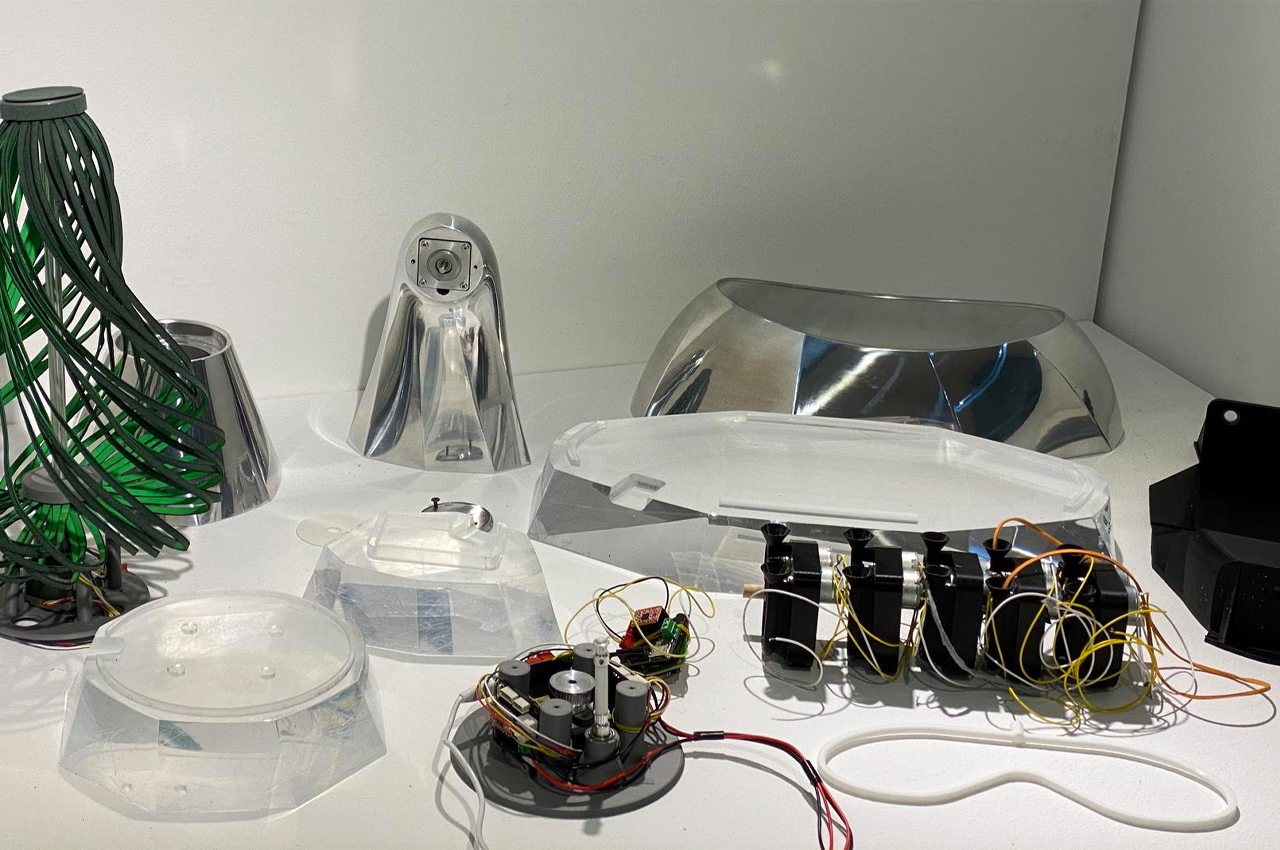
Most often, we only see plants moving and growing when they’re filmed in slow-motion for nature documentaries. But even in those slow scenes, watching plants bloom and grow into themselves feels emotional. It’s like watching a baby tiger wake up from a cat nap on the big screen, except it doesn’t have a face and it’s green, not furry. Inspired by the growth cycle and emotive movement of plant life, student designer Keunwook Kim designed Post-Plant, a collection of non-humanoid robots that respond to and move through non-verbal, physical interaction.
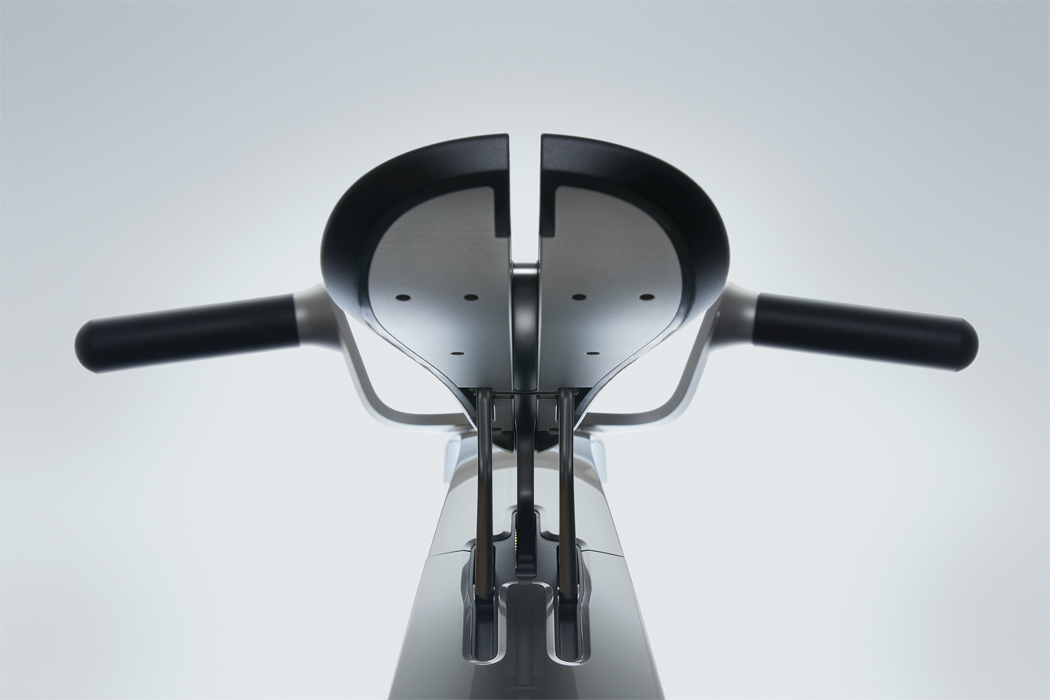
Following a period of researching how humans can read emotion from non-verbal cues, Kim gathered that arousal (dynamic energy), valence (intrinsic attractiveness), and stance (visual disposition) can each be interpreted as signs for emotional analysis. Applying this information to Post-Plant, Kim’s non-humanoid robots do not express emotion through facial expression, but through movement and changing forms. Built into each one of his Post-Plant robots, Kim incorporated a motor interface that combines an input and output system, registering when the robot is touched and responding with movement.
