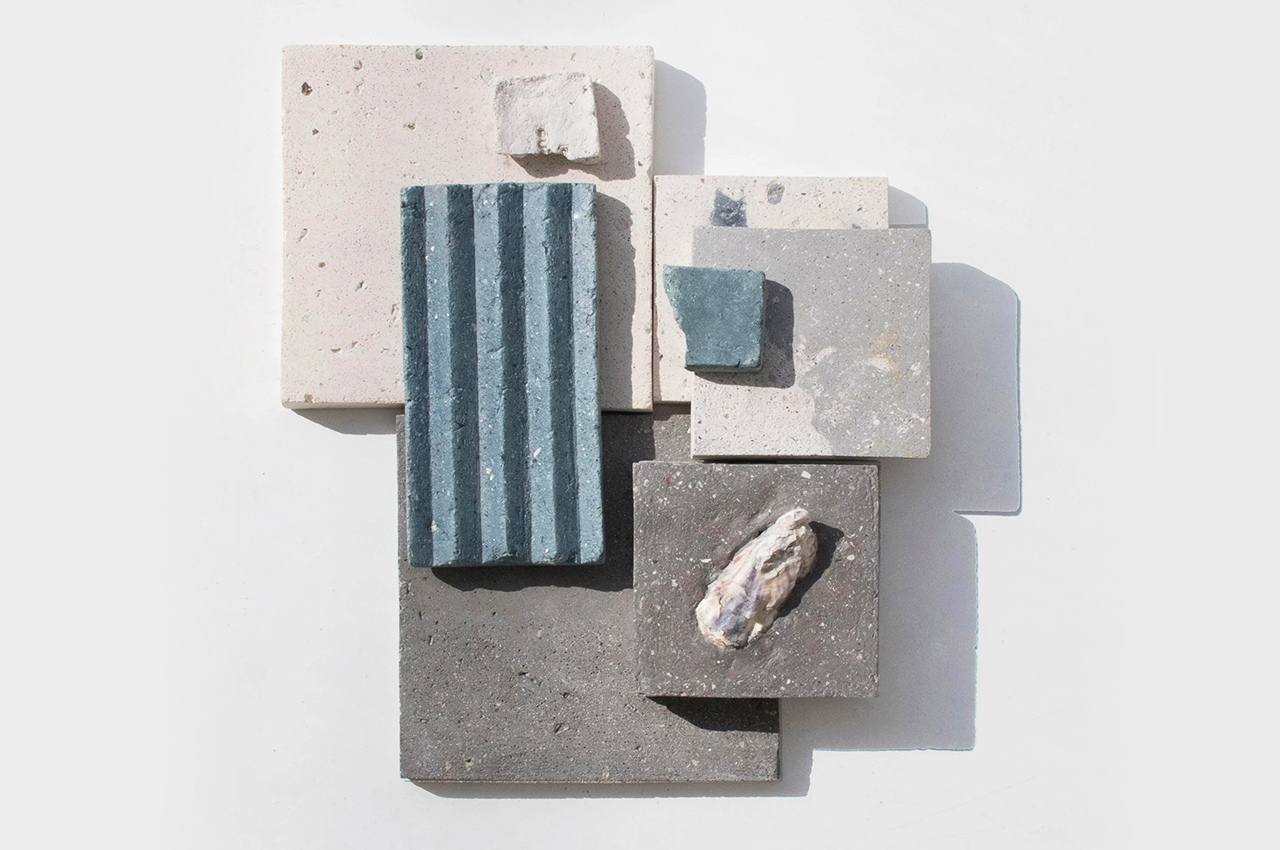

“Even though some of the seashells have been recycled and used as fertilisers, the majority of them are being thrown into landfills or by the seaside. The discarded seashells, which are uncleaned or rotten, have not been cleared away at all and they have been piling up near the beach for a long time, thus causing odour pollution and polluting the surrounding land in the long run. Sea Stone proposes the use of discarded seashells to create environmentally and economically sustainable material rather than contributing to the world’s rubbish problem,” explained Newtab-22.
