
So Apple could be working on an iPhone with a thinner display, you say. Look what we have here, possibly in the nick of time: it's a newly granted Apple patent for a screen with in-cell touch, where the LCD and touch recognition are integrated into one panel instead of stacking up in separate layers. Apple's implementation would slim things down by either having electrodes share duties, both driving the display and taking finger input, or stuffing two electrodes into each pixel to accomplish the same goal. The net effect isn't just one of squeezing a device into a thinner chassis; the company also envisions costs coming down by reducing the number of parts and streamlining the manufacturing process. As envisioned, the screen looks like an ideal fit for a significant revamp of Apple's mobile display technology, although we'd be careful about assuming that this or any in-cell touch implementation is a lock for potentially imminent iOS hardware. Apple first filed the patent in early June 2007, before the original iPhone had even marched into a retailer -- display technology has come a long way since then.
Filed under: Cellphones, Displays
Apple gets patent for in-cell touch display with impeccable timing originally appeared on Engadget on Tue, 14 Aug 2012 12:55:00 EDT. Please see our terms for use of feeds.
Permalink  AppleInsider
AppleInsider |
 USPTO
USPTO |
Email this |
Comments
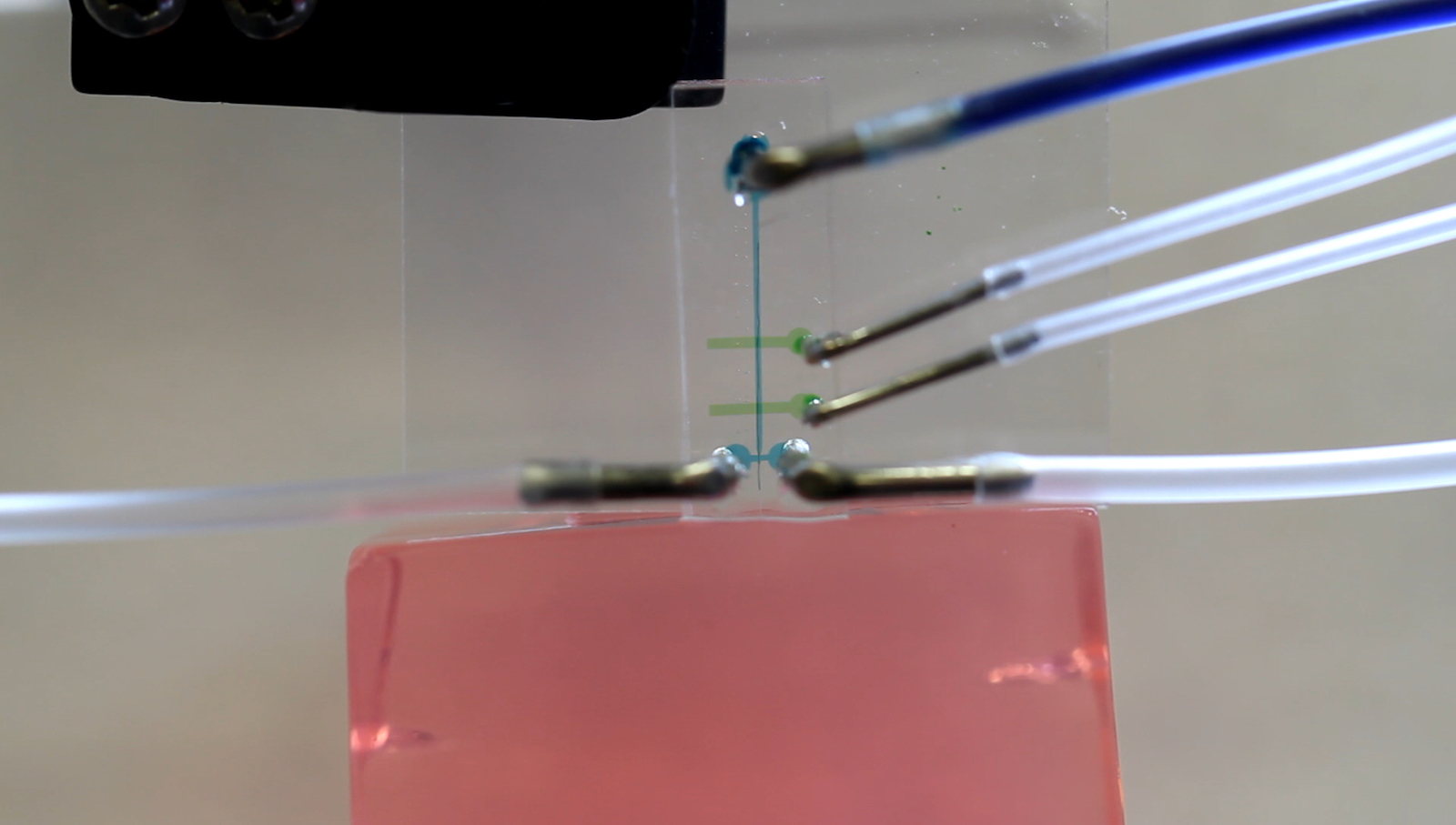 Our neurons are firing all the time, receiving signals from other neurons and sending signals of their own. To get a better understanding of how the brain works, scientists often listen in to those signals to see what kind of messages certain neurons...
Our neurons are firing all the time, receiving signals from other neurons and sending signals of their own. To get a better understanding of how the brain works, scientists often listen in to those signals to see what kind of messages certain neurons...
 Our neurons are firing all the time, receiving signals from other neurons and sending signals of their own. To get a better understanding of how the brain works, scientists often listen in to those signals to see what kind of messages certain neurons...
Our neurons are firing all the time, receiving signals from other neurons and sending signals of their own. To get a better understanding of how the brain works, scientists often listen in to those signals to see what kind of messages certain neurons...
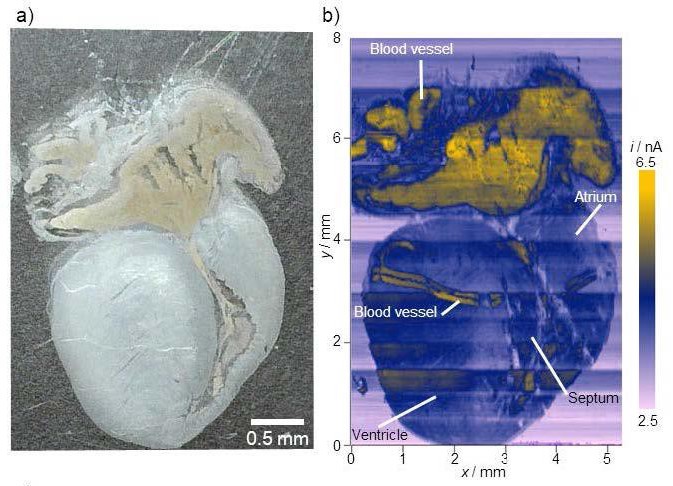 In a study published recently in Angewandte Chemie, researchers demonstrated that an imaging technique called scanning electrochemical microscopy could become a very useful medical tool. Rather than having to use additional chemicals like dyes or flu...
In a study published recently in Angewandte Chemie, researchers demonstrated that an imaging technique called scanning electrochemical microscopy could become a very useful medical tool. Rather than having to use additional chemicals like dyes or flu...