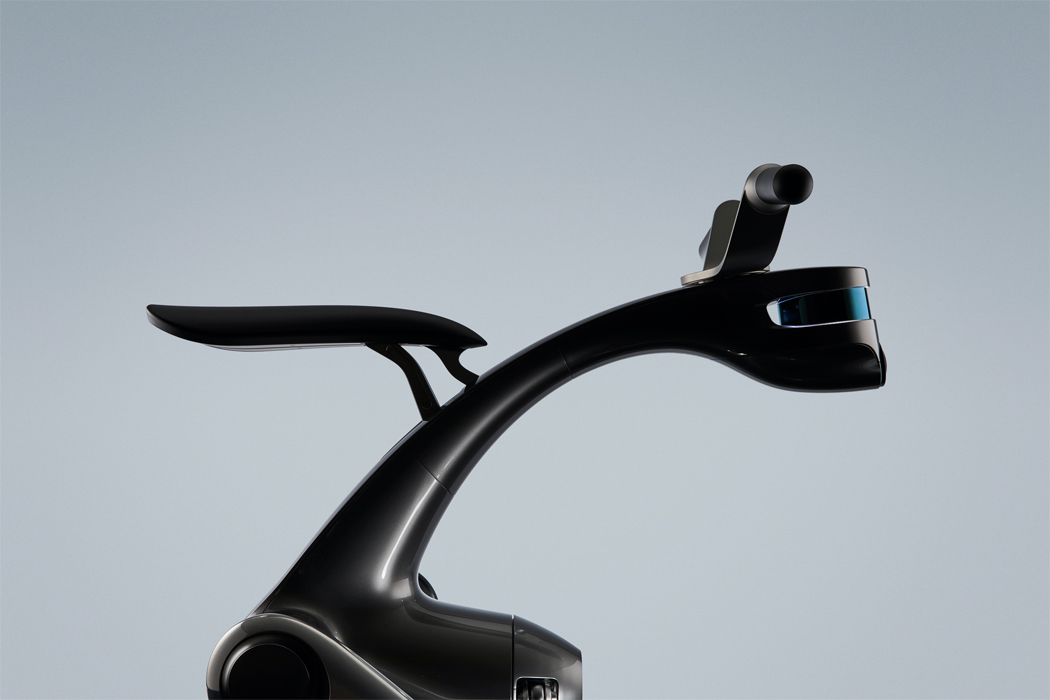
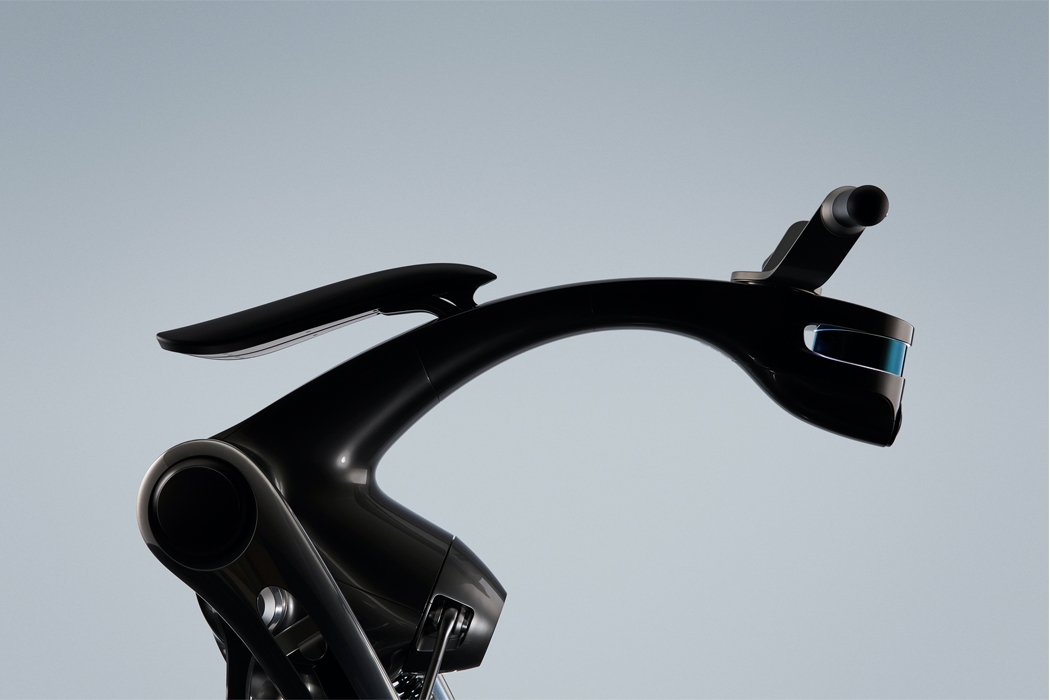
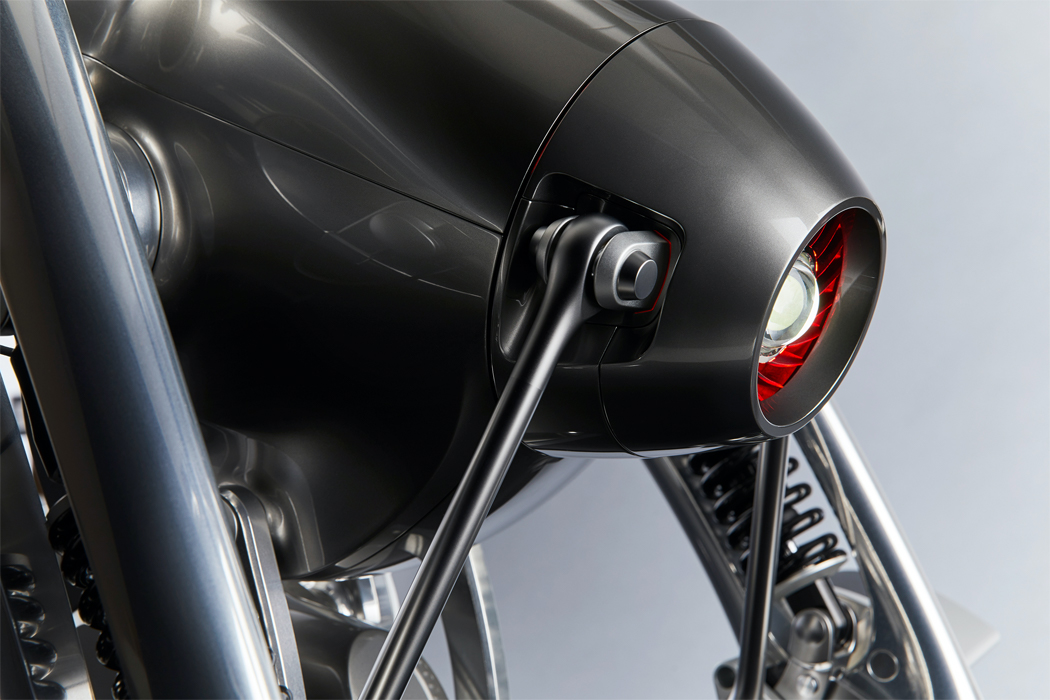
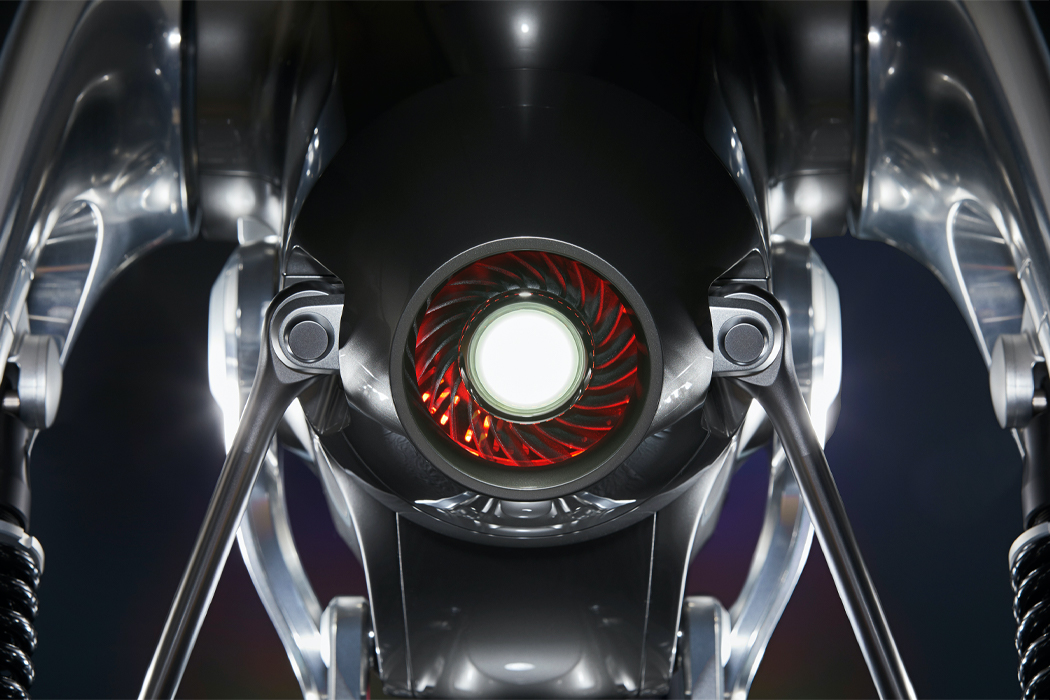
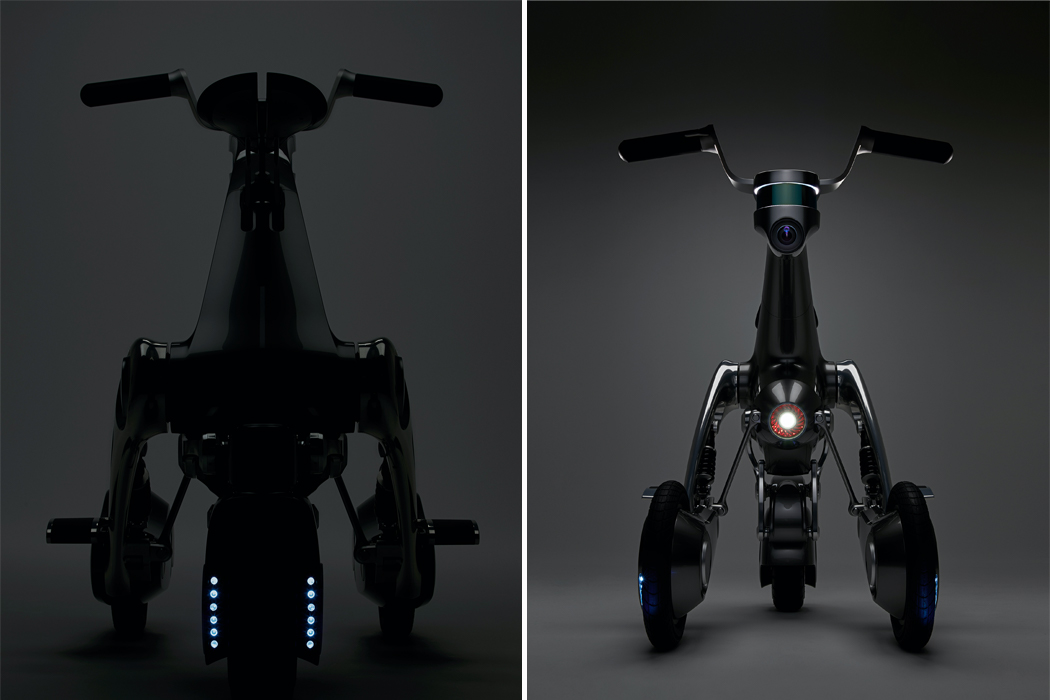
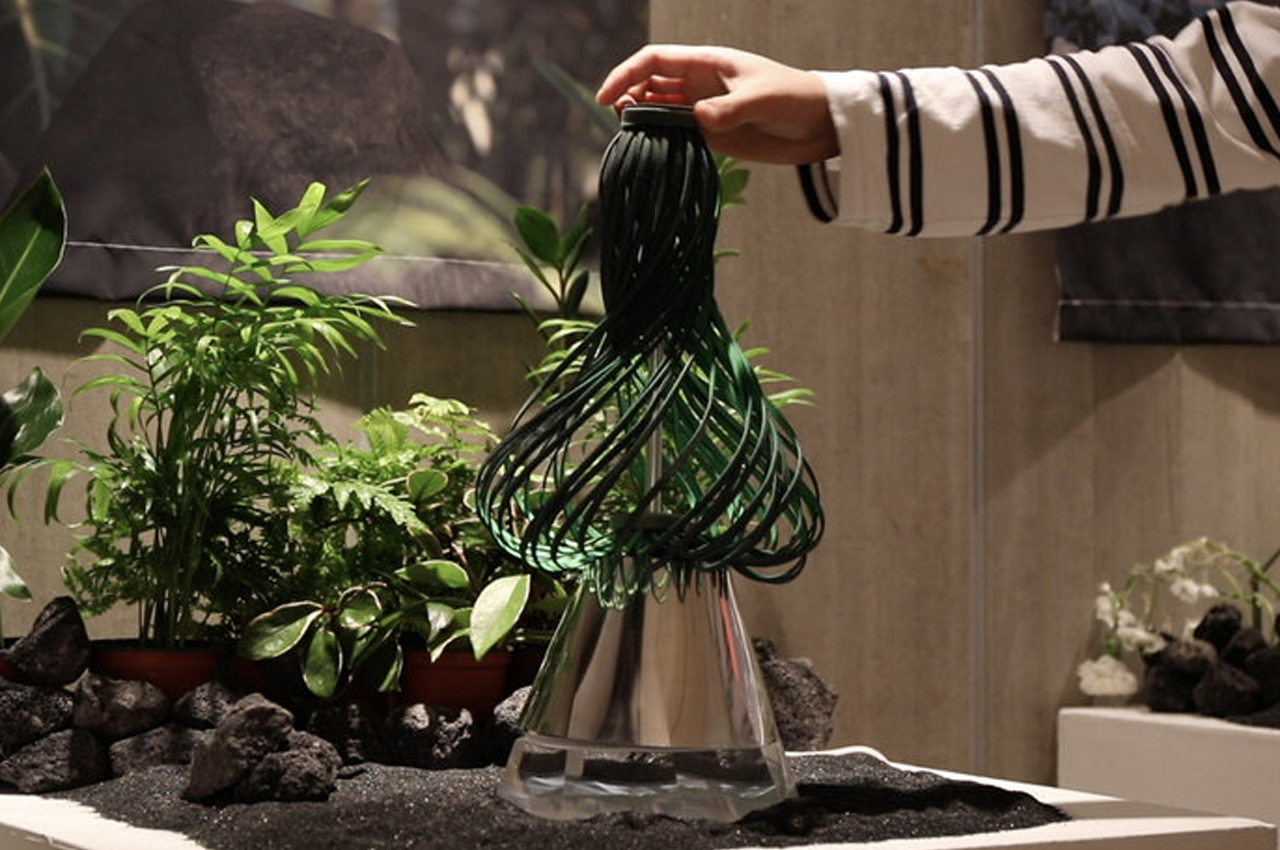
For example, when the top of Kim’s green robot, which could also be an interpretation of Maypole dancing from Midsommar, is turned, the robot responds with arousal, by spinning its ‘leaves.’ Signaling when its valence is turning negative, the Post-Plant robot binds its leaves tightly together. Once those leaves are touched by a human, the robot spins its leaves out once more, indicating a changed, positive valence. Similarly, Post-Plant’s white robot spins its propeller-like leaves in response to being touched but shivers to express unhappiness, indicating a need to be touched once more. By studying how humans read emotion, Kim hopes to cultivate the emotional relationship we have with robots and the potential to express a robot’s emotion through non-humanoid, kinetic gestures.
Designer: Keunwook Kim
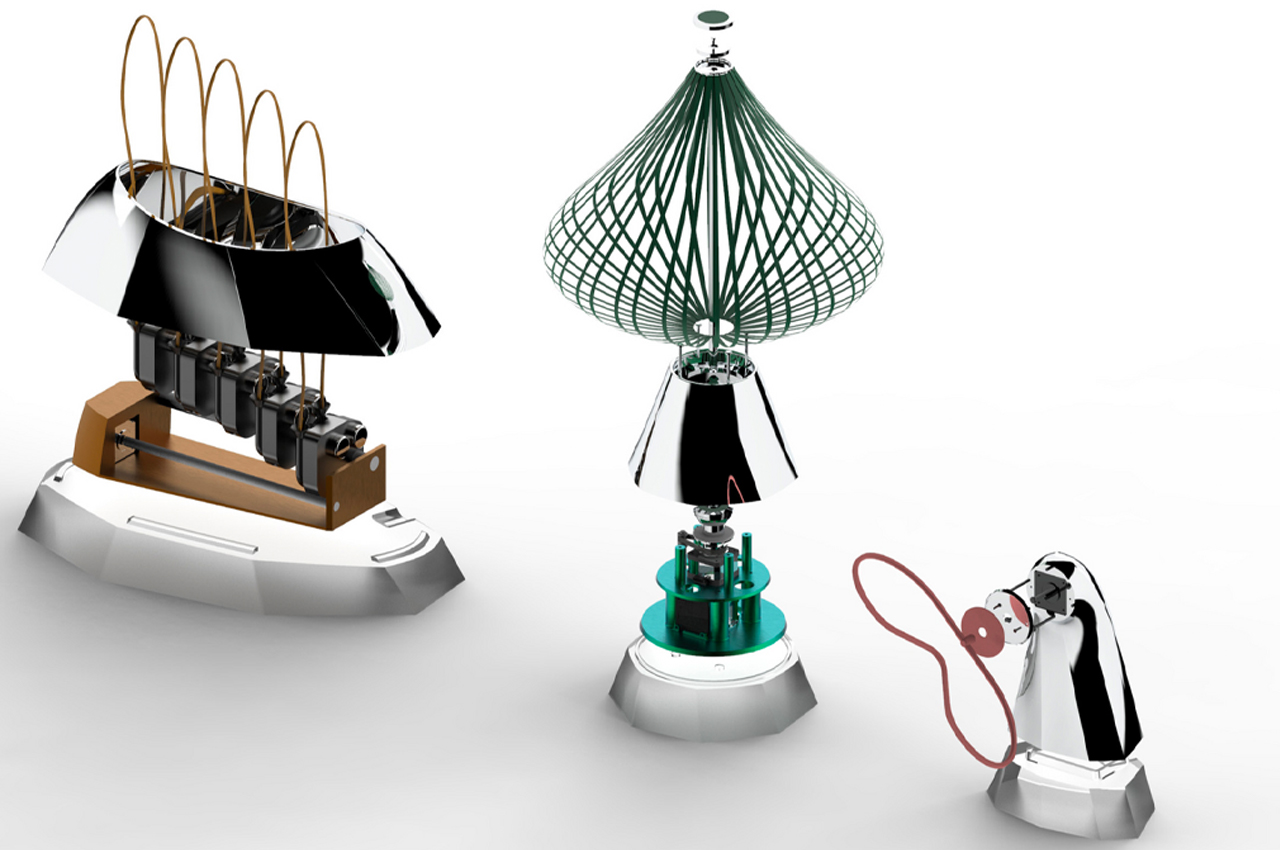


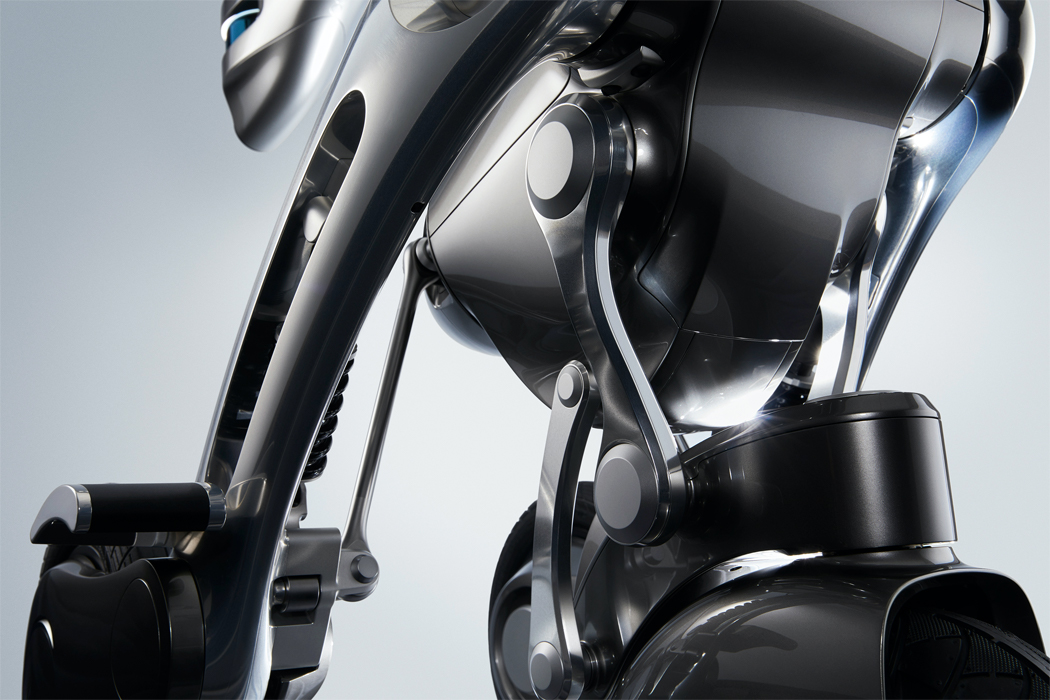
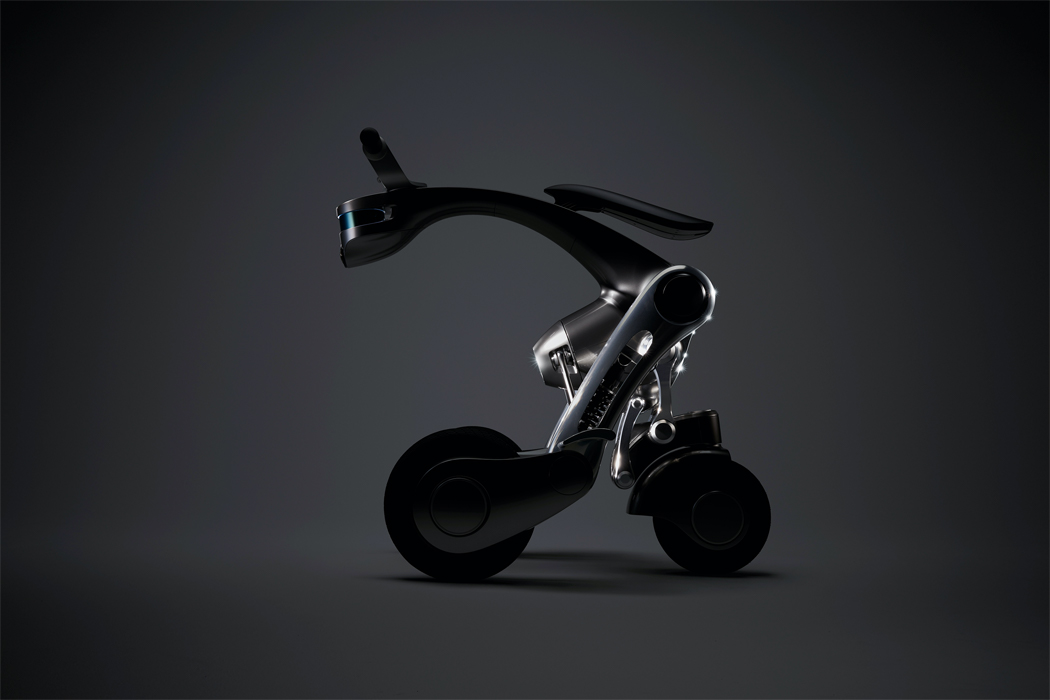
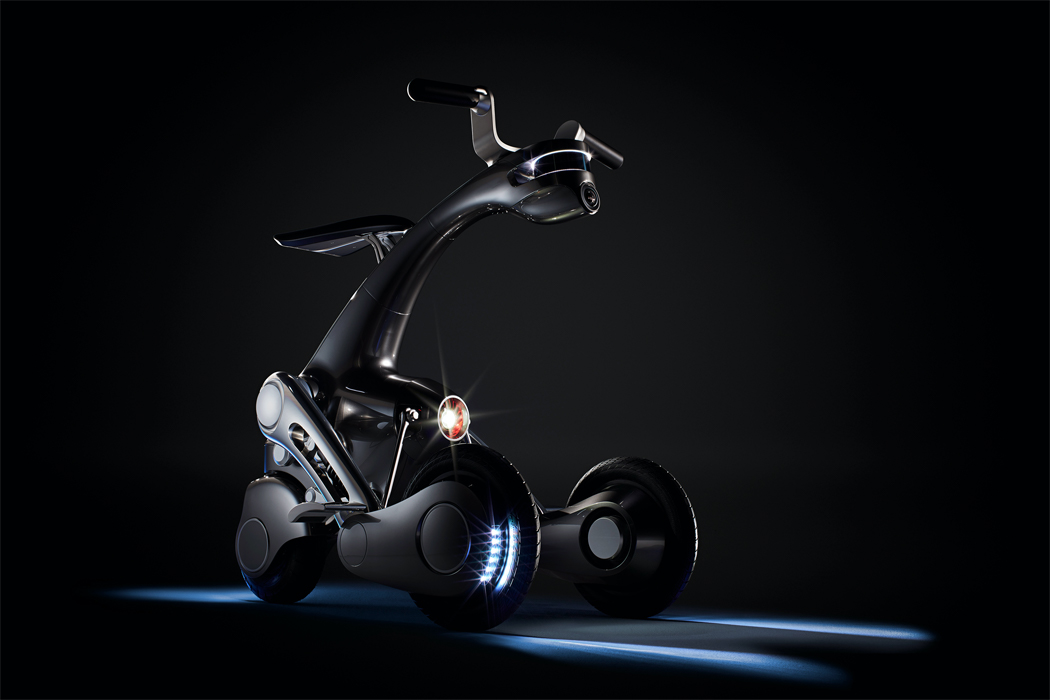
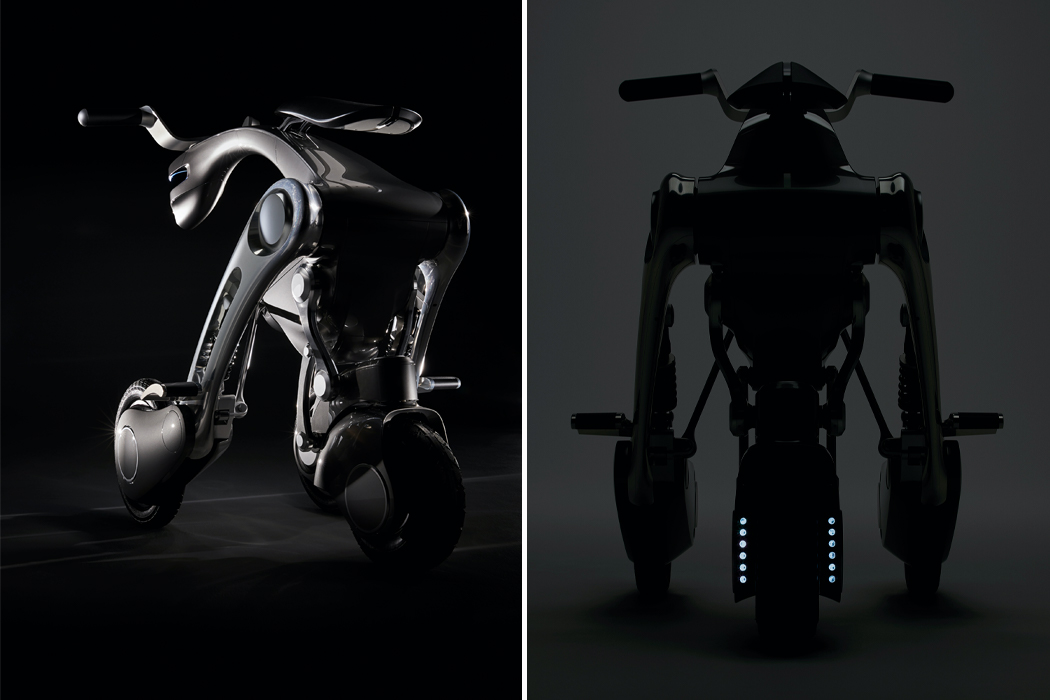
Keunwook Kim built three different non-humanoid robots resembling various forms of plant life.
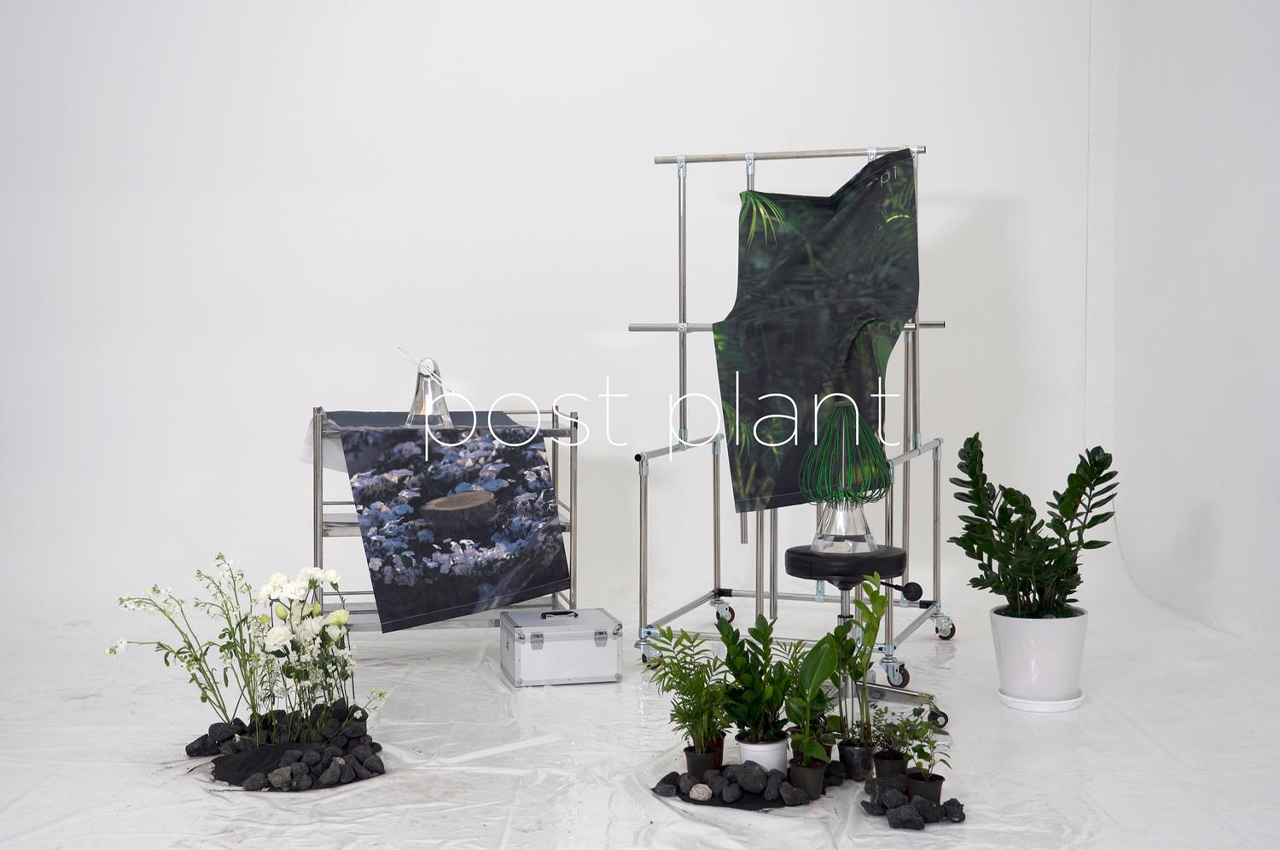

Taking cues from nature, Keunwook Kim researched the different ways humans can read emotion through non-human gestures.
