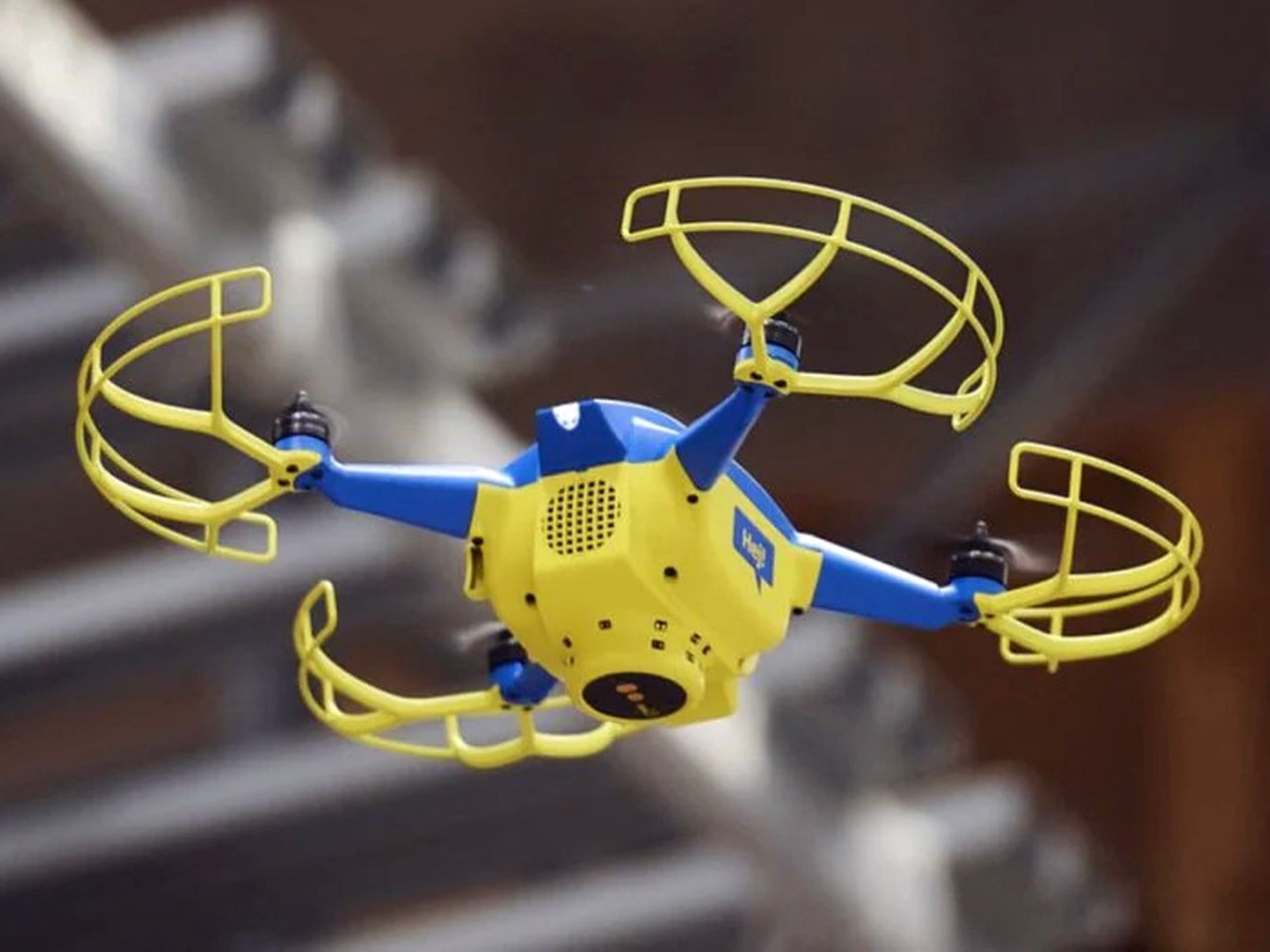
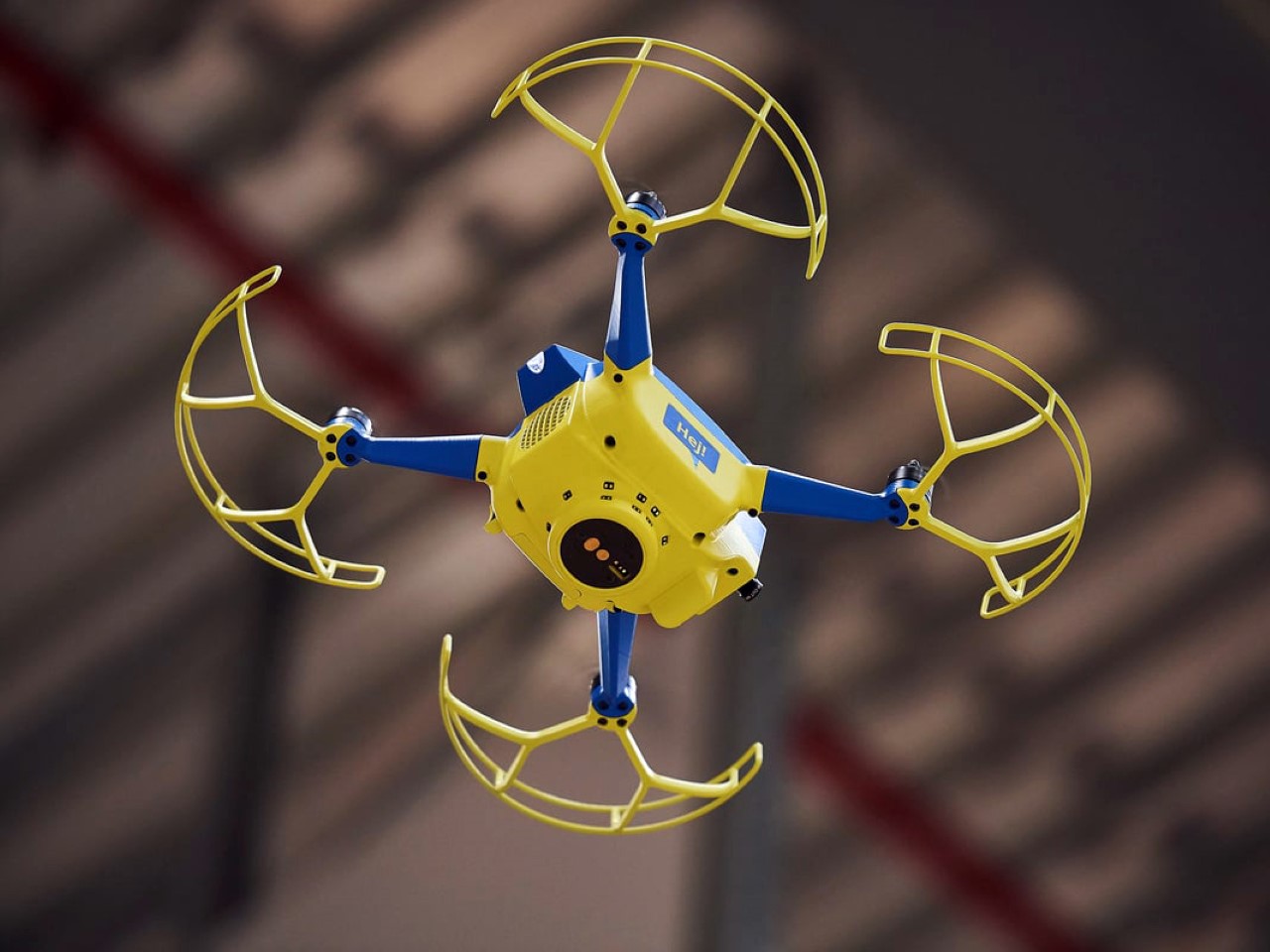
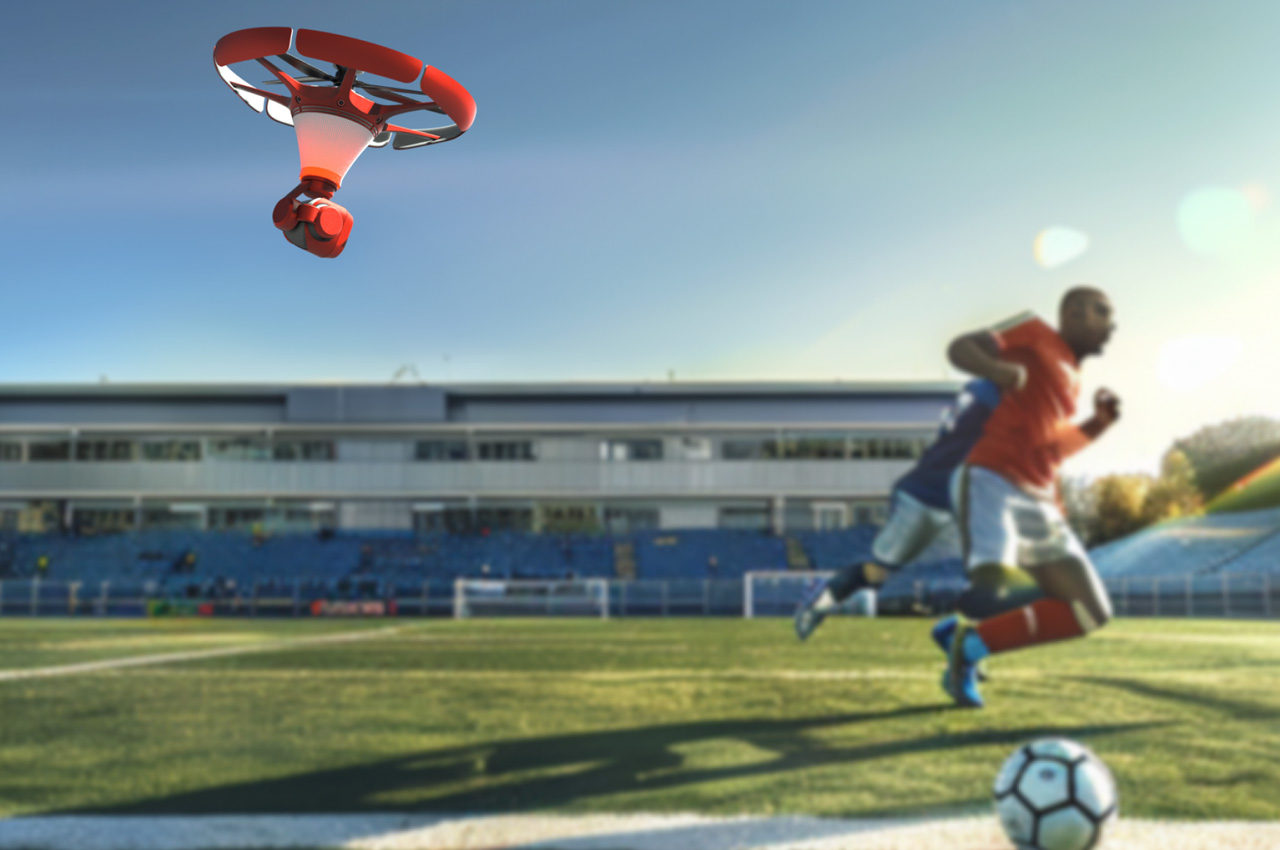
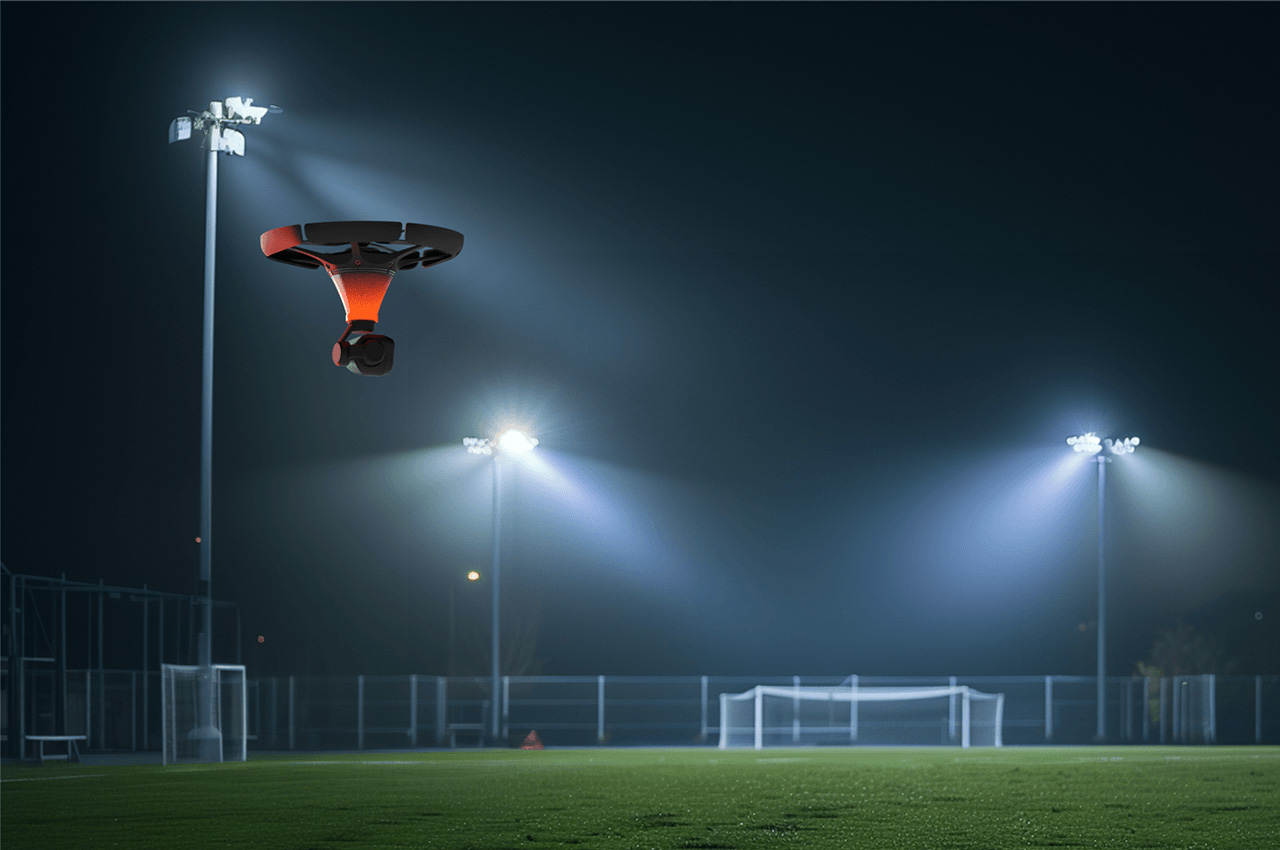
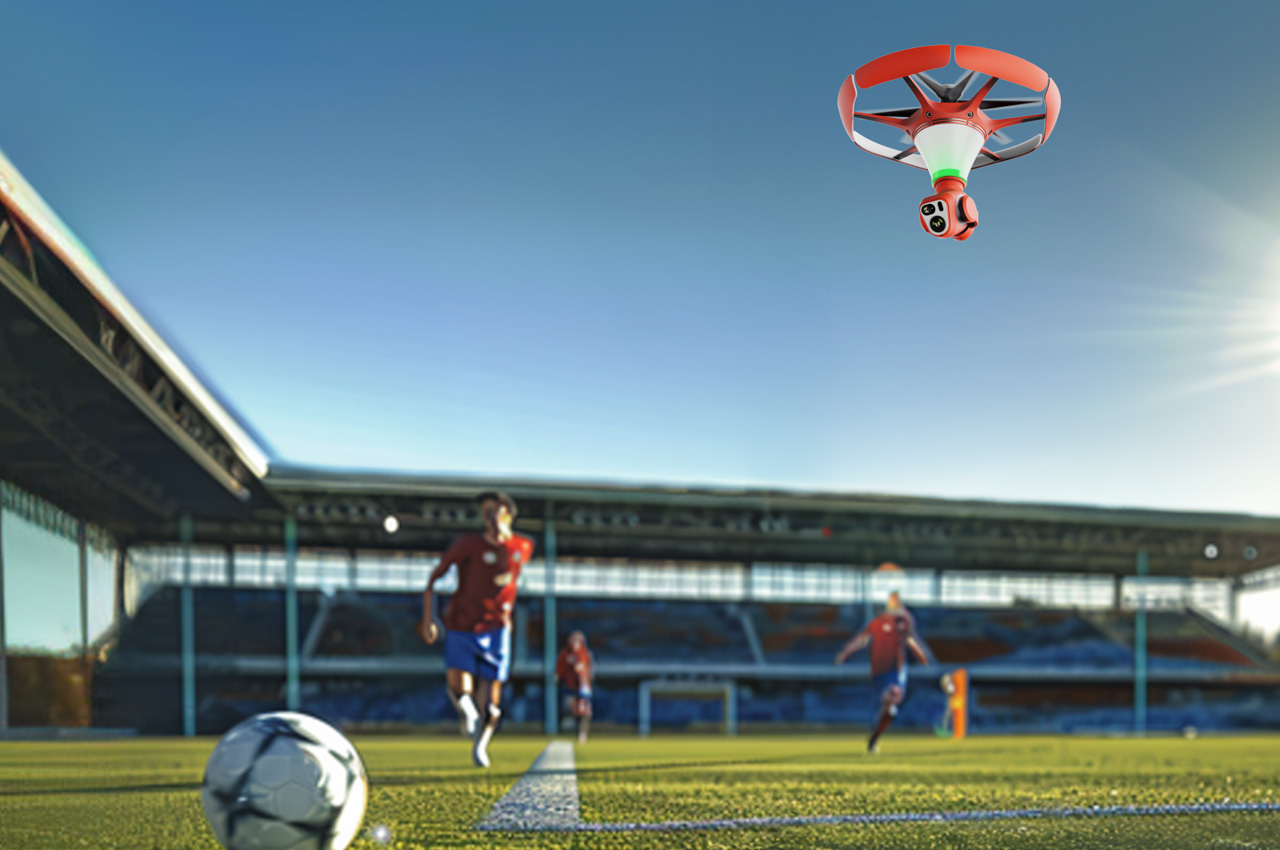
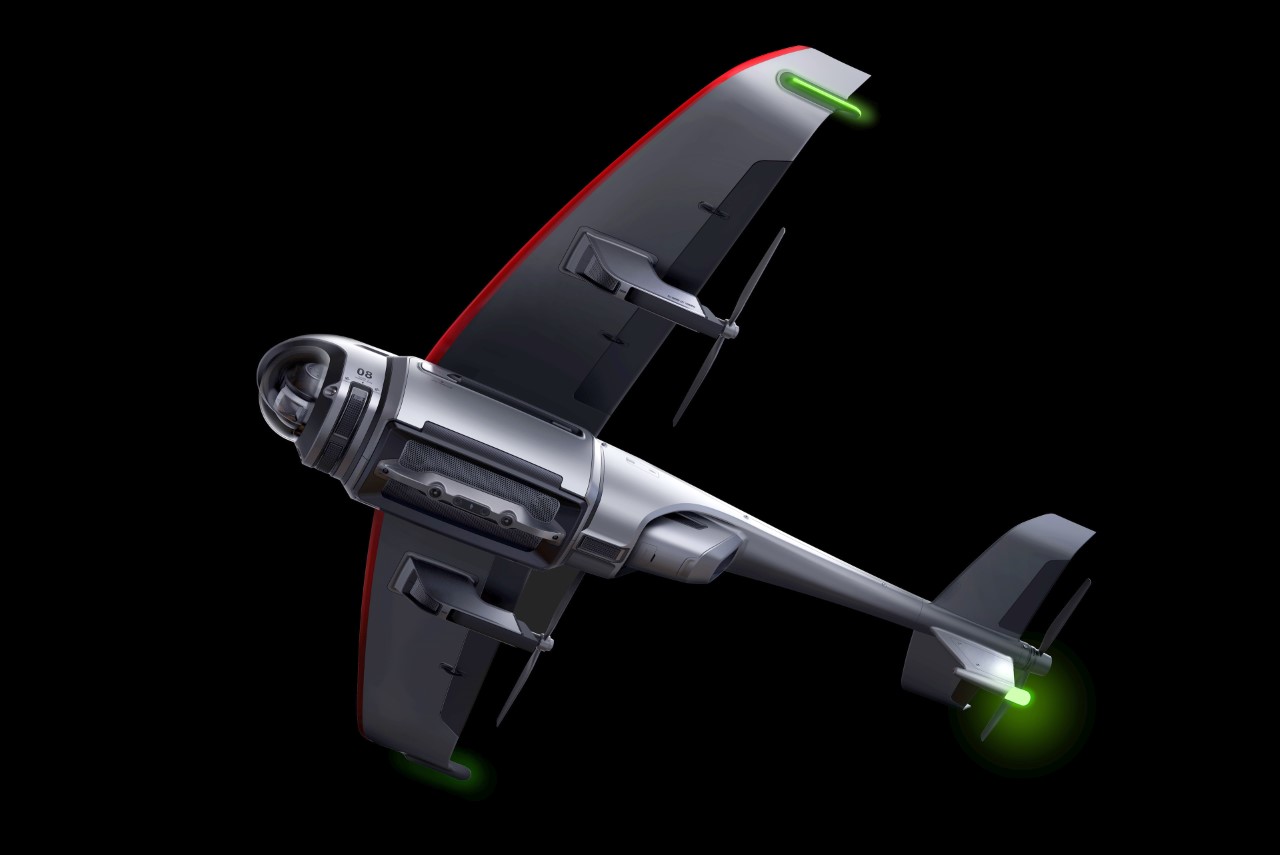
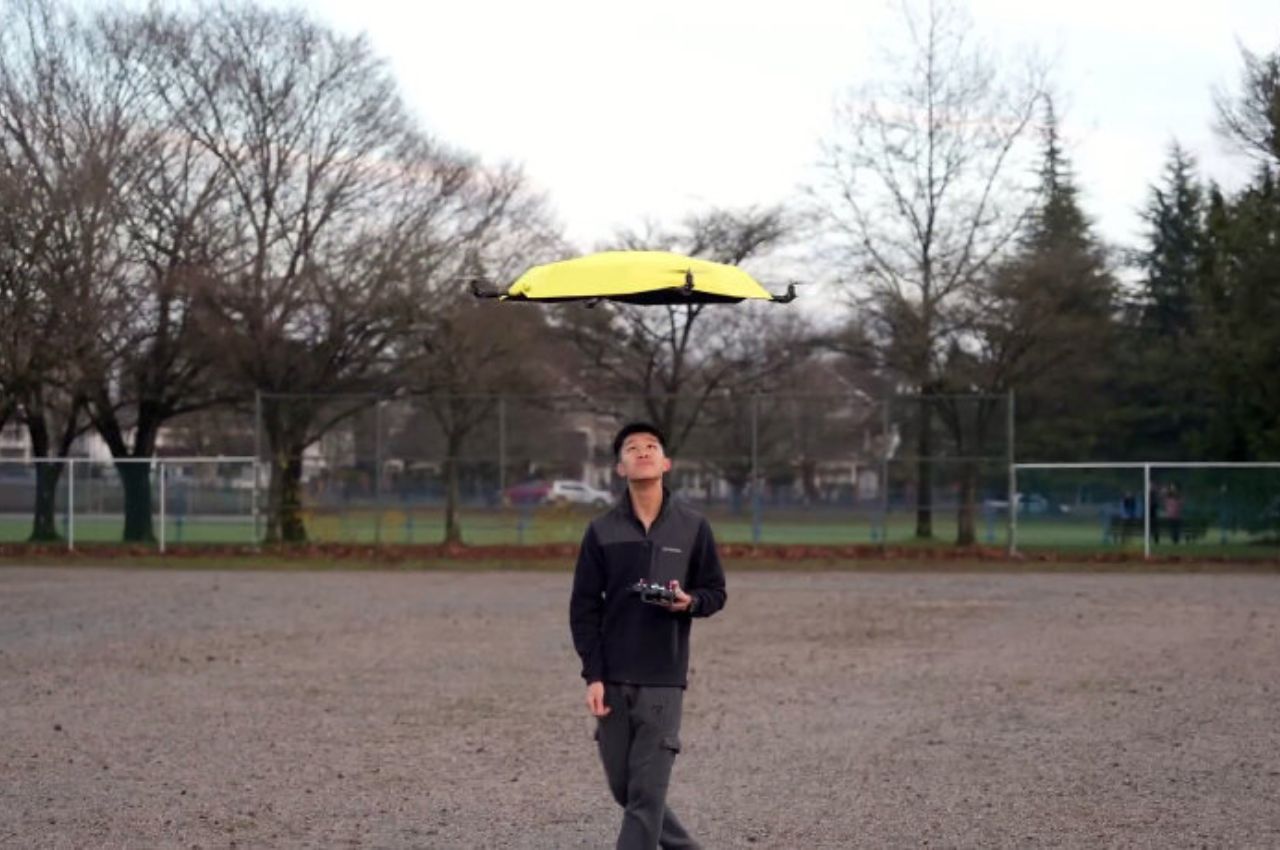
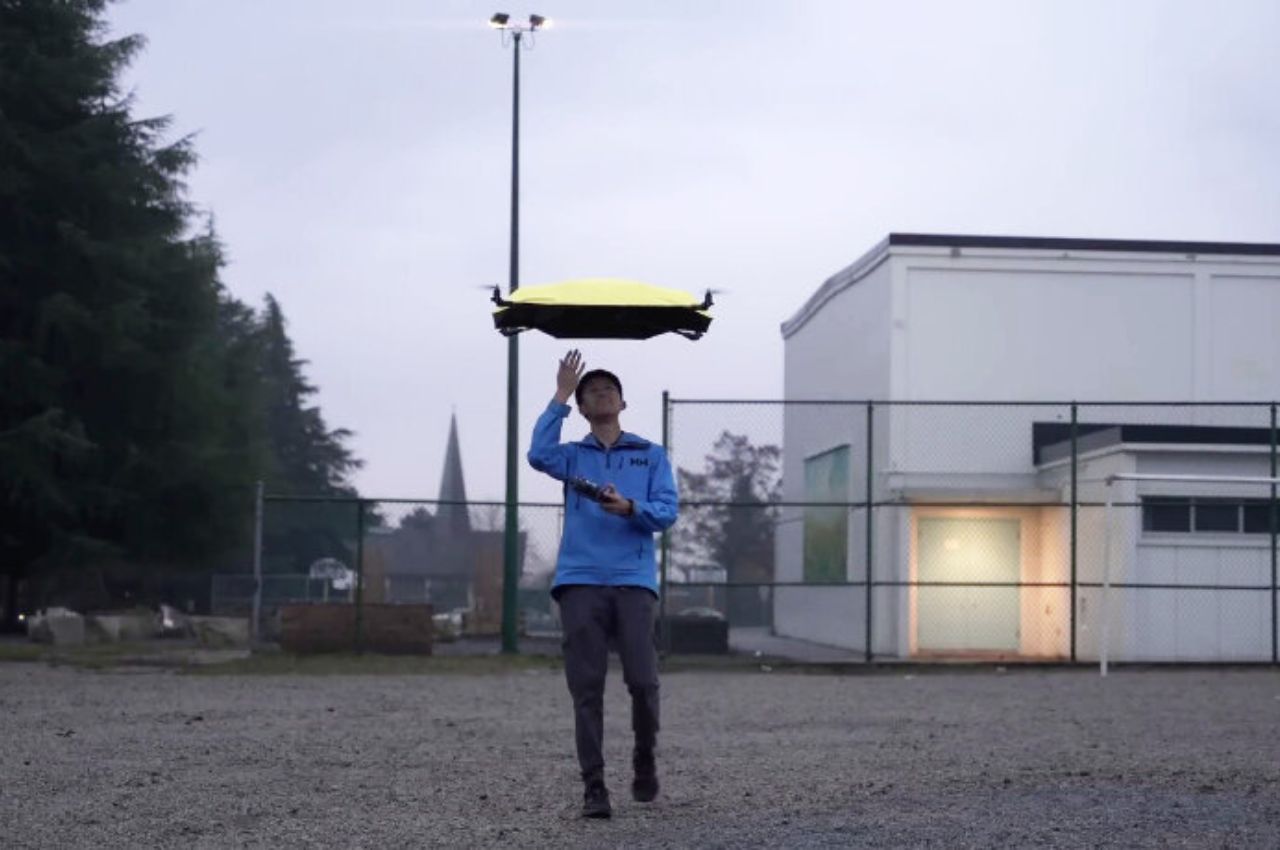
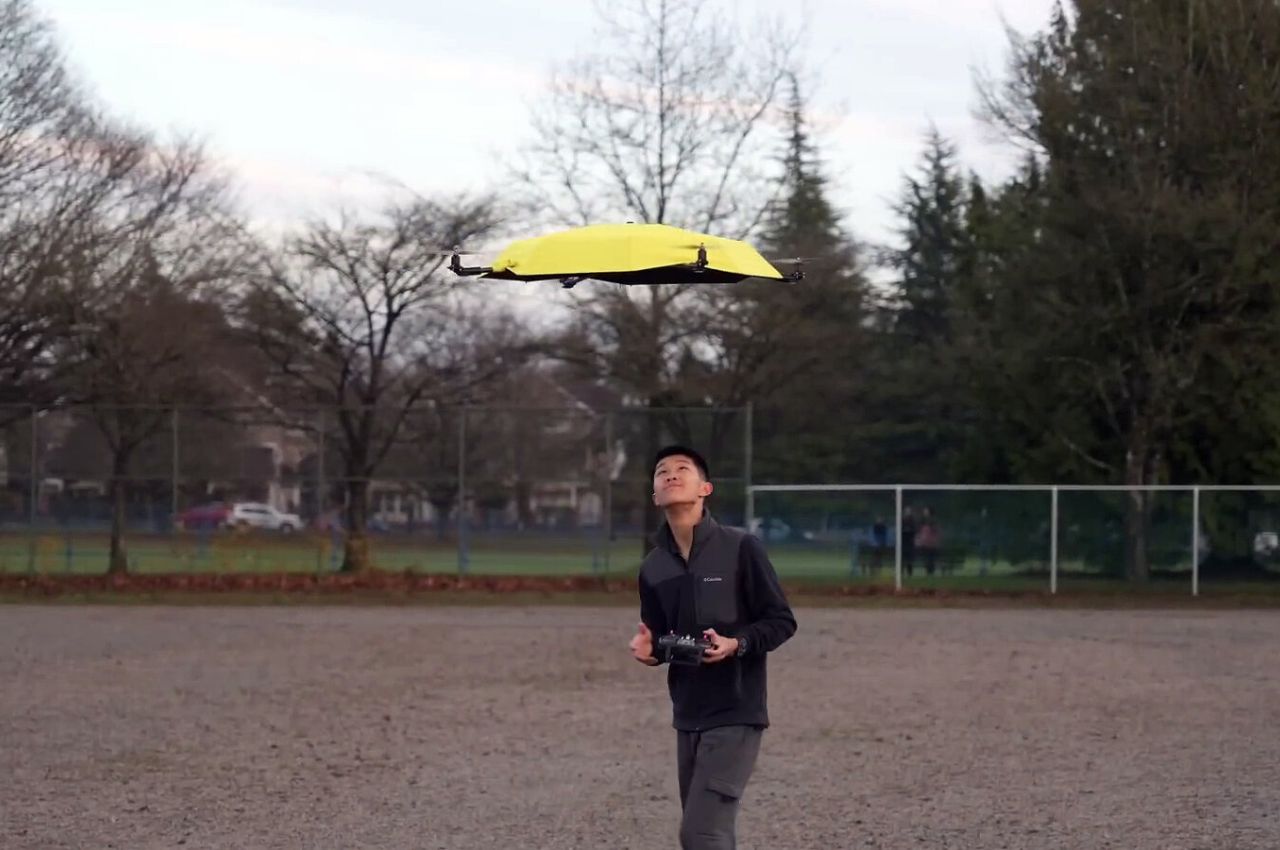
Your phone has a pretty phenomenal camera, but unless it’s an absolute flagship device, it probably won’t record 8K video. And it for sure won’t fly around in the air taking dramatic shots of you while you pose on the top of a mountain or dirt bike on a rocky trail or dive into a lake. You’ll probably need a selfie drone for that, but before you go spending hundreds of dollars on a drone that’s fragile, expensive, and comes with a massive learning curve involving controllers and joysticks, the folks at HOVERAir might have built the perfect consumer-grade pro drone, or as they call it – a flying