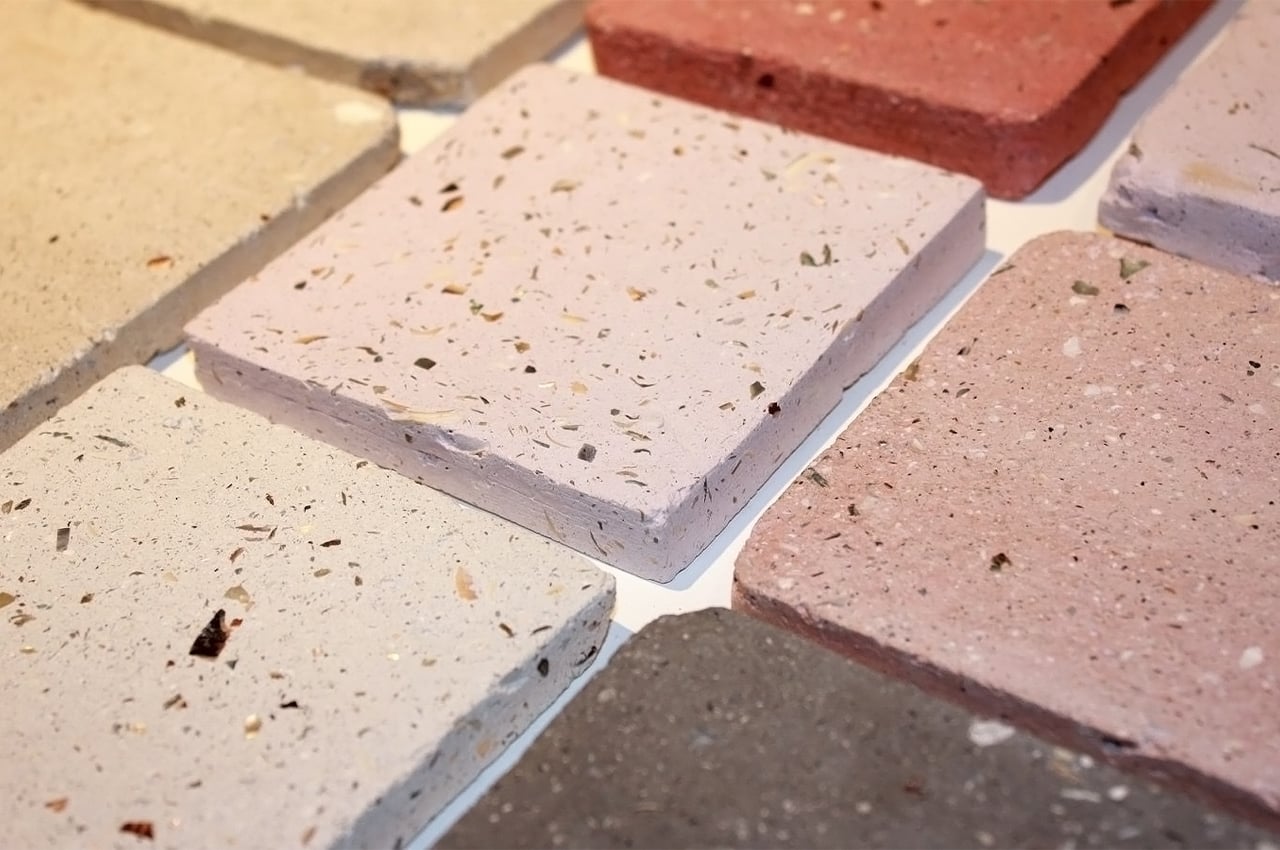

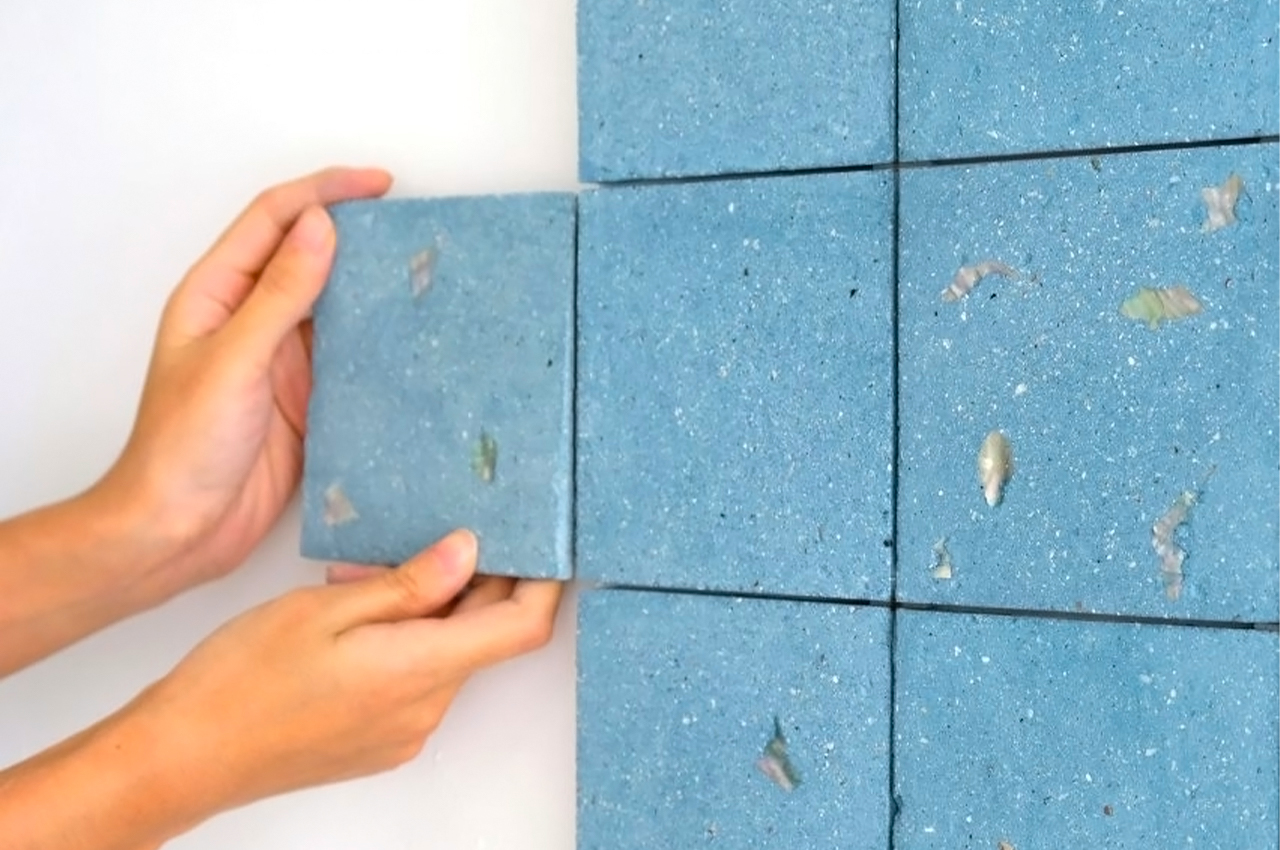
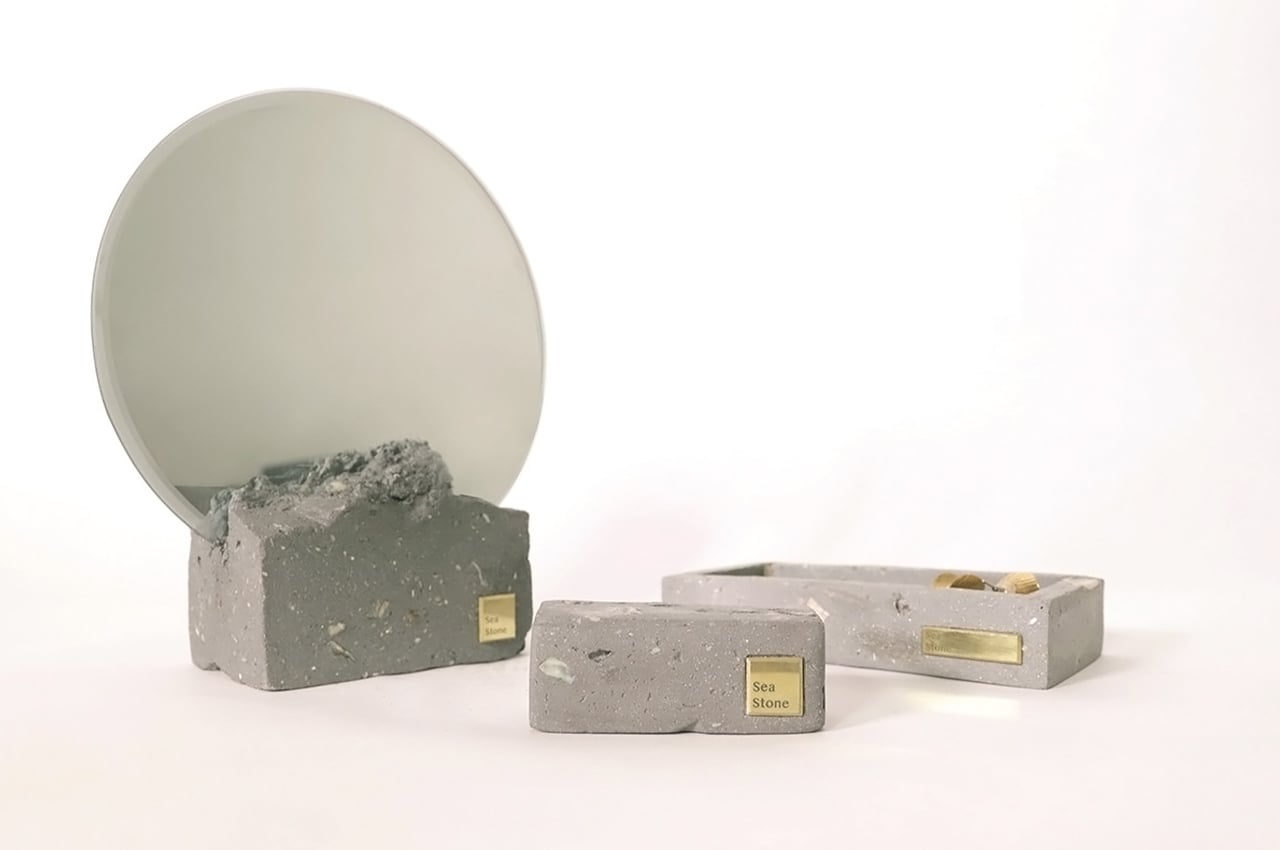
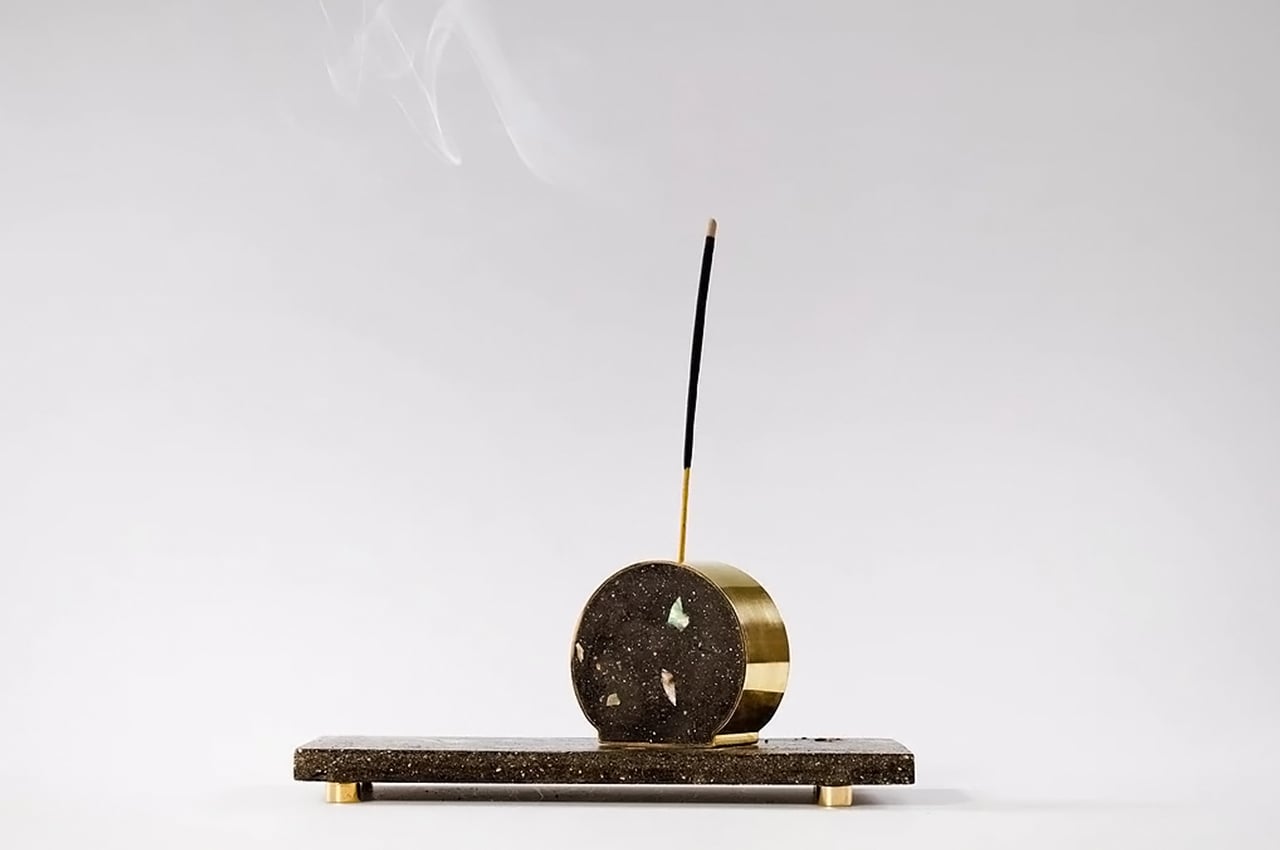
Newtab-22 has experimented with an array of natural binders in the development of Sea Stone, including