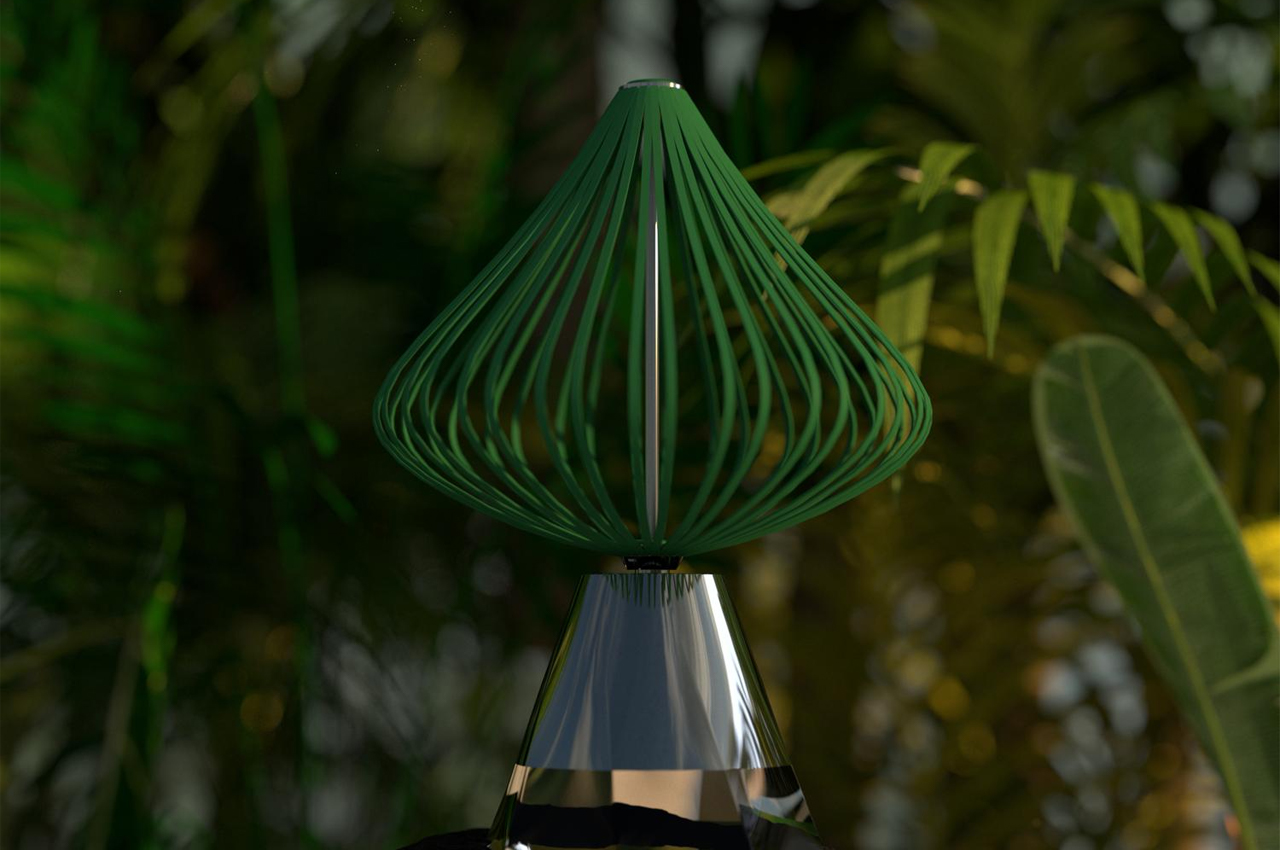

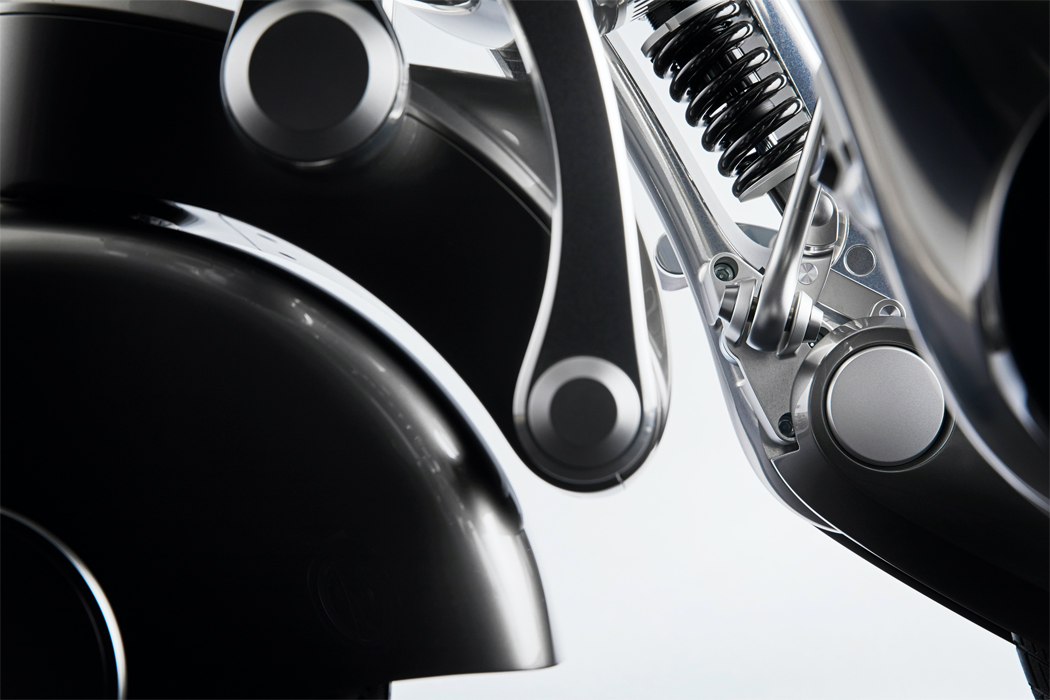
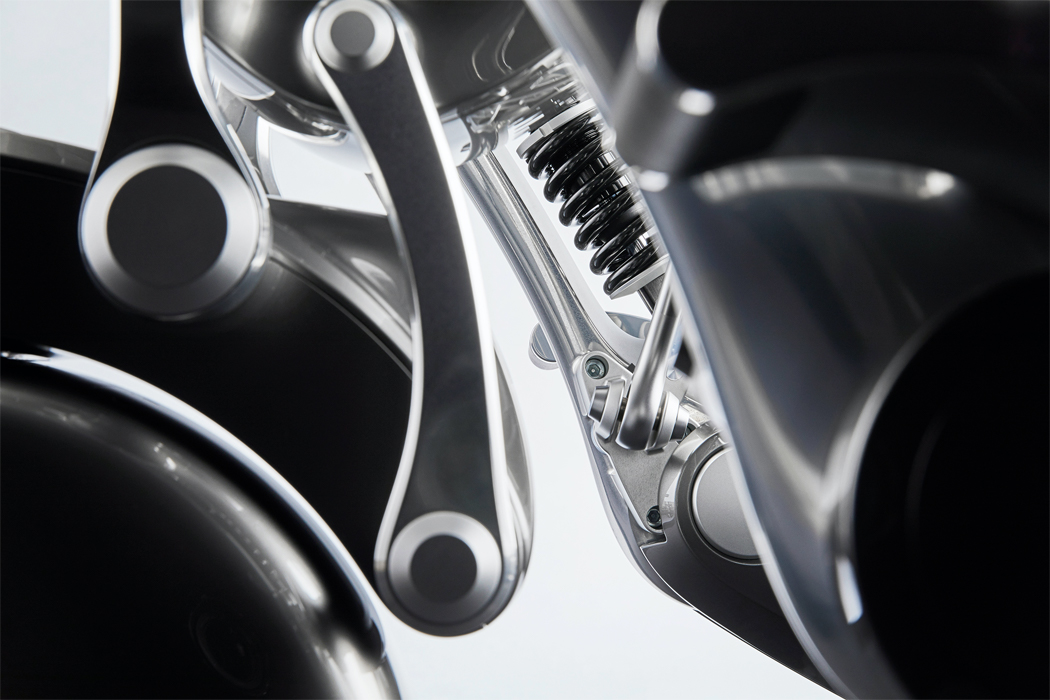
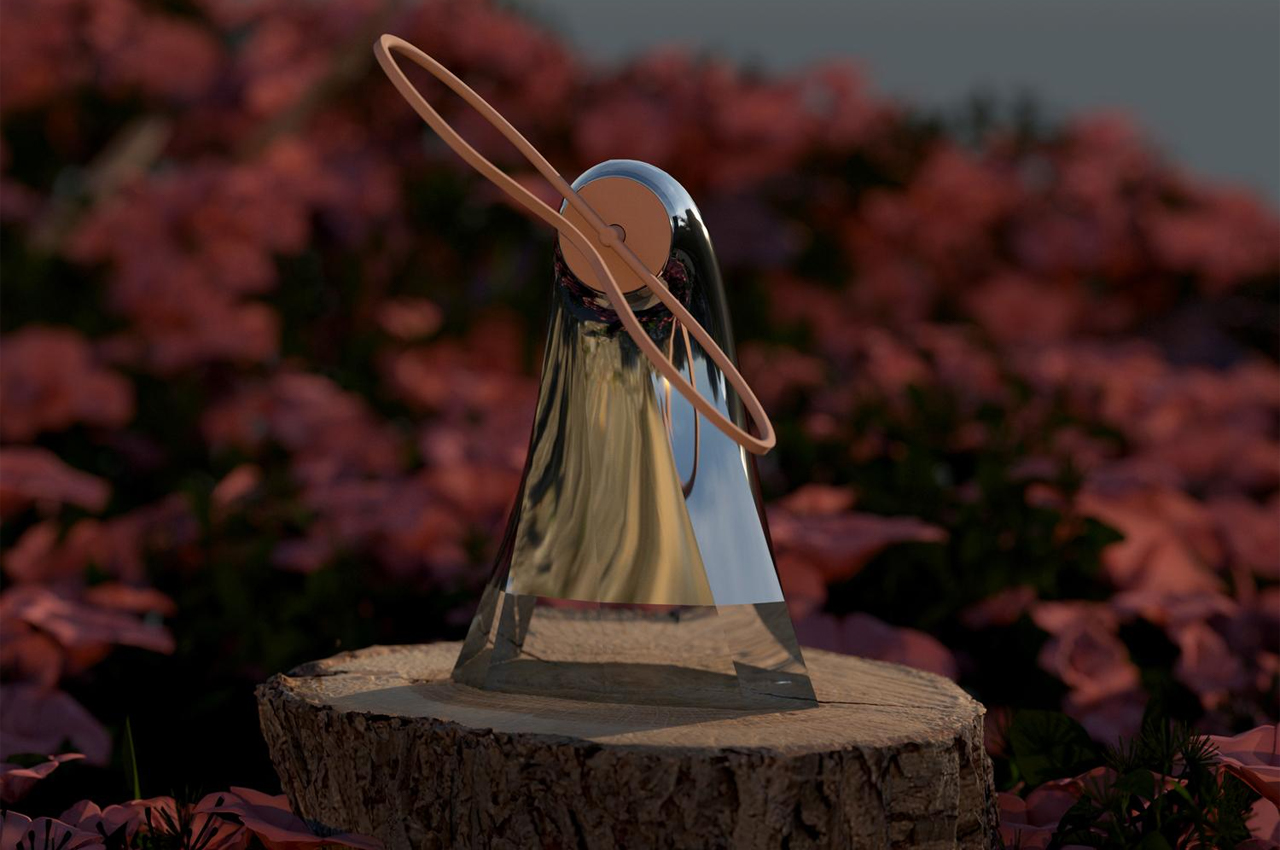
When expressing happiness, this robot spins out its leaves, binding them together to express a negative valence.