action camera. Designed to be foldable, small enough to fit in your pocket, and durable enough to withstand any rookie accidents The HOVERAir X1 PROMAX still packs a state-of-the-art flying system and an 8K camera capable of outshining any other drone its size. It works on voice commands (but also comes with an optional Wi-Fi 6-enabled Beacon), takes off from your palm, reaches speeds of up to 60 km/h (37.2 mph), can capture slow-motion videos at 120fps, and even works in sub-zero temperatures just in case you want to film yourself skiing or snowboarding. The best part, the X1 PRO’s $499 starting price, along with its compact size which makes it compliant with FAA guidelines so anyone can use one.
Designer: HOVERAir
Click Here to Buy Now: $499. Hurry, only 30 left! Raised over $4.6 million.
You may remember HOVERAir from years ago when they first debuted their folding selfie-drone cameras. More than 8 years later, the company’s still sticking to its wildly popular and innovative folding drone template, but has managed to outfit its device with some very impressive tech. Available in two variants – the X1 PRO and the X1 PROMAX, these flying action cameras are capable of recording at 4K and 8K respectively. Both devices weigh under the FAA-regulated 250-gram limit, hit speeds of 42 km/h (26mph) with bursts of up to 60 km/h (37.2mph), shoot slow-mo, take photos, and also capture vertical videos for social media. The X1 PROMAX just packs a slightly better camera system that has a marginally higher FoV at 107° (compared to the X1 PRO’s 104° FoV), and uses vision-based sensors for rear active collision detection. Think of the X1 PRO as the perfect hands-free drone for filming sports, landscapes, and your dance reels, while the X1 PROMAX just being a notch higher for serious professionals and content creators who also want great photography capabilities in their drone. No controllers, no learning curve, no fuss.