sugar and agar. It is now reliant on two undisclosed and patent-pending sources. The material is currently being developed for commercial purposes and has so far been used to make products such as decorative tiles, tabletops, plinths and vases.
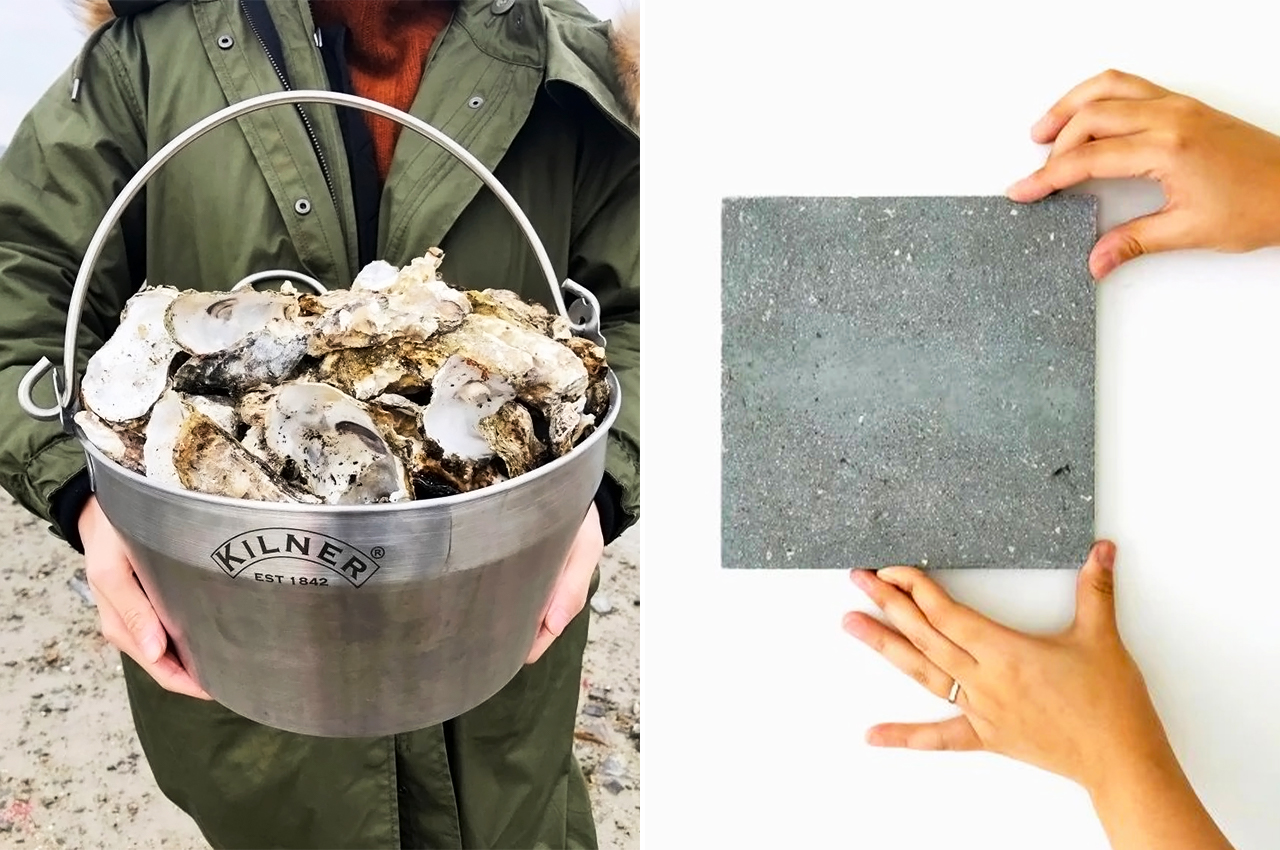

While the properties of the concrete and Sea Stone are similar, to truly replicate the strength of traditional concrete required in large-scale projects like buildings, an energy-intensive heating process would be required. This would be comparable to the method used to make cement, which accounts for half of all the CO2 emissions that result from using concrete. “The power of the material is different, we do not want to harm the environment in the process or the outcome,” said Hyein Choi, co-founder of the studio.
