
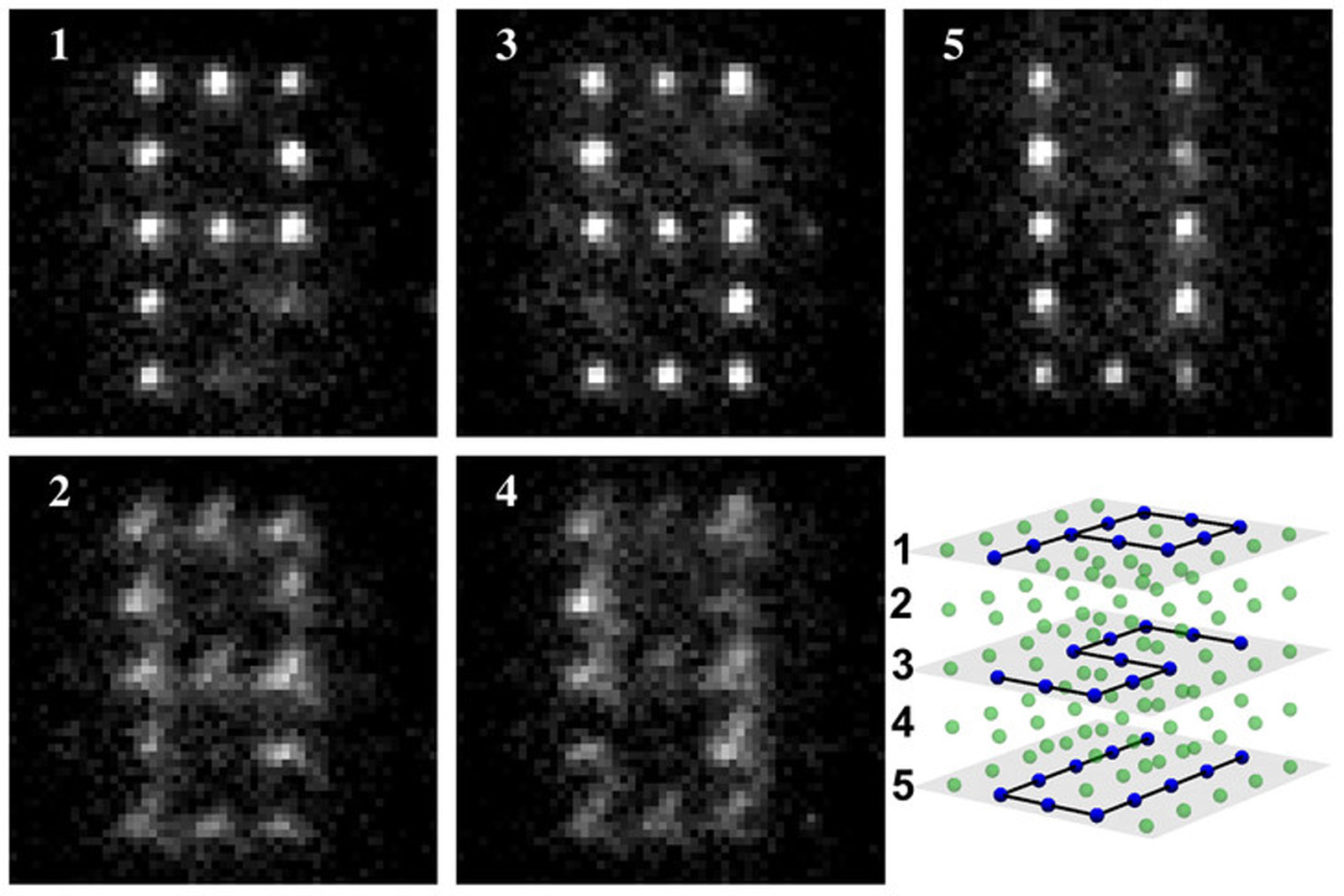
If you've been paying attention, you know the quantum computing revolution is coming -- and so far the world has a mini quantum network, not to mention the $10,000 D-Wave One, to show for it. Researchers from the University of Melbourne and University College, London, have now developed the "first working quantum bit based on a single atom of silicon." By measuring and manipulating the magnetic orientation, or spin, of an electron bound to a phosphorus atom embedded in a silicon chip, the scientists were able to both read and write information, forming a qubit, the basic unit of data for quantum computing.
The team used a silicon transistor, which detects the electron's spin and captures its energy when the spin's direction is "up." Once the electron is in the transistor, scientists can change its spin state any way they choose, effectively "writing" information and giving them control of the quantum bit. The next step will be combing two qubits into a logic step, with the ultimate goal being a full-fledged quantum computer capable of crunching numbers, cracking encryption codes and modeling molecules that would put even supercomputers to shame. But, you know, baby steps.
Filed under: Science, Alt
Researchers create working quantum bit in silicon, pave way for PCs of the future originally appeared on Engadget on Fri, 21 Sep 2012 00:47:00 EDT. Please see our terms for use of feeds.
Permalink  The Register
The Register |
 UNSW Australia
UNSW Australia |
Email this |
Comments
 If you're going to craft a quantum computer, you need to corral lots of quantum bits (qubits) to perform calculations... and Penn State researchers have found a way to make that happen. They've developed a technique that relies on lasers and microwa...