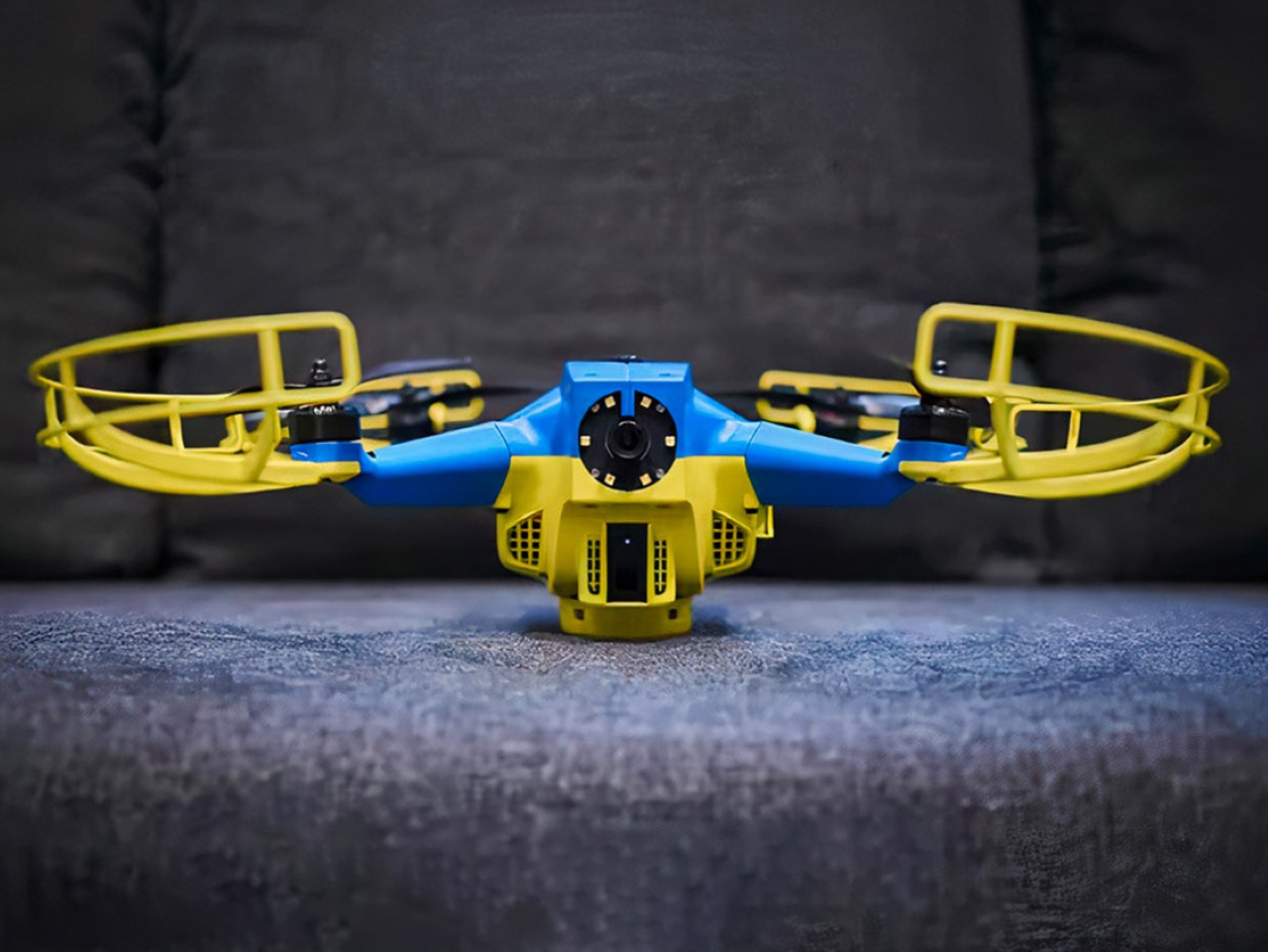
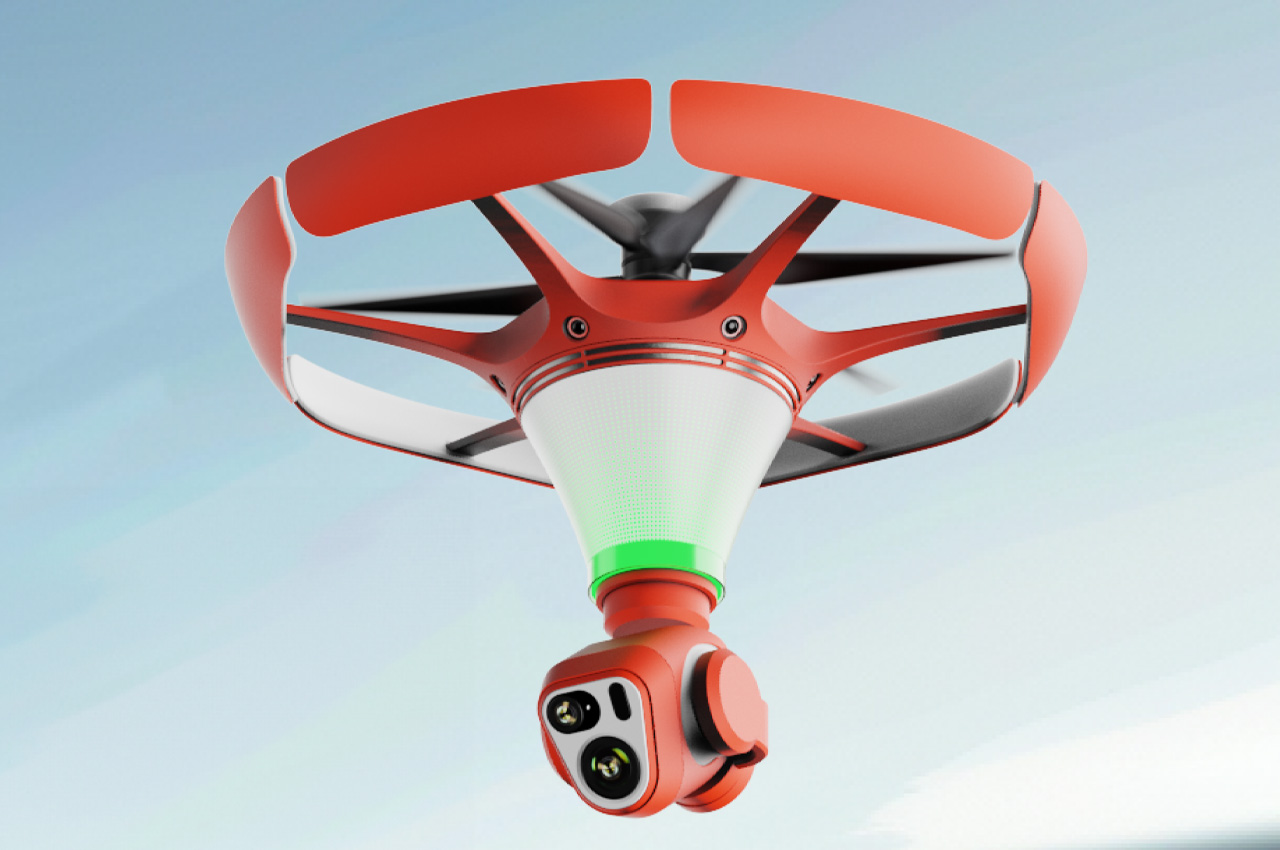
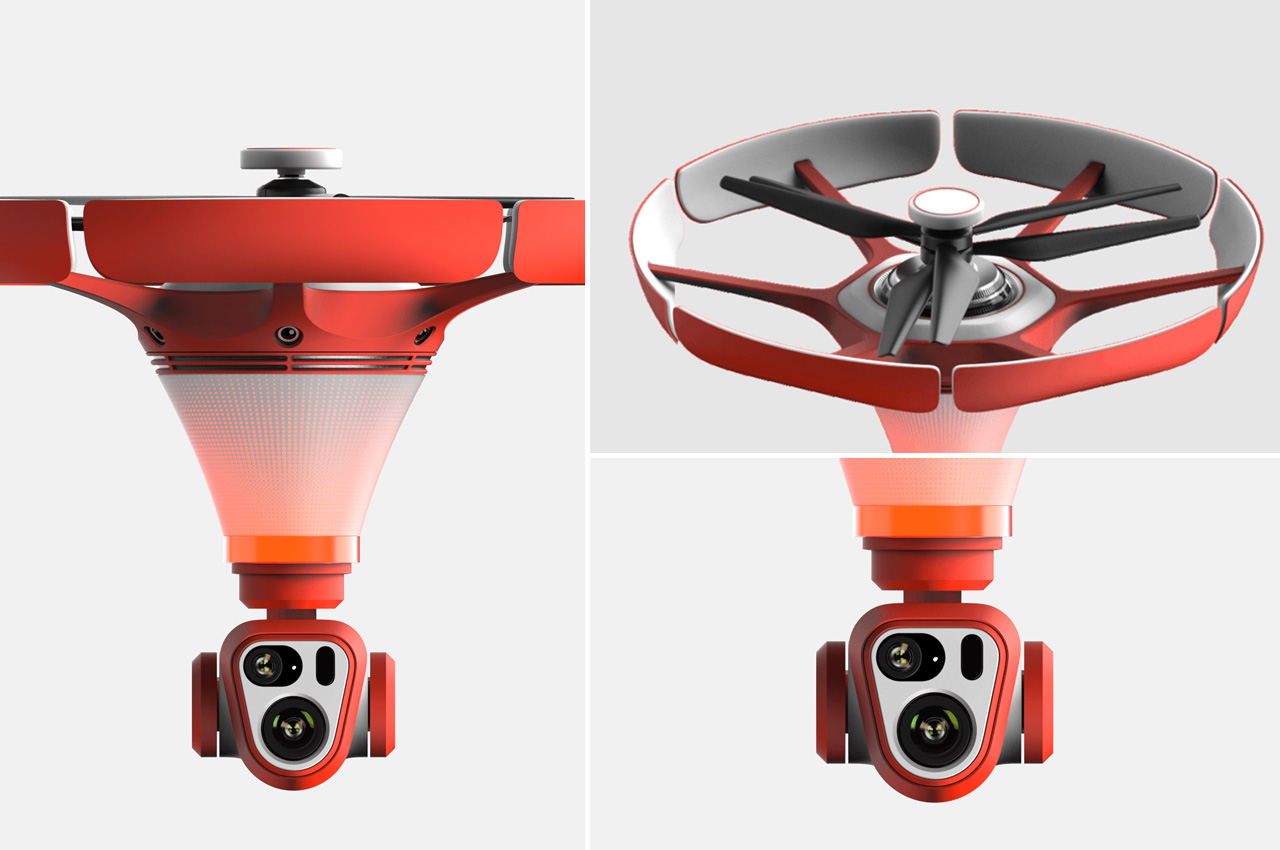
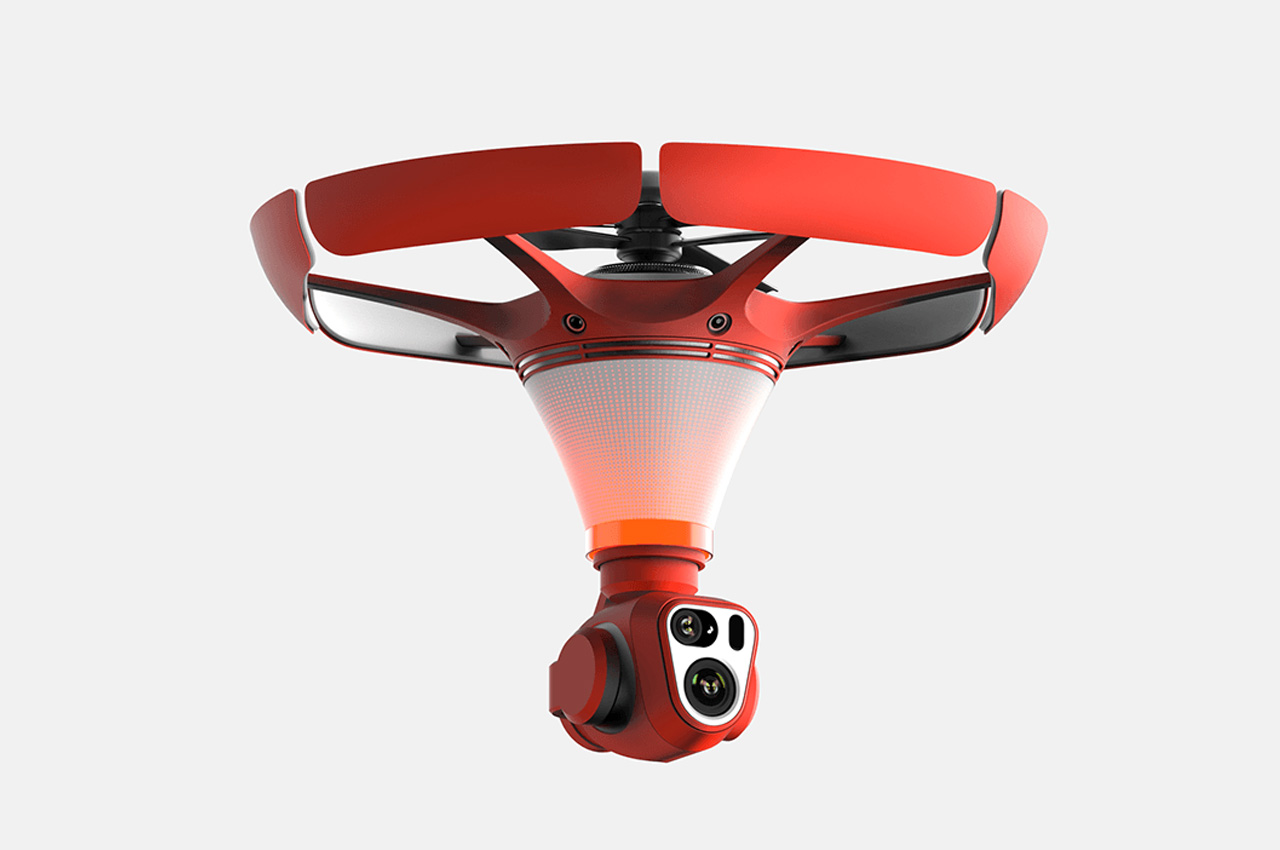
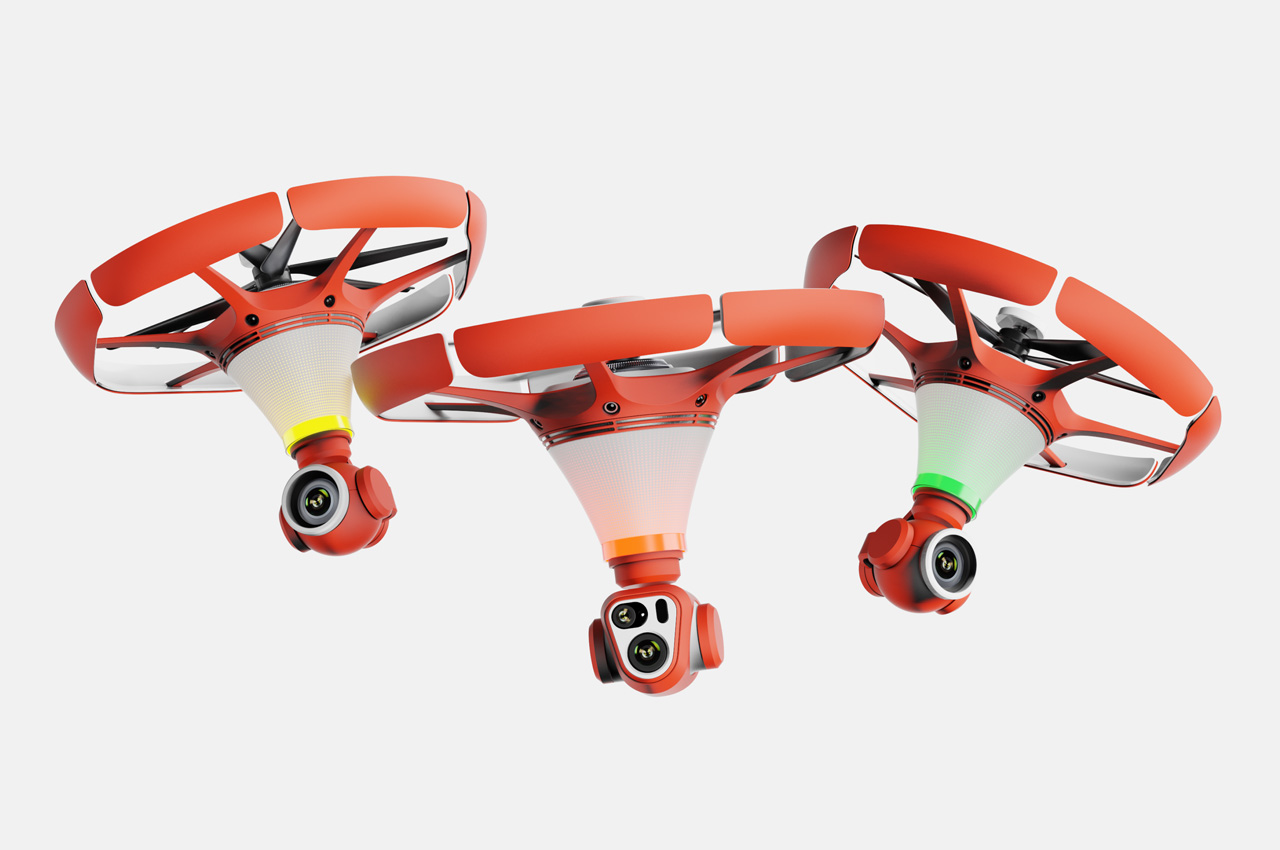
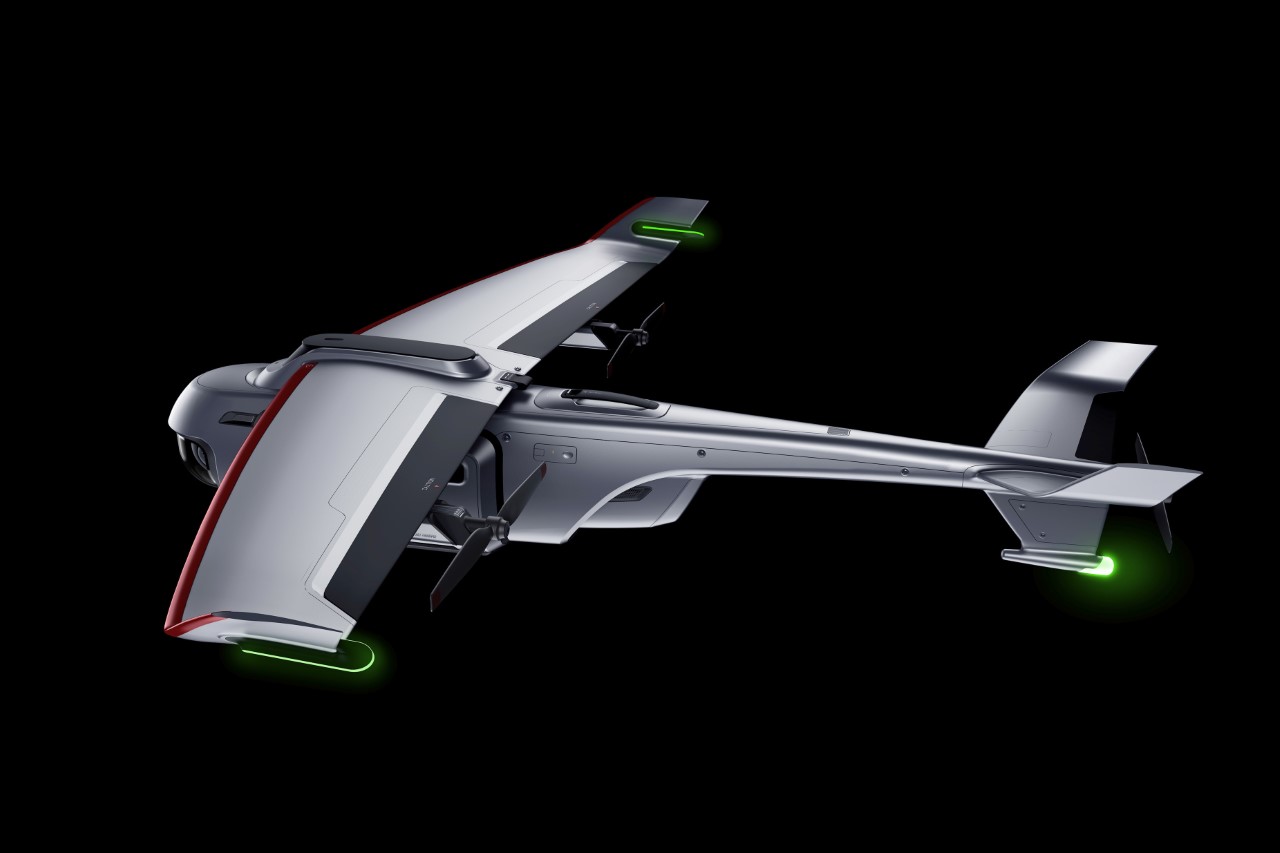
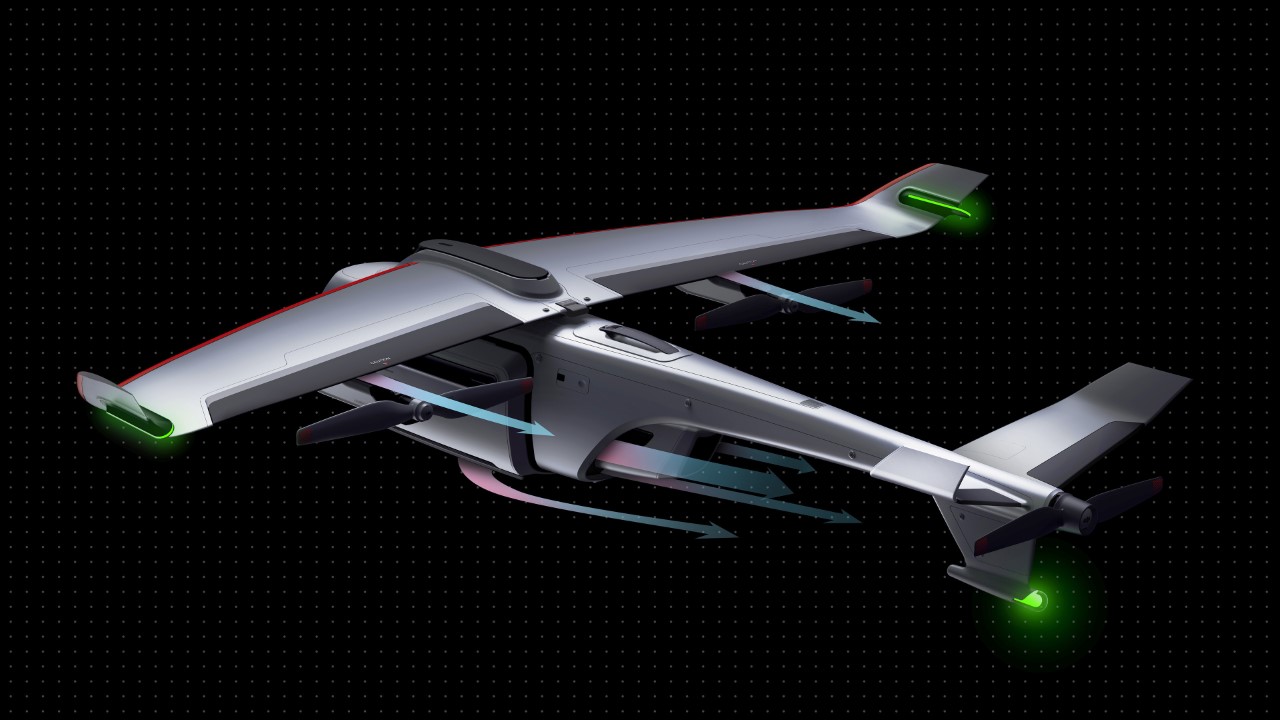
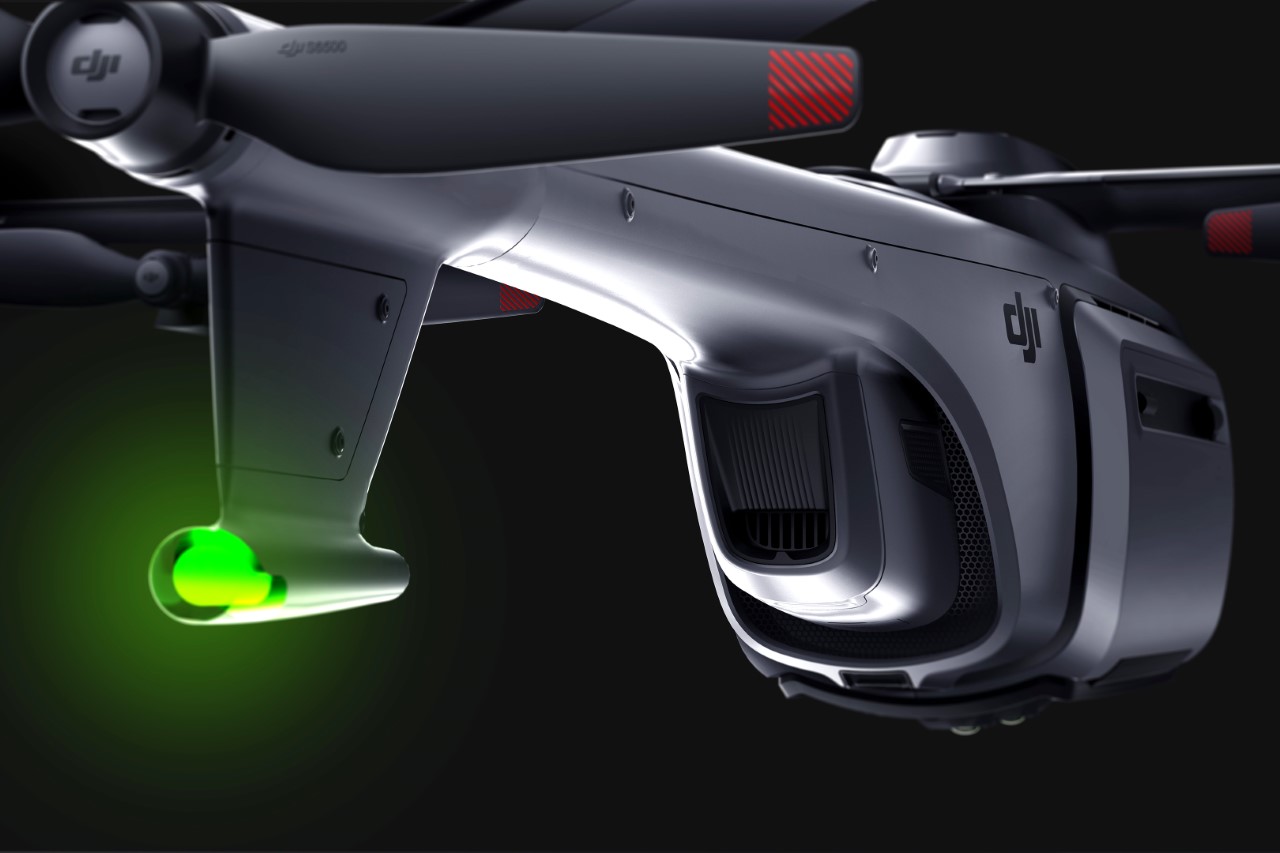
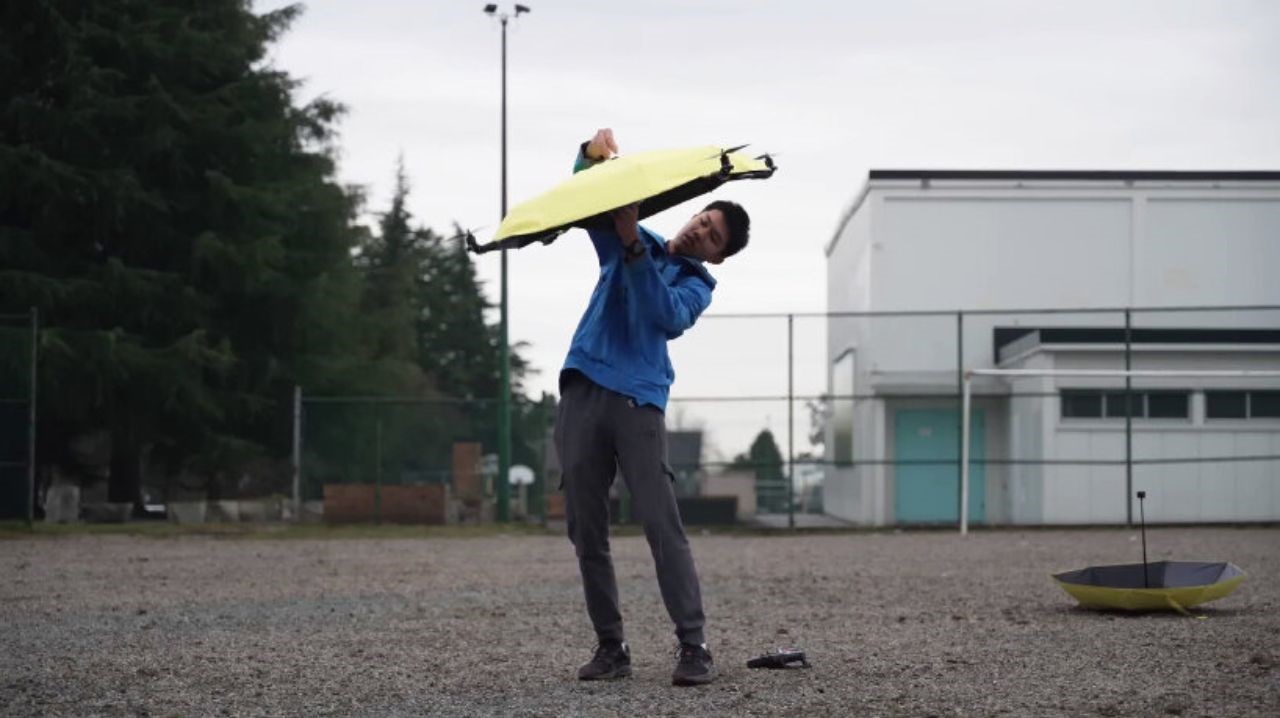
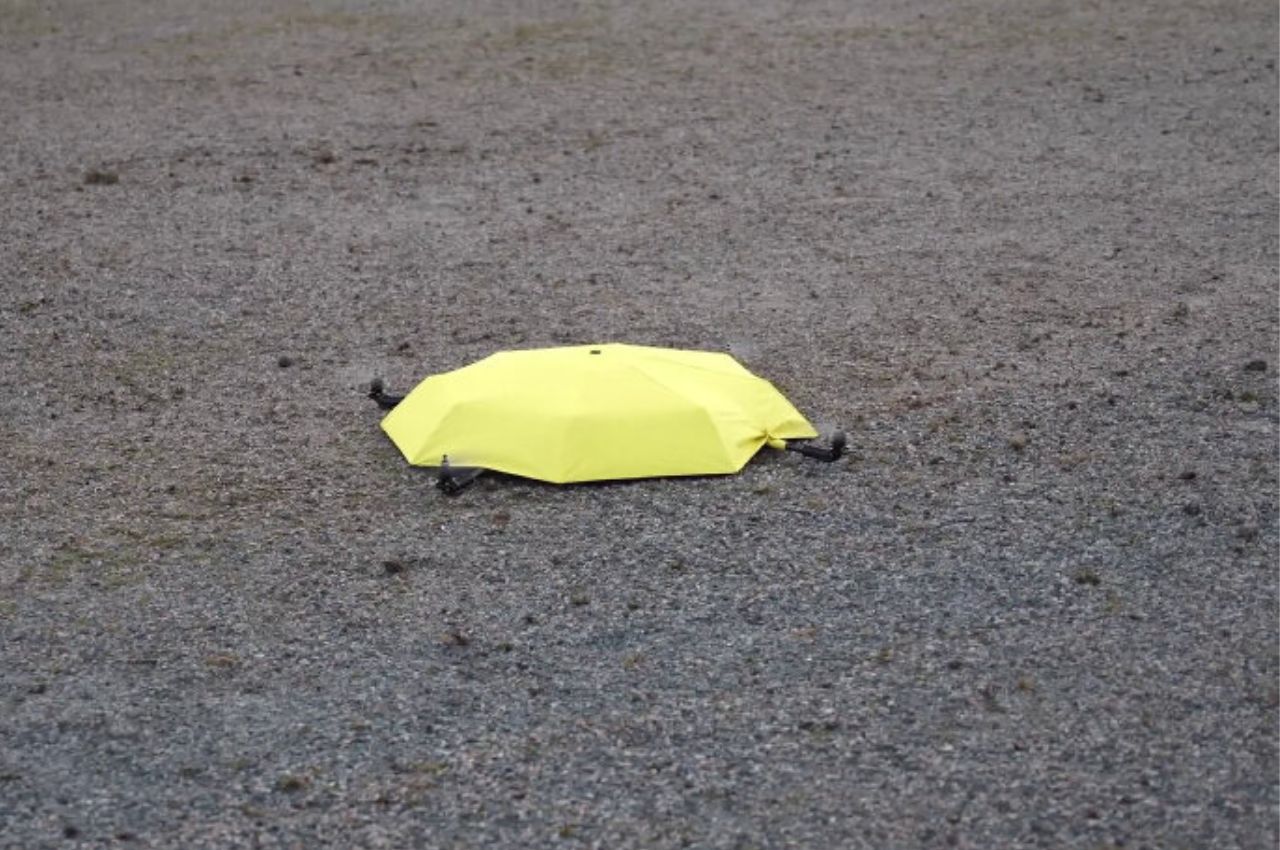
The X1 PRO and PROMAX’s design remains their strongest selling point. The flying action camera opens and closes like a book, with a camera and battery system in the ‘spine’, while the four propellers sit on either side, enclosed within a flexible, durable cage-like structure made from cutting-edge HEM materials to protect them from damage during transit or flight. To use the selfie drone, open it up and you’re ready to hit the skies. The X1 PRO and PROMAX operate on voice commands, but for more expert and intuitive tracking, HOVERAir designed a hardware Beacon that packs controls, tracking sensors, and a screen for viewing your flying action camera’s PoV. There’s no traditional remote, although the Beacon transforms into one using a series of modules like a Joystick for motion control and haptic feedback, or even the ability to snap on your smartphone to give you a true RC experience with a drone’s PoV preview. In short, the drone will fly on its own and play cinematographer to all your stunts, but if you want to get behind the ‘wheel’, it’s more than happy to relinquish control. However, if you’re looking to have your flying action camera perform a set of standard flight paths, the X1 PRO and PROMAX’s automated flight modes let you choose from in-built settings like Hover, Zoom Out, Bird’s Eye, and Orbit that capture dynamic cinematic moments, or Follow, Side Follow, and Dolly Track which are better suited for action shots. HOVERAir also plans to add more modes through OTA updates.