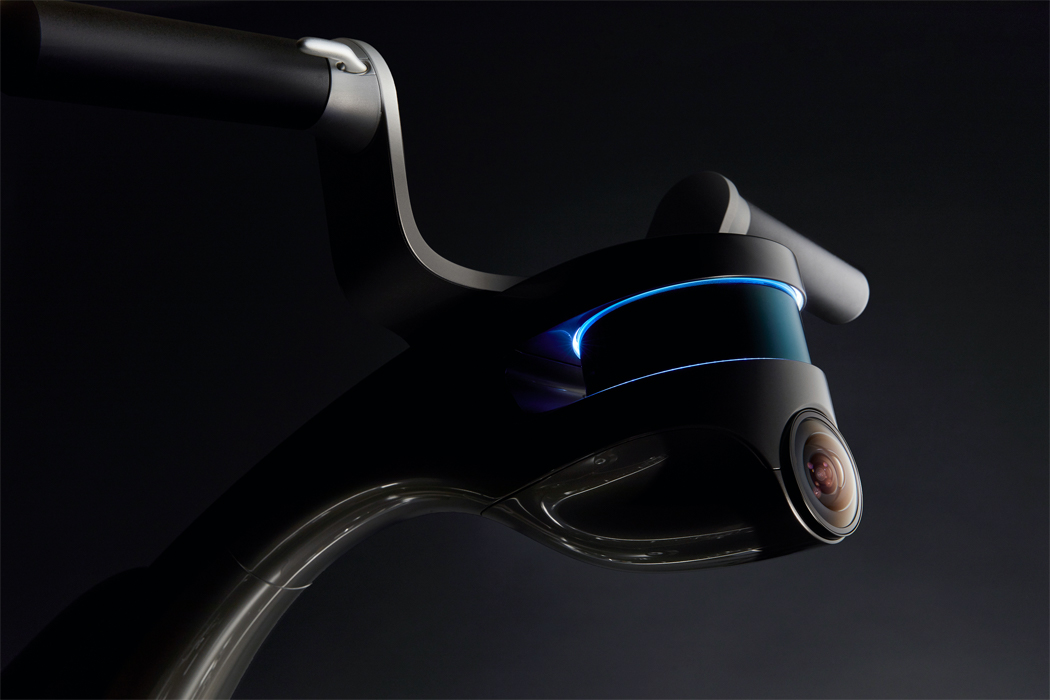
This robot spins its propeller-like leaves to express happiness, shivering to express the opposite.
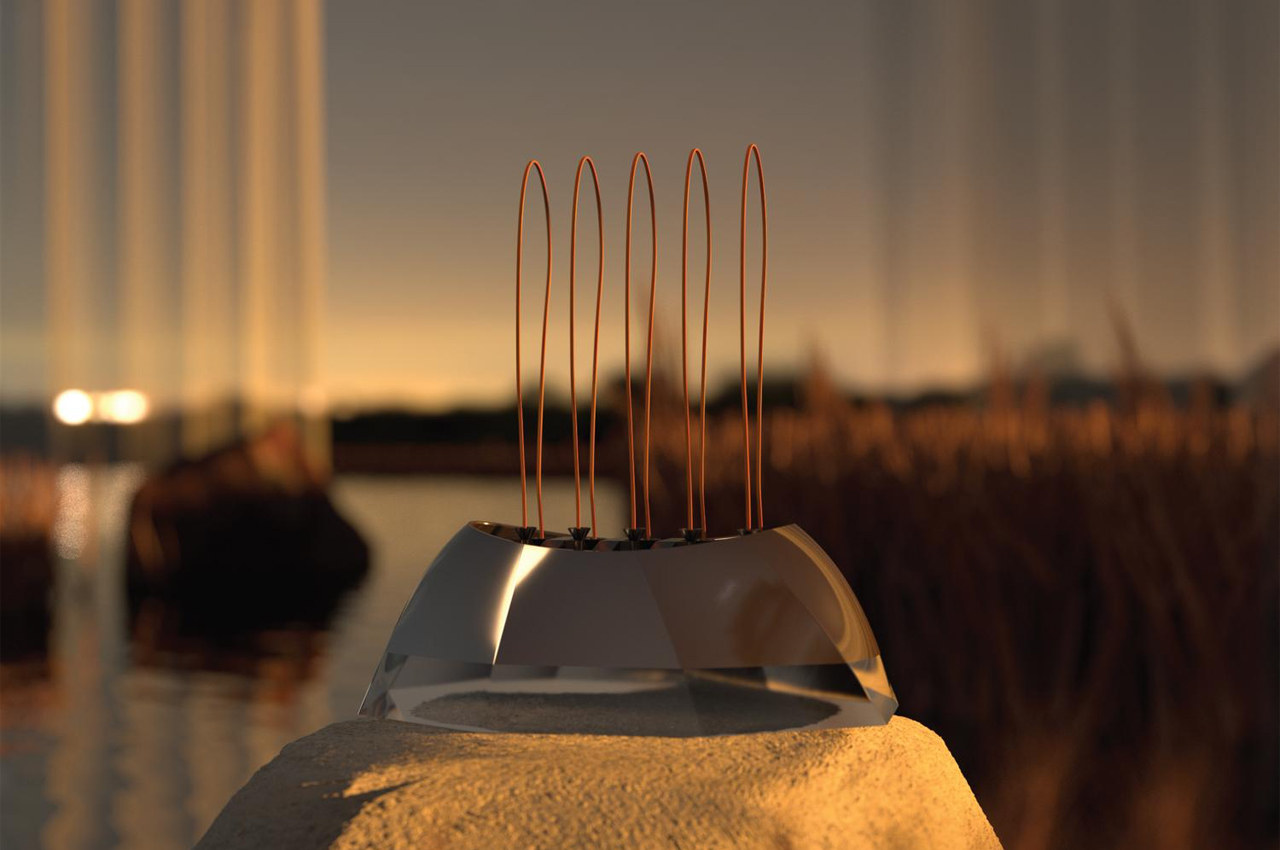
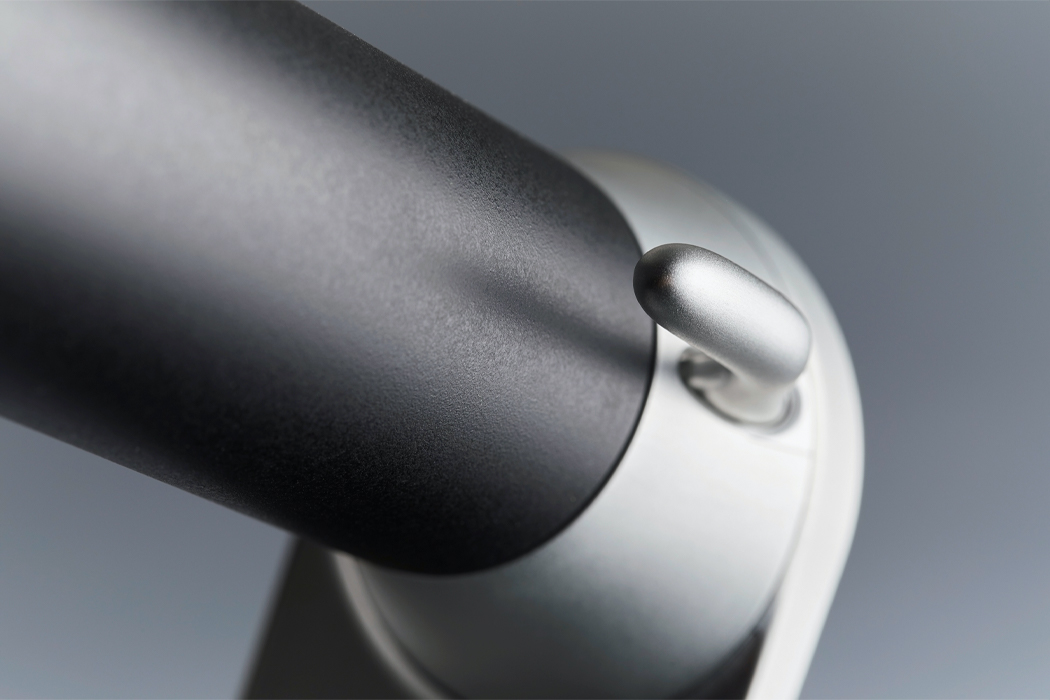
To express happiness, the single electrical string that flows through this robot stands erect.