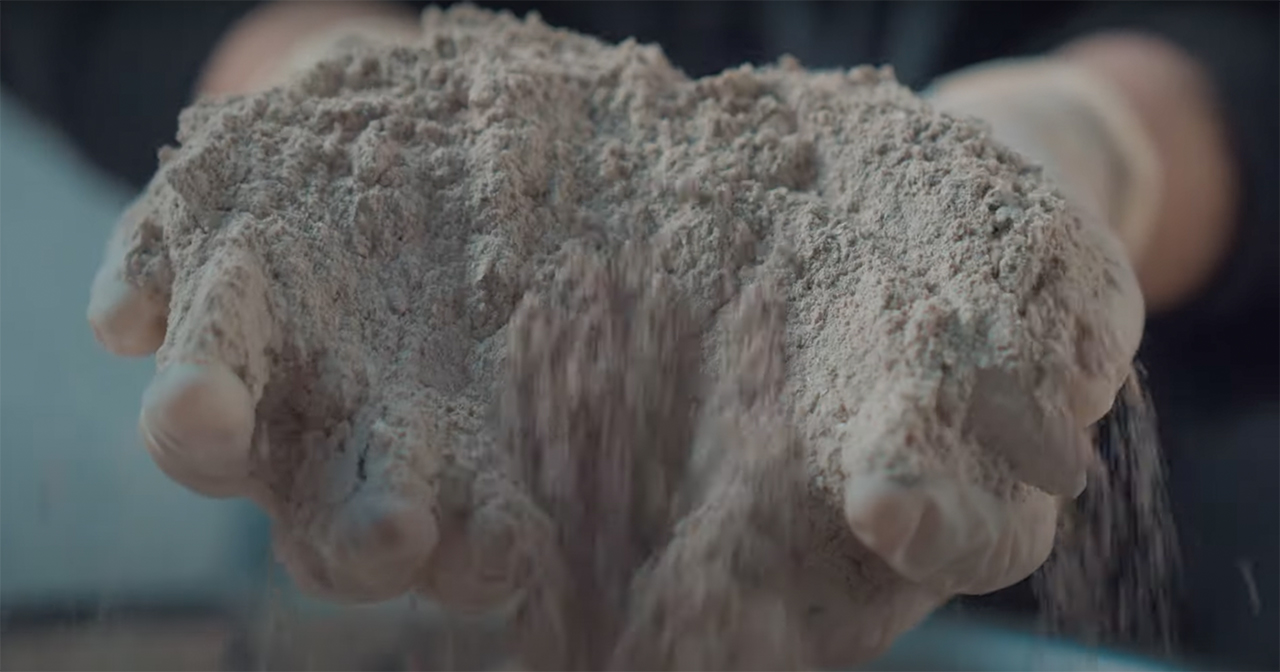

Sea Stone is versatile, durable and a lightweight alternative to not only concrete but also plastic – it can be used to produce several objects while repurposing waste, reducing carbon emissions of the toxic counterpart materials and keeping the costs low. Time to find that girl who sells sea shells by the sea shore, eh?
Designer: Newtab-22