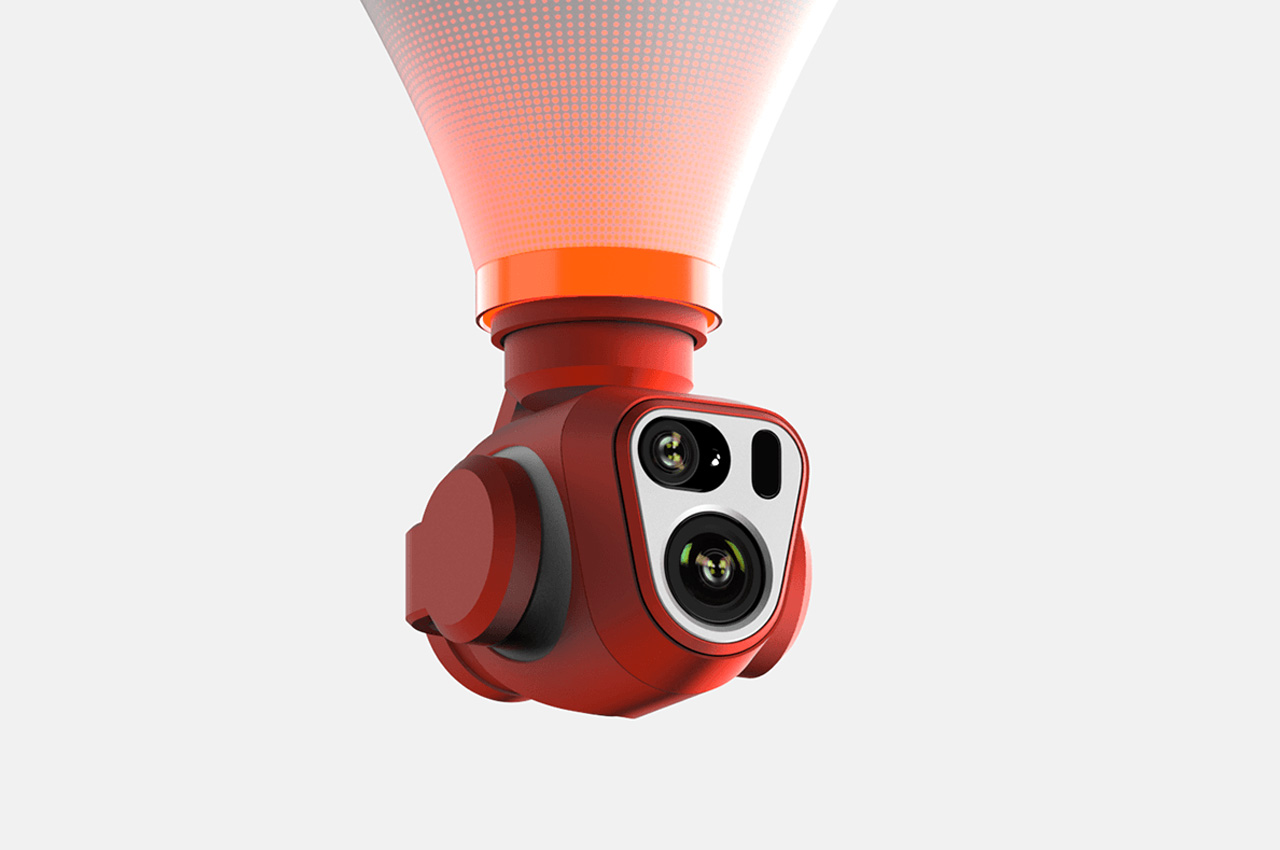
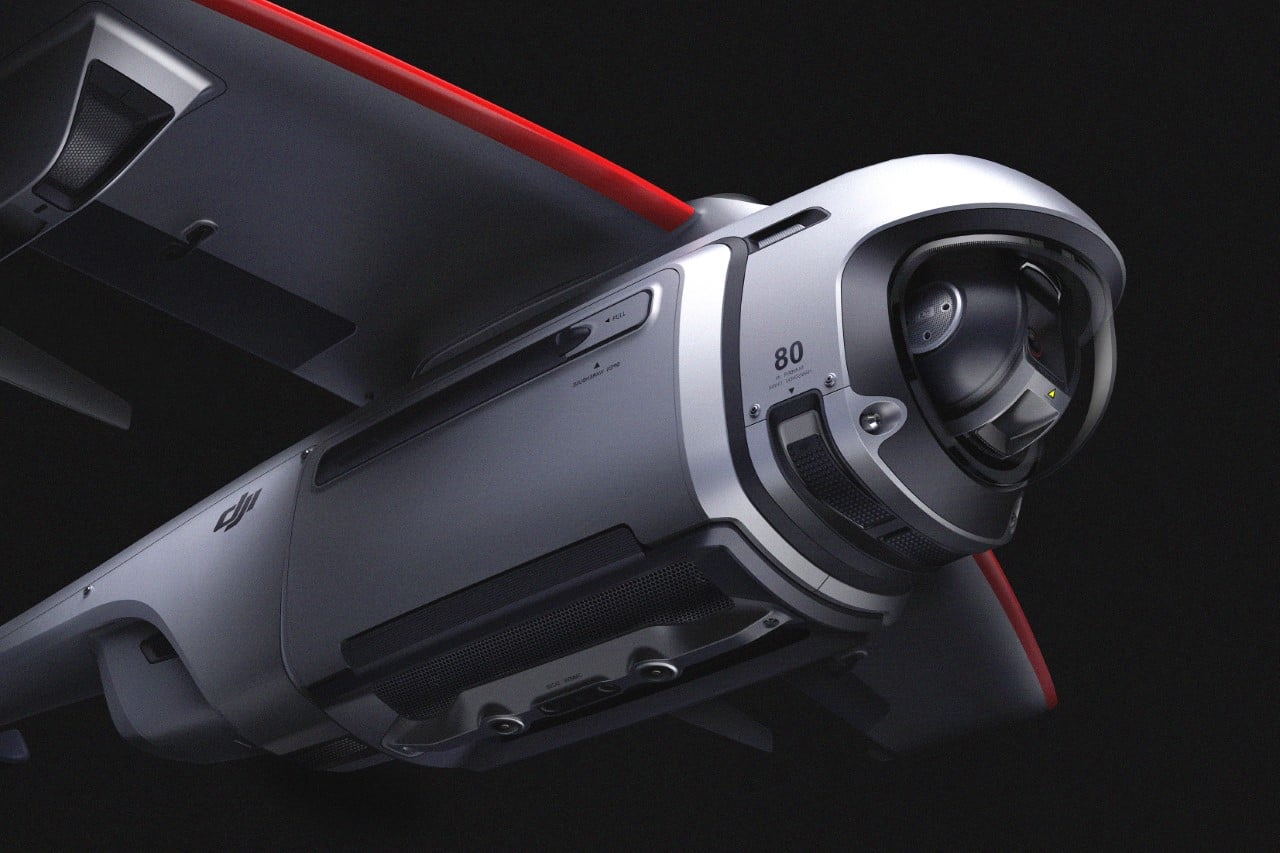
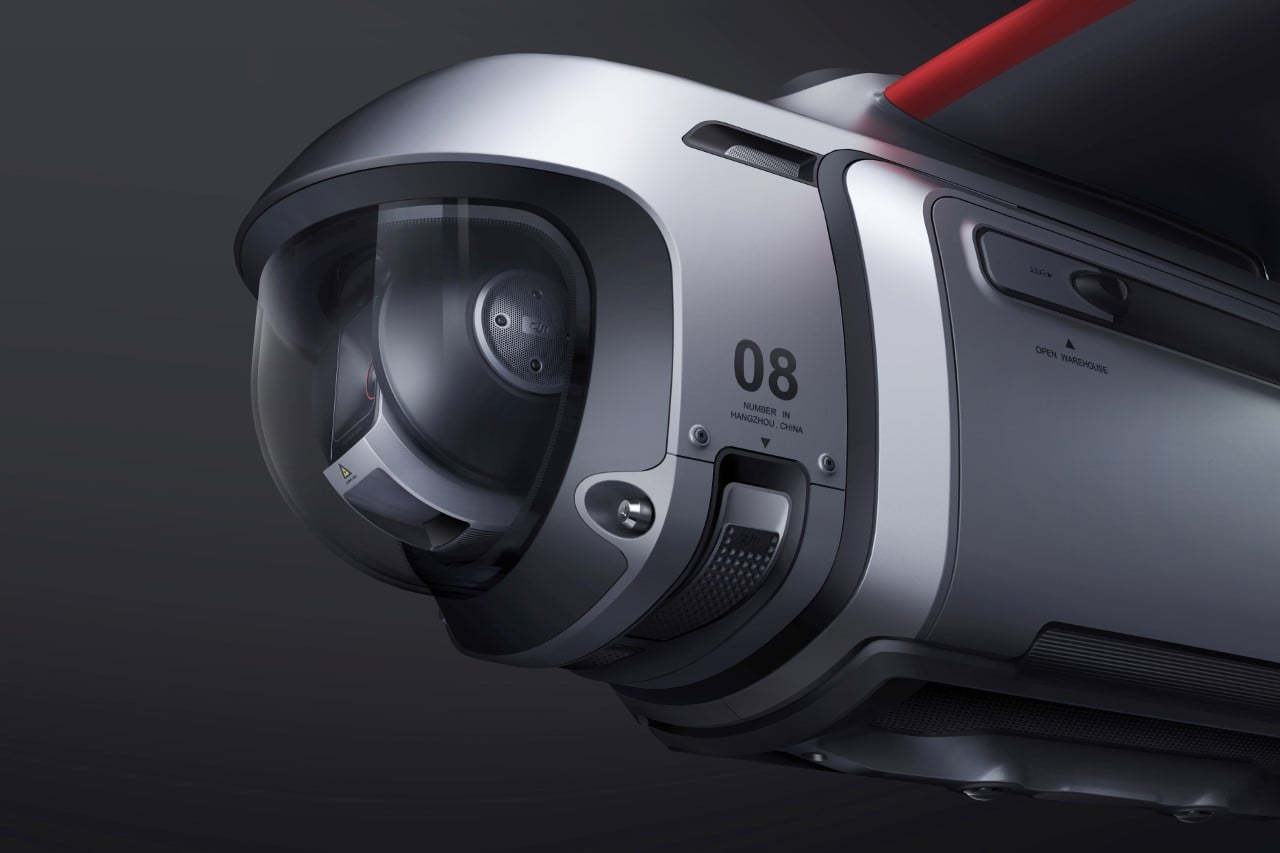
Of course, all of this ease of use wouldn’t matter much without an impressive camera. Fortunately, the HOVERAir X1 PRO delivers on that front too. Its 17mm wide-angle lens offers a generous 104° field of view, letting you capture expansive vistas and unique angles that would be impossible from the ground. The X1 PRO can shoot in 1080p at 120 frames per second, making it perfect for those stunning slow-motion shots. Want to take things even further? Enter the X1 PROMAX, which ups the ante with 8K resolution, 4K@120fps slow-motion, and a 107° FoV, giving you the tools to create breathtaking cinematic footage. The PROMAX model also introduces an extra vision-based sensor for rear active collision detection, adding an additional layer of protection when you’re flying in tight or unpredictable spaces – ideal for those moments when you’re pushing boundaries (and maybe your luck).

The PRO and PROMAX both have a two-axis gimbal with EIS (electronic image stabilization) and HL (horizon leveling), so your footage will be rock steady even when the adventure is rough.
When it comes to camera drones, stability is everything. No one wants shaky footage from a breezy afternoon at the beach or during a fast-paced tracking shot through a forest trail. The HOVERAir X1 PRO and PROMAX rise to the challenge with built-in video stabilization that they call SmoothCapture 2.0. A two-axis gimbal with EIS (electronic image stabilization) and HL (horizon leveling) kicks in while the drone’s in flight, allowing you to focus on capturing the scene rather than compensating for jitters. For more accurate honing in on your subject, you’ve got the HoverAir Beacon, a nifty add-on that clips onto your handlebar while you’re riding, allowing you to quickly see the flying action camera’s PoV while also giving it a target it can track. This companion device unlocks live previews and expanded control options, transforming your flying experience into something closer to autonomous filmmaking. The Beacon uses HoverLink Technology for ultra-precise tracking, so you can leave the steering to the X1 PRO or PROMAX and focus on getting the shot.
Technology for ultra-precise tracking, so you can leave the steering to the X1 PRO or PROMAX and focus on getting the shot.
Once you’ve filmed your shot, Wi-Fi 6 integration ensures your aerial masterpiece doesn’t stay stuck in the device’s memory. Quick file transfers mean you can start editing almost immediately after landing. Plus, the selfie drone’s long-range video transmission of up to 1 km (with the Beacon) lets you explore and shoot from afar, capturing wide-open landscapes or large events without sacrificing video quality. It’s the kind of feature that makes you feel like the director of your own blockbuster.
Beyond the camera and flight smarts, the Hover X1 PRO is built to be a winning combination of portable and durable. The foldable design doesn’t affect the drone’s ability to fly with great dexterity, and even with those collision-prevention mechanisms in place, the X1 PRO and PROMAX can dust off mild bumps and accidents thanks to a flexible, shock-absorbing propeller cage. And then there’s the thrill of taking this thing off-road—literally. The X1 Pro’s Omni terrain capability makes it versatile enough to fly over lakes, through snowy forests, or along cliff edges with ease. It adds a whole new layer of adventure to your flights. The control system adapts right along with it, allowing you to turn the Hover Beacon into a one-handed joystick or opt for the more traditional two-handed smartphone setup. Either way, it adjusts to how you want to fly and where you’re flying.