If you're going to craft a quantum computer, you need to corral lots of quantum bits (qubits) to perform calculations... and Penn State researchers have found a way to make that happen. They've developed a technique that relies on lasers and microwa...
 If you're going to craft a quantum computer, you need to corral lots of quantum bits (qubits) to perform calculations... and Penn State researchers have found a way to make that happen. They've developed a technique that relies on lasers and microwa...
If you're going to craft a quantum computer, you need to corral lots of quantum bits (qubits) to perform calculations... and Penn State researchers have found a way to make that happen. They've developed a technique that relies on lasers and microwa...
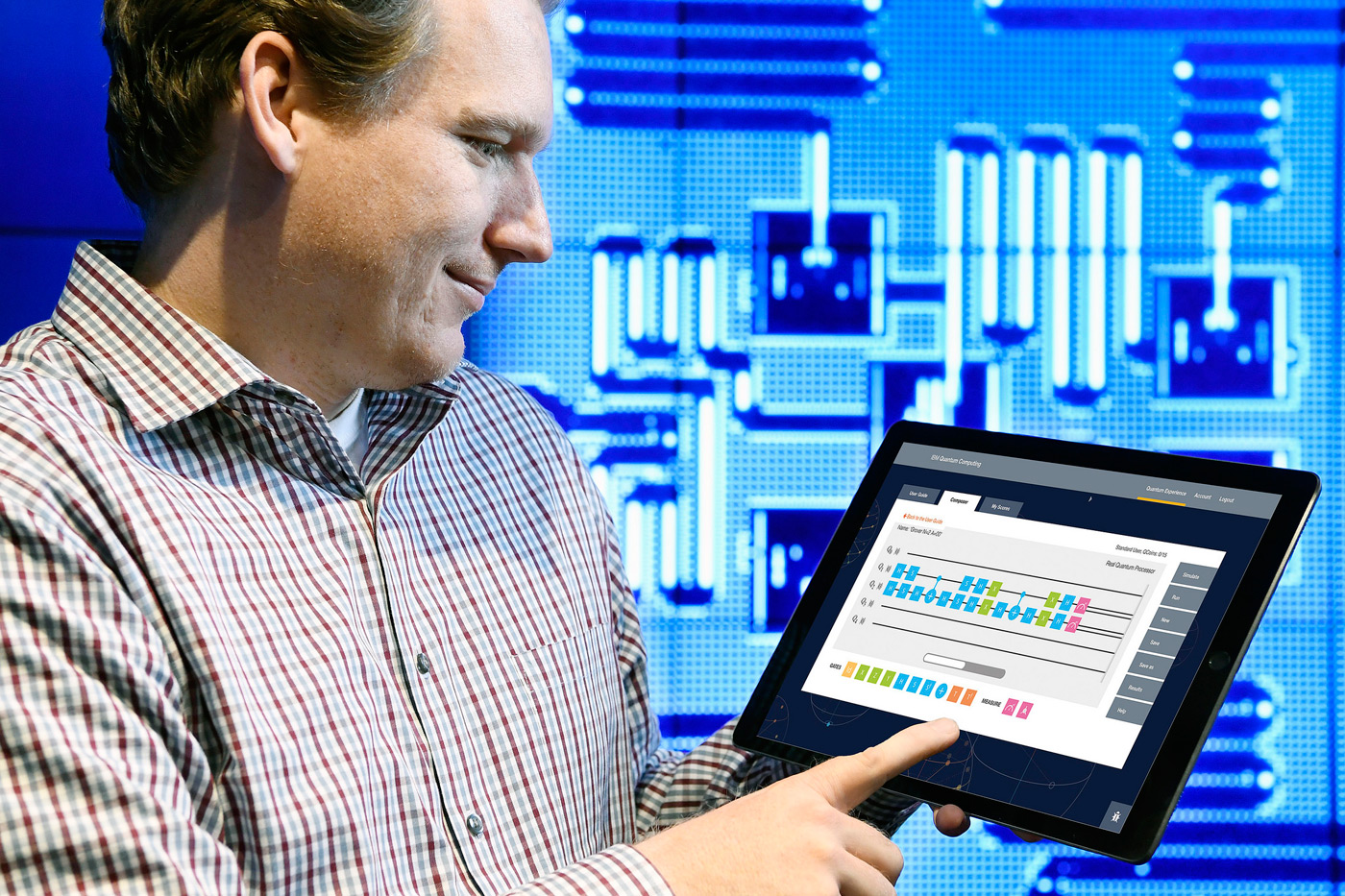 Want to use a real, honest-to-goodness quantum computer yourself? Now's your chance. IBM has introduced a cloud-based platform, the Quantum Experience, that lets anyone try a 5-qubit quantum computer for themselves. You can run algorithms and expe...
Want to use a real, honest-to-goodness quantum computer yourself? Now's your chance. IBM has introduced a cloud-based platform, the Quantum Experience, that lets anyone try a 5-qubit quantum computer for themselves. You can run algorithms and expe...
 Justin Trudeau, Canada's prime minister, paid a visit to the Perimeter for Theoretical Physicals in Waterloo earlier today. There, he encountered a sassy reporter who seemingly didn't expect him to know much about quantum computing. But, as it turns...
Justin Trudeau, Canada's prime minister, paid a visit to the Perimeter for Theoretical Physicals in Waterloo earlier today. There, he encountered a sassy reporter who seemingly didn't expect him to know much about quantum computing. But, as it turns...