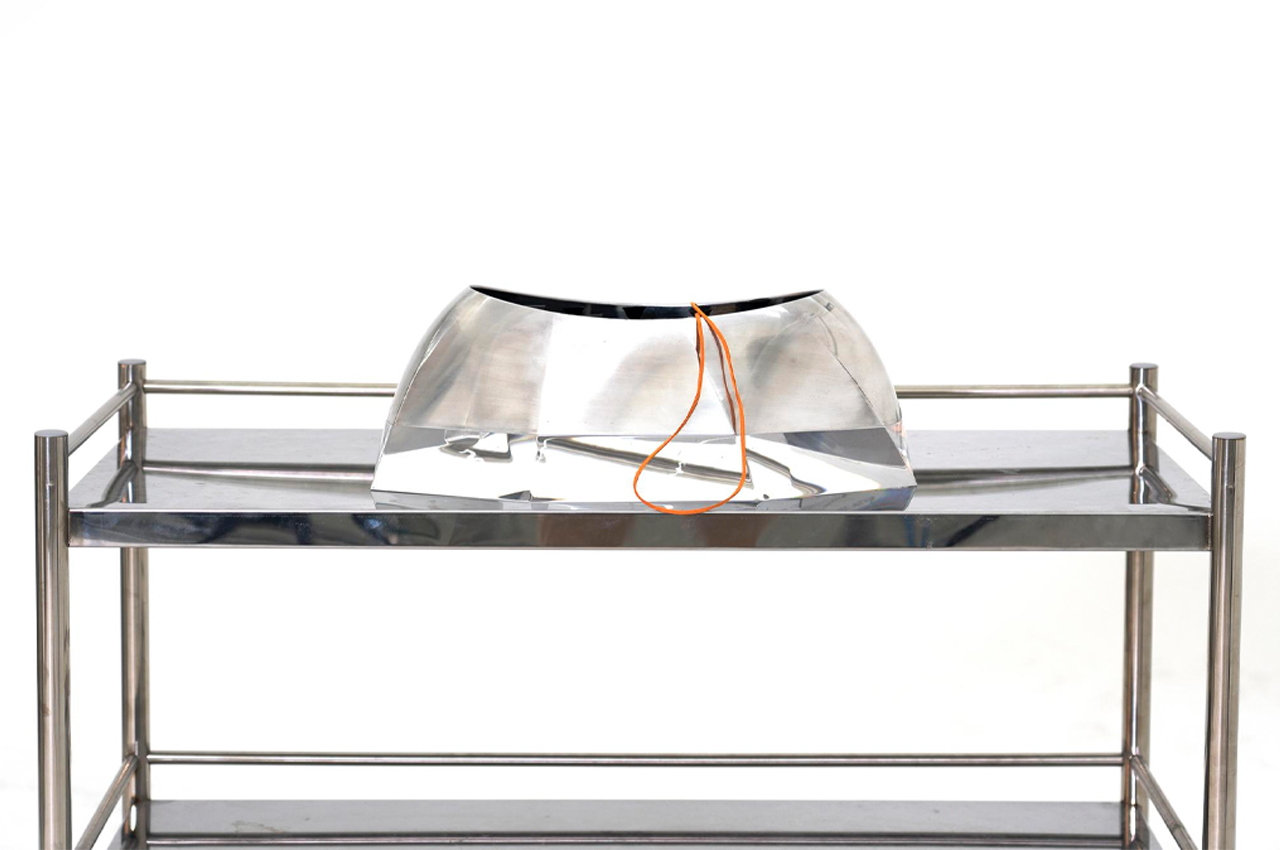
When unhappy, the string falls limp.
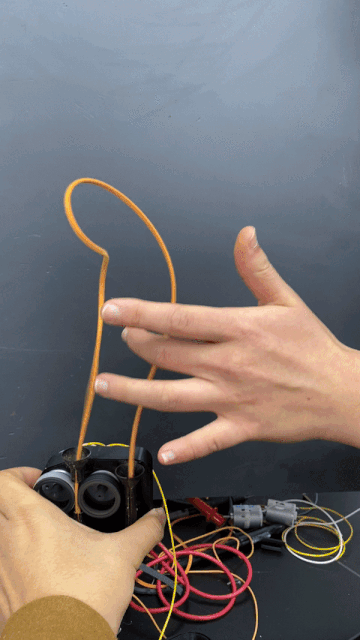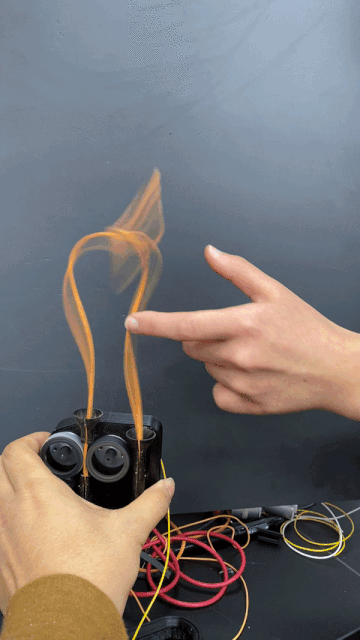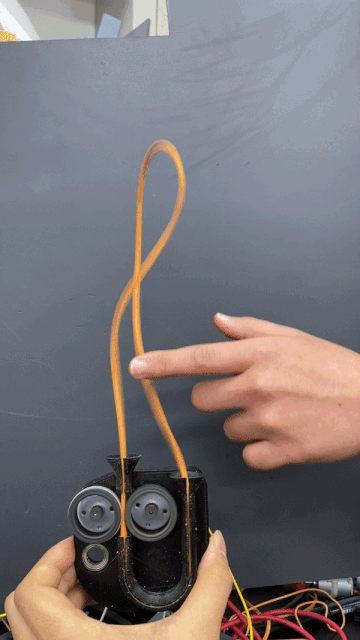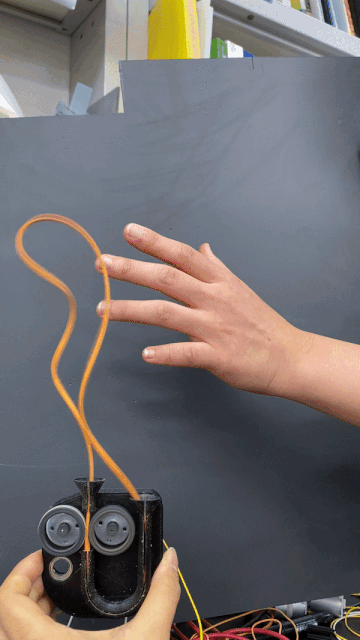