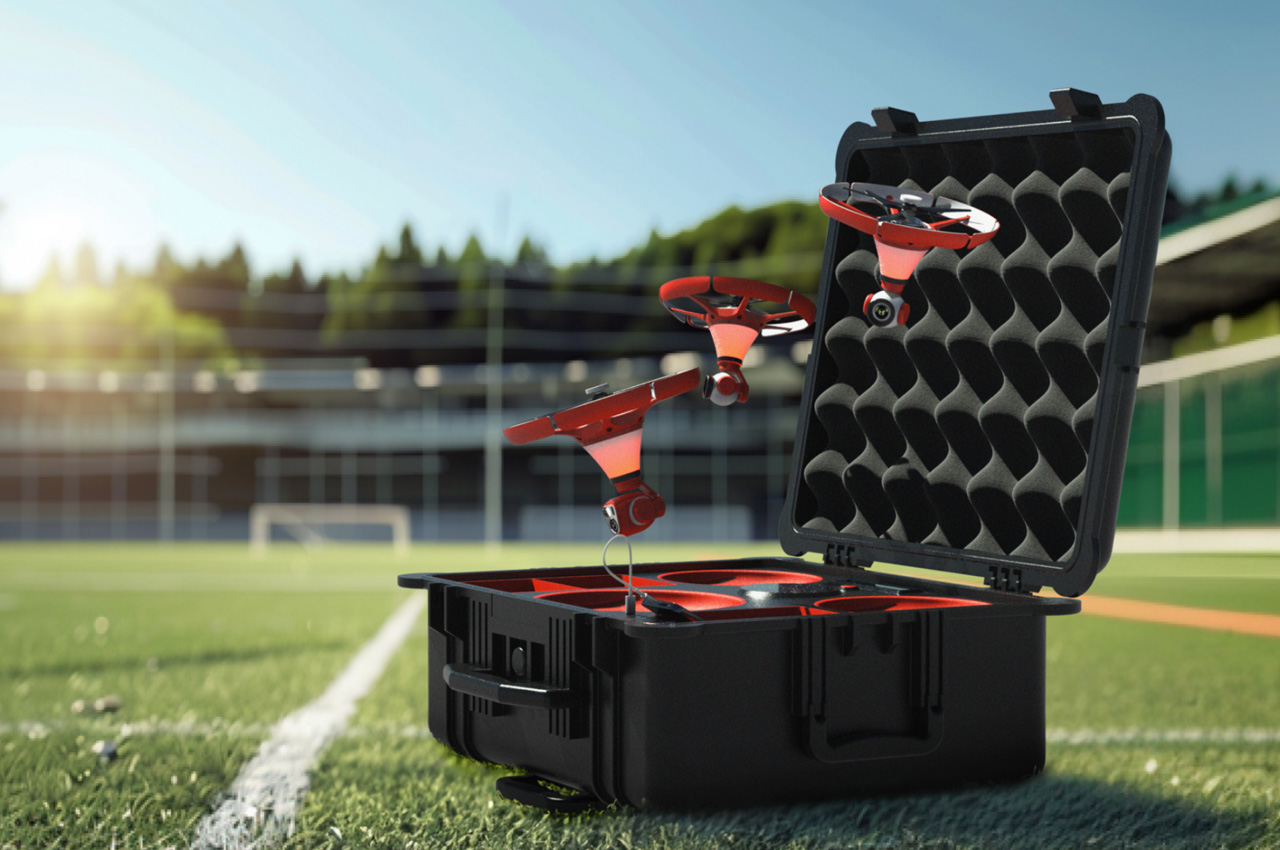
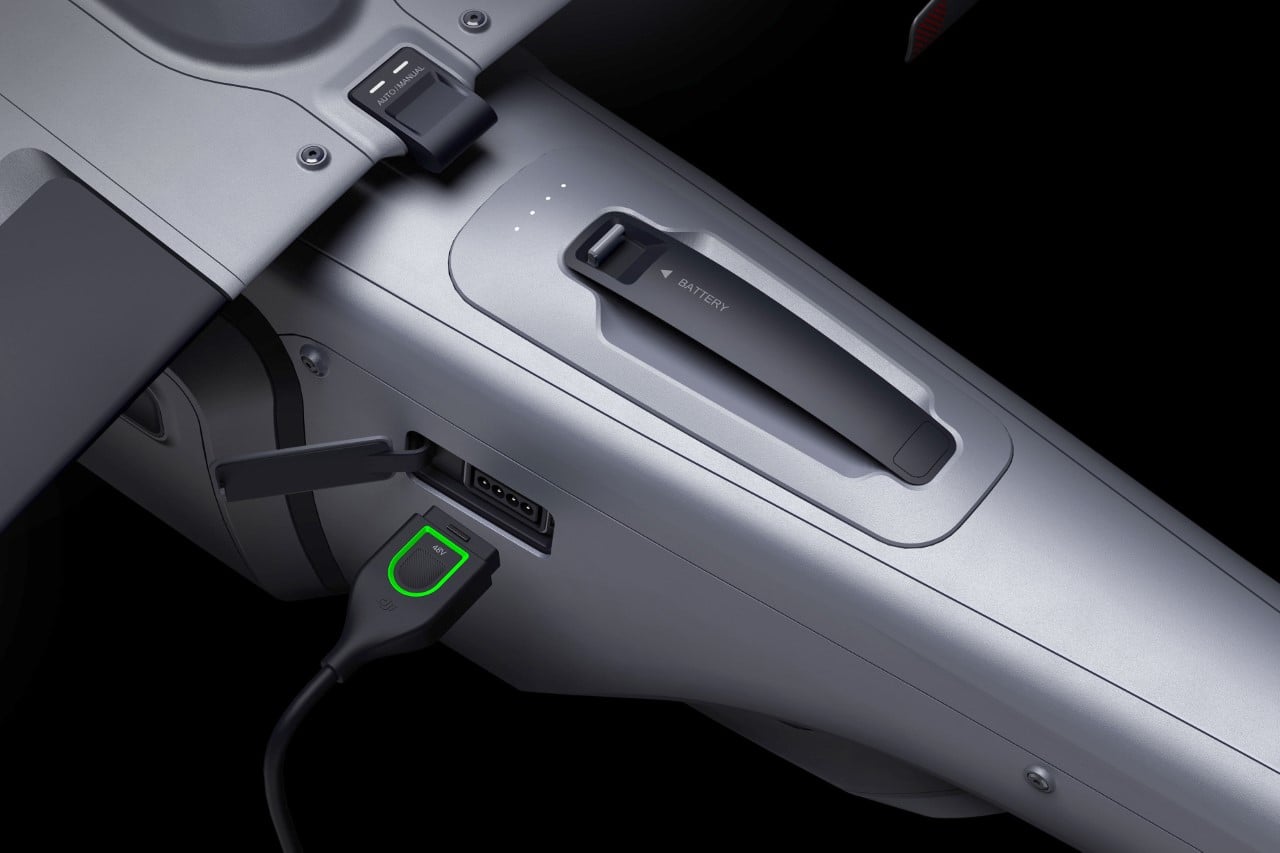
You can either fold the device and carry it around in your pocket when not in use, but HOVERAir also makes a slick leather carrying case to haul your compact aerial camera around wherever you go. However, if you’re looking for an upgrade, HOVERAir’s even designed a PowerCase, which both houses your flying action camera and even supplements it with up to two additional battery charges. Designed specifically for use in extreme cold weather, the PowerCase works at temperatures even as low as -4°F (-20°C) to keep your device charged and ready for flight. Of course, flying your drone in sub-zero temperatures is yet another challenge, which is why HOVERAir even sells a special ‘Thermo Battery’ that you can fit into either the X1 PRO or X1 PROMAX, giving it an operating temperature range of -4°F to 113°F.
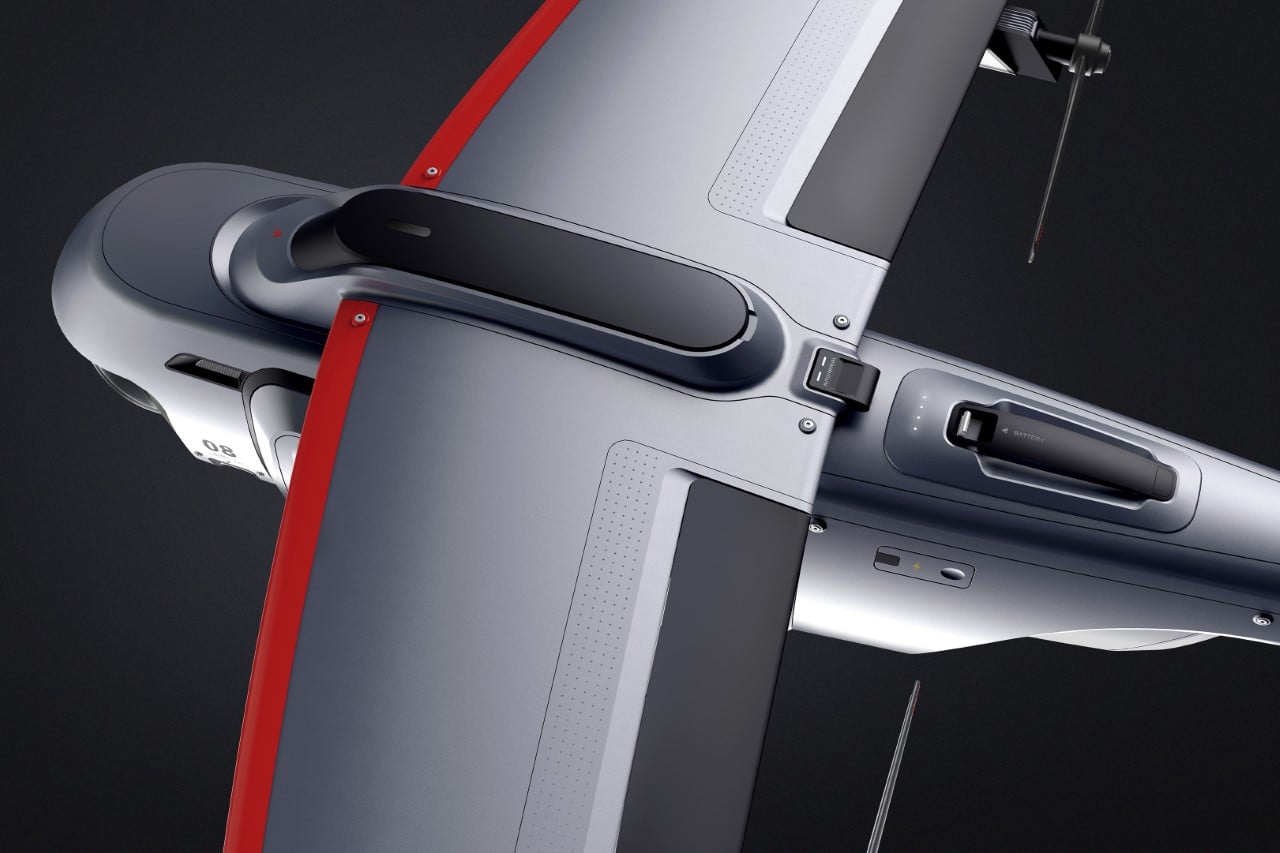
Both the HOVERAir X1 PRO and PROMAX come with built-in 64GB storage, upgradable up to 1TB thanks to an SD card slot located on the flying action camera’s body. The X1 PRO and PROMAX run in conjunction with the HOVERAir X1 app, which allows you to configure flight modes, download and share content, launch manual control, and even install firmware updates on your flying action camera. The app offers a transmission range of 500m, while the Beacon bumps it up to an entire kilometer. You can grab the X1 PRO and PROMAX either as standalone devices, or opt for cycling or skiing combos that include the leather carrying case, PowerCase, Thermo Battery, the Beacon, or the modular accessories that turn the Beacon into a joystick. The X1 PRO and PROMAX have already begun shipping as of end-September with a 12-month warranty, and the batteries get a 12-month warranty too (applicable up to 100 cycles).
Click Here to Buy Now: $499. Hurry, only 30 left! Raised over $4.6 million.
The post HOVERAir: World’s First 8K Flying Action Camera fits in your pocket and operates without a remote first appeared on Yanko Design.