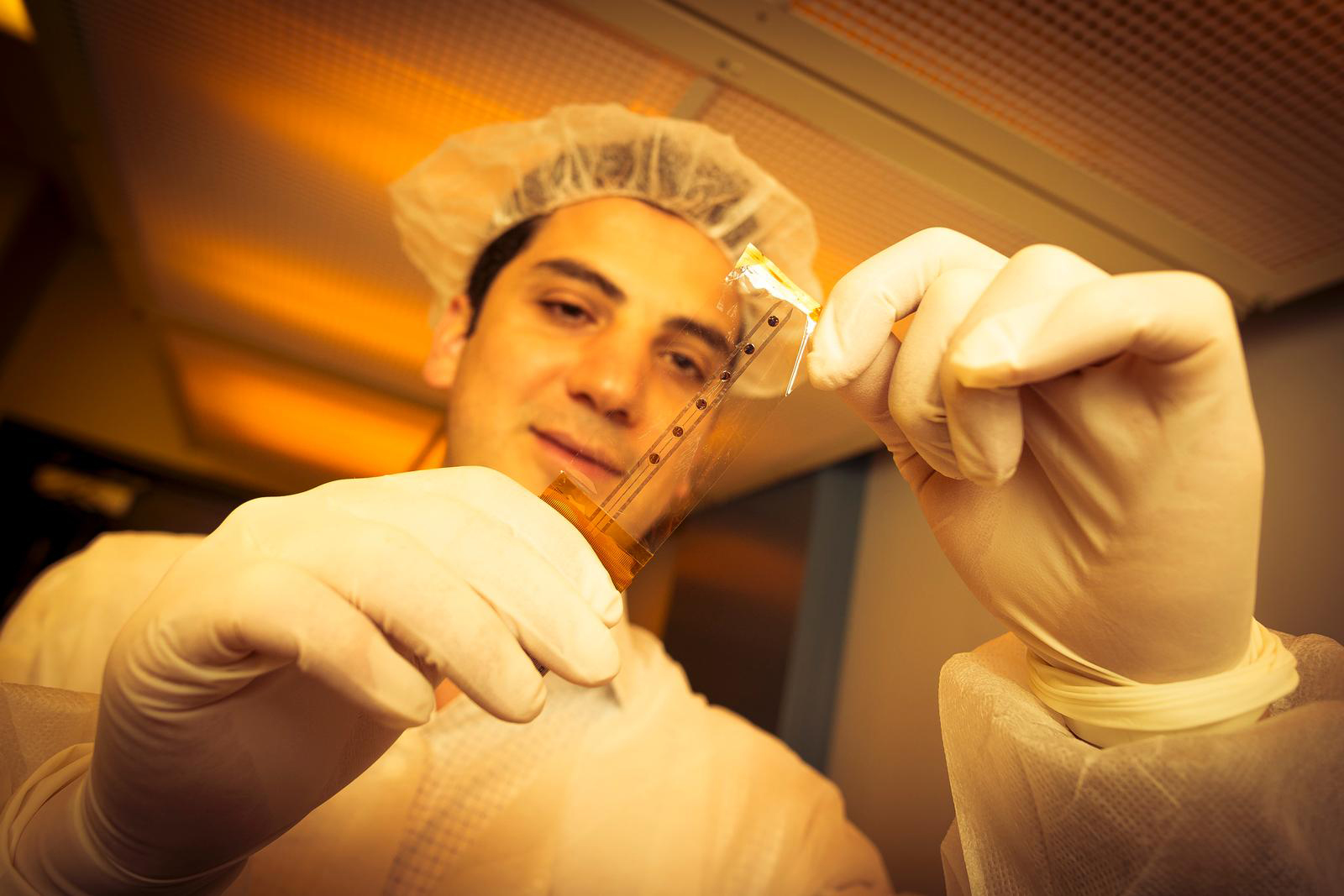 It almost goes without saying that brain surgery requires extreme precision, but there hasn't been much advancement in brain mapping techniques for the past two decades. What good is a breakthrough procedure if you're still using bulky, imprecise 199...
It almost goes without saying that brain surgery requires extreme precision, but there hasn't been much advancement in brain mapping techniques for the past two decades. What good is a breakthrough procedure if you're still using bulky, imprecise 199...


 Today on In Case You Missed It: Researchers from Purdue University and the Office of Naval Research teamed up to develop a new kind of glue that even works underwater. The synthetic compound is derived from proteins used by muscles to keep themse...
Today on In Case You Missed It: Researchers from Purdue University and the Office of Naval Research teamed up to develop a new kind of glue that even works underwater. The synthetic compound is derived from proteins used by muscles to keep themse...



