
Physics' big announcement had more in common with a leaky product launch than the serious business of re-writing the science books. But slack asset management aside, it's official: a new boson has been observed with a standard deviation of 5 (confidence of 99.9%). The highly anticipated announcement came this morning direct from CERN's press conference (via ICHEP in Melbourne,) and is the result of an intense, ongoing search for the elusive particle. The observation is of a boson particle with a mass of 125.3 ± 0.6 GeV, at a significance of 4.9 sigma. Joe Incandela -- giving the presentation -- said that this is "In agreement with the standard model at 95% confidence range." The boson is the heaviest ever found, and although this is still a preliminary result, it's by far the strongest case yet for the existence of the elusive Higgs.
The sought-after particle is essential for supporting the current understanding of sub-atomic world, and its bearing on nuclear, and electromagnetic interactions. The next stage will be to determine the exact characteristics of the new particle and whether it matches the expectations of the Higgs, or is it in fact something more "exotic." This part will take much more time, but for now, a (very) small, but important piece of the puzzle has been found.
Update: We're sure you've got many questions, and CERN apparently anticipated this. Check out the more coverage link for a helpful FAQ about everything Higgs.
[Image credit: CERN]
Continue reading CERN confirms existence of new particle consistent with Higgs boson (video)
CERN confirms existence of new particle consistent with Higgs boson (video) originally appeared on Engadget on Wed, 04 Jul 2012 03:44:00 EDT. Please see our terms for use of feeds.
Permalink |
 CERN (webcast)
CERN (webcast) |
Email this |
Comments
 As sweet as it might be to dream of making your own Internet of Things device, there's one big problem: keeping it online at all times. How do you connect that smart sensor in your backyard when it's nowhere near WiFi? Particle (aka Spark) thinks it...
As sweet as it might be to dream of making your own Internet of Things device, there's one big problem: keeping it online at all times. How do you connect that smart sensor in your backyard when it's nowhere near WiFi? Particle (aka Spark) thinks it...
 As sweet as it might be to dream of making your own Internet of Things device, there's one big problem: keeping it online at all times. How do you connect that smart sensor in your backyard when it's nowhere near WiFi? Particle (aka Spark) thinks it...
As sweet as it might be to dream of making your own Internet of Things device, there's one big problem: keeping it online at all times. How do you connect that smart sensor in your backyard when it's nowhere near WiFi? Particle (aka Spark) thinks it...
 The rejuvenated Large Hadron Collider might have achieved another breakthrough... provided everything lines up, that is. Two teams of CERN scientists have detected an excess of gamma ray pairs that they suspect might represent the radioactive decay...
The rejuvenated Large Hadron Collider might have achieved another breakthrough... provided everything lines up, that is. Two teams of CERN scientists have detected an excess of gamma ray pairs that they suspect might represent the radioactive decay...
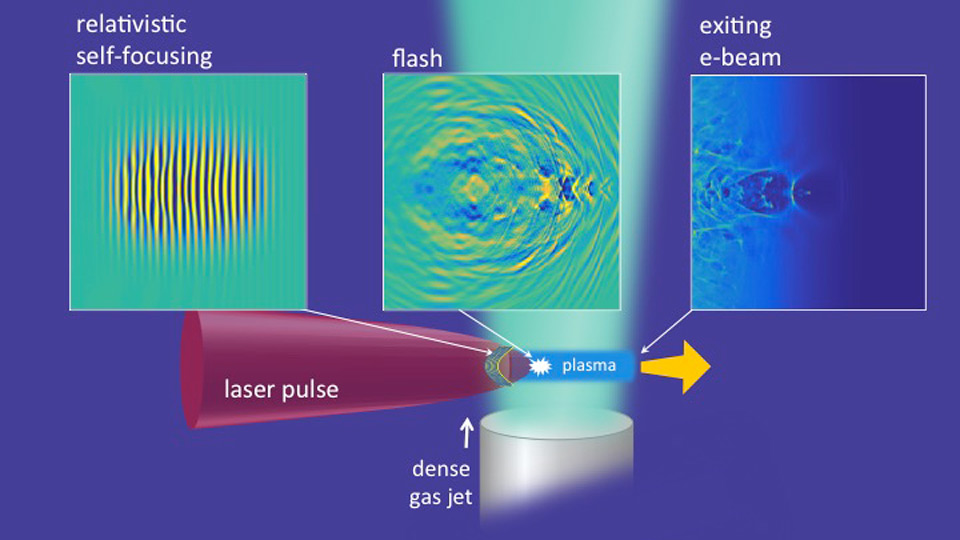 Modern particle accelerators are big, to put it mildly -- even the smallest ones tend to occupy large rooms. Researchers at the University of Maryland, however, have found a way to shrink them down to where they're genuinely portable. By shooting p...
Modern particle accelerators are big, to put it mildly -- even the smallest ones tend to occupy large rooms. Researchers at the University of Maryland, however, have found a way to shrink them down to where they're genuinely portable. By shooting p...