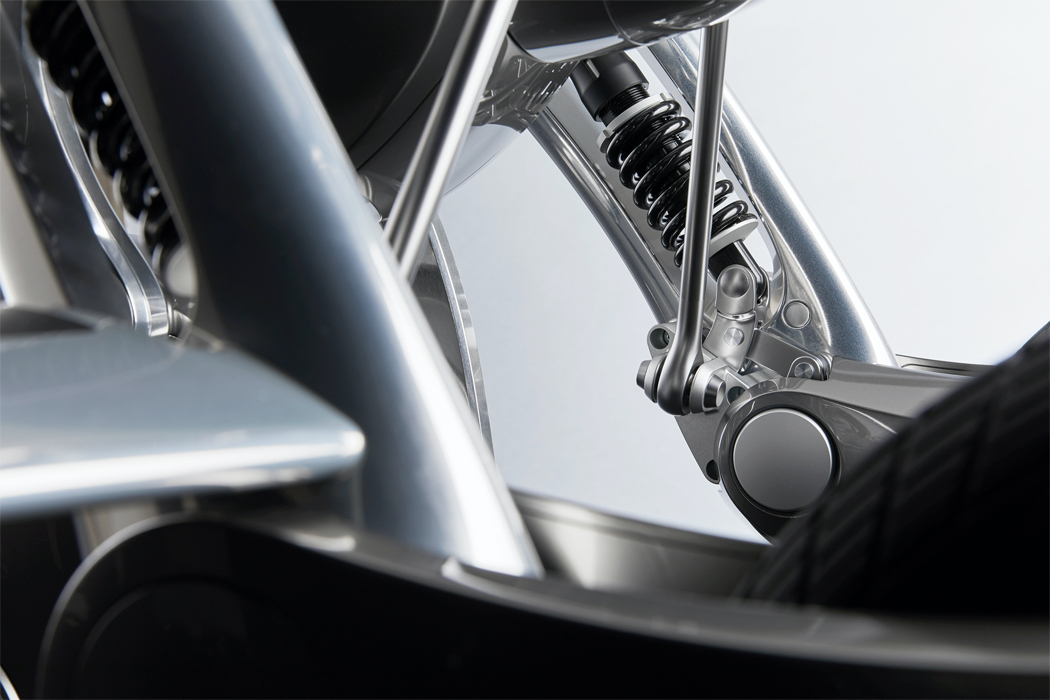
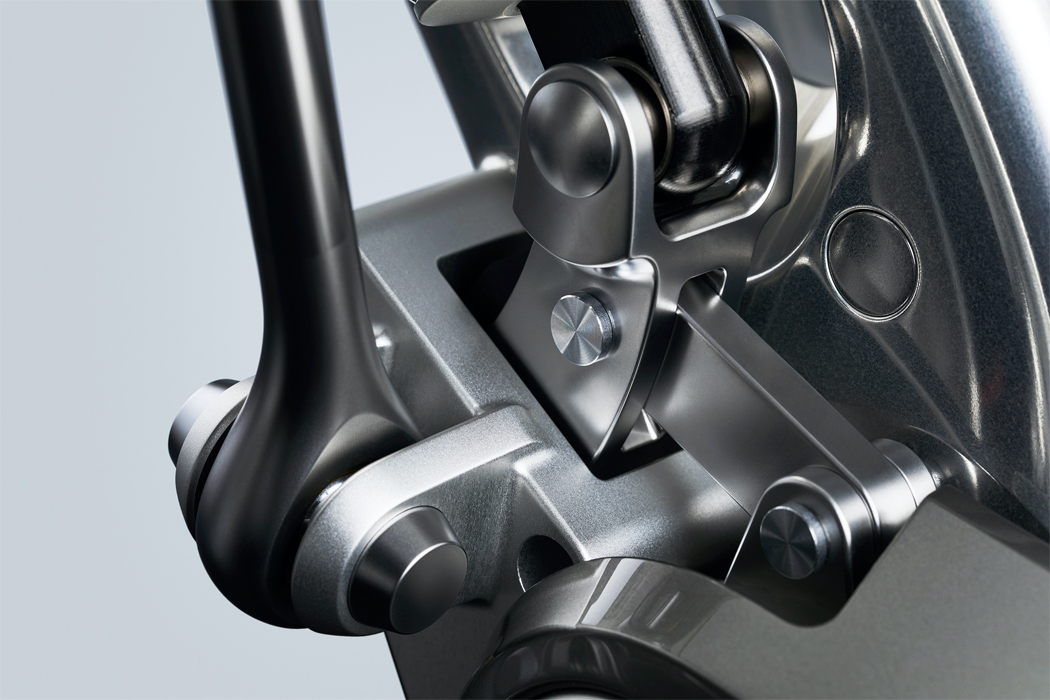
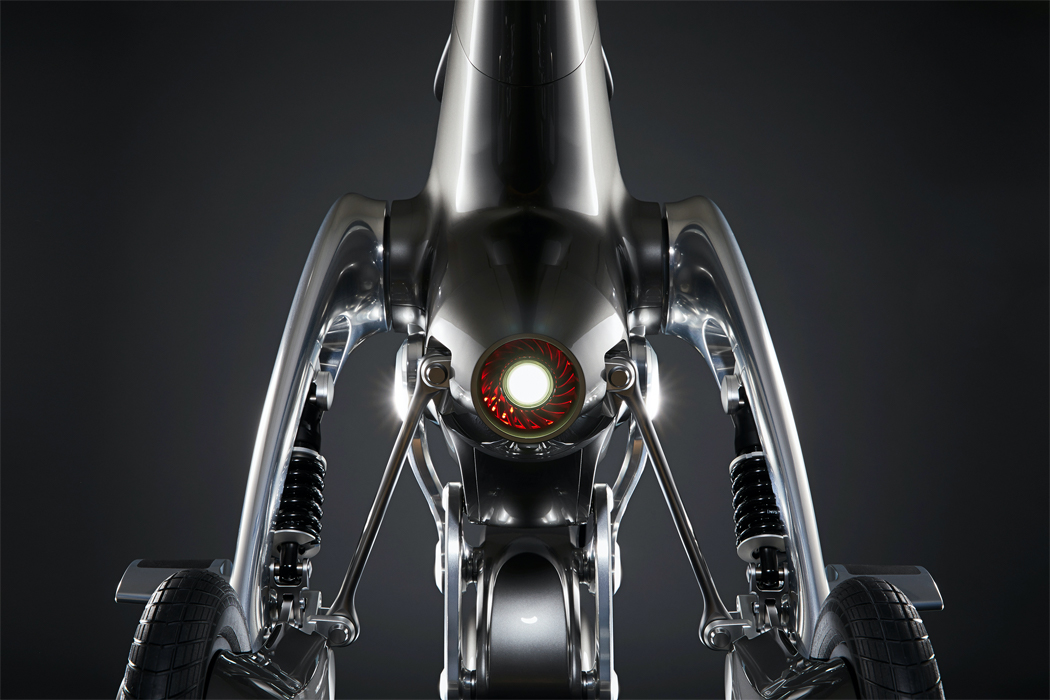
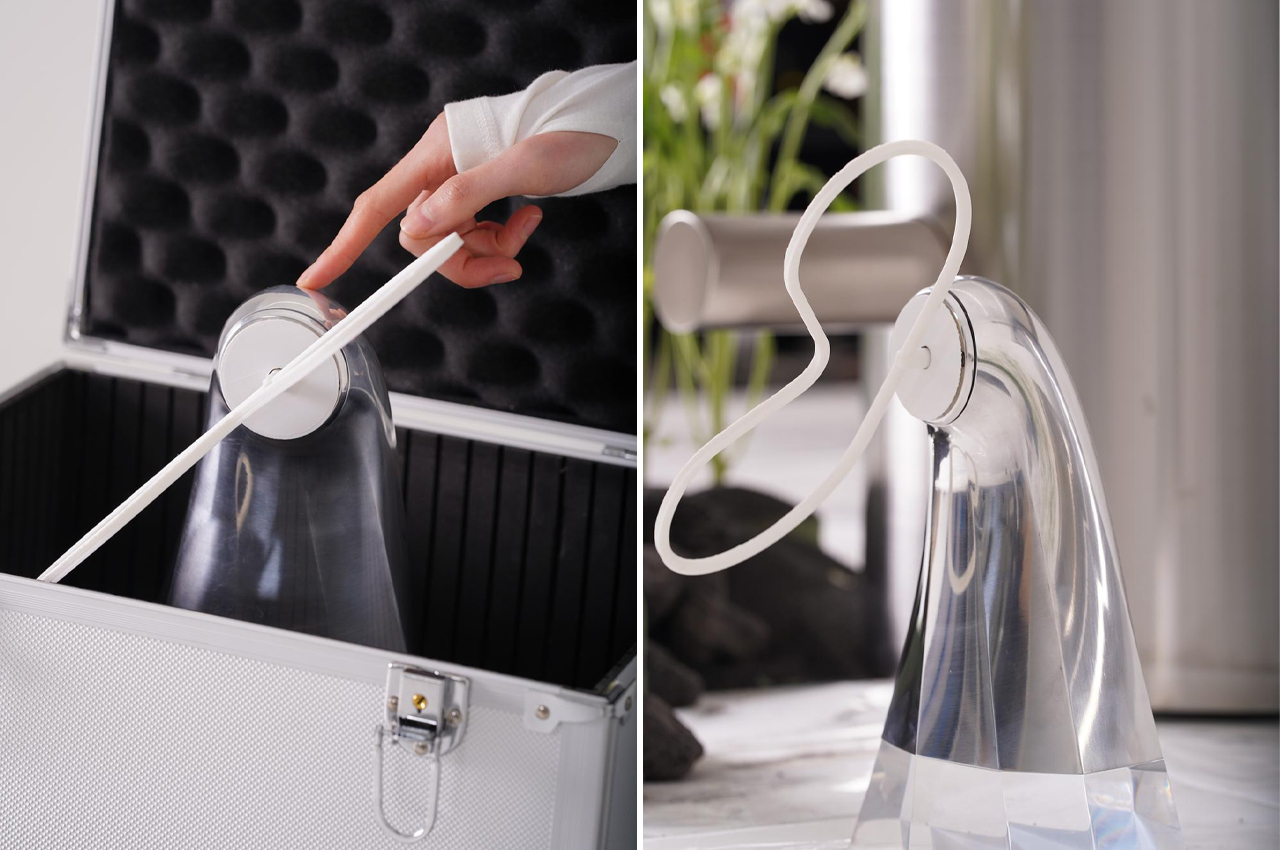
A built-in motor translates input and output information acquired via touch to respond with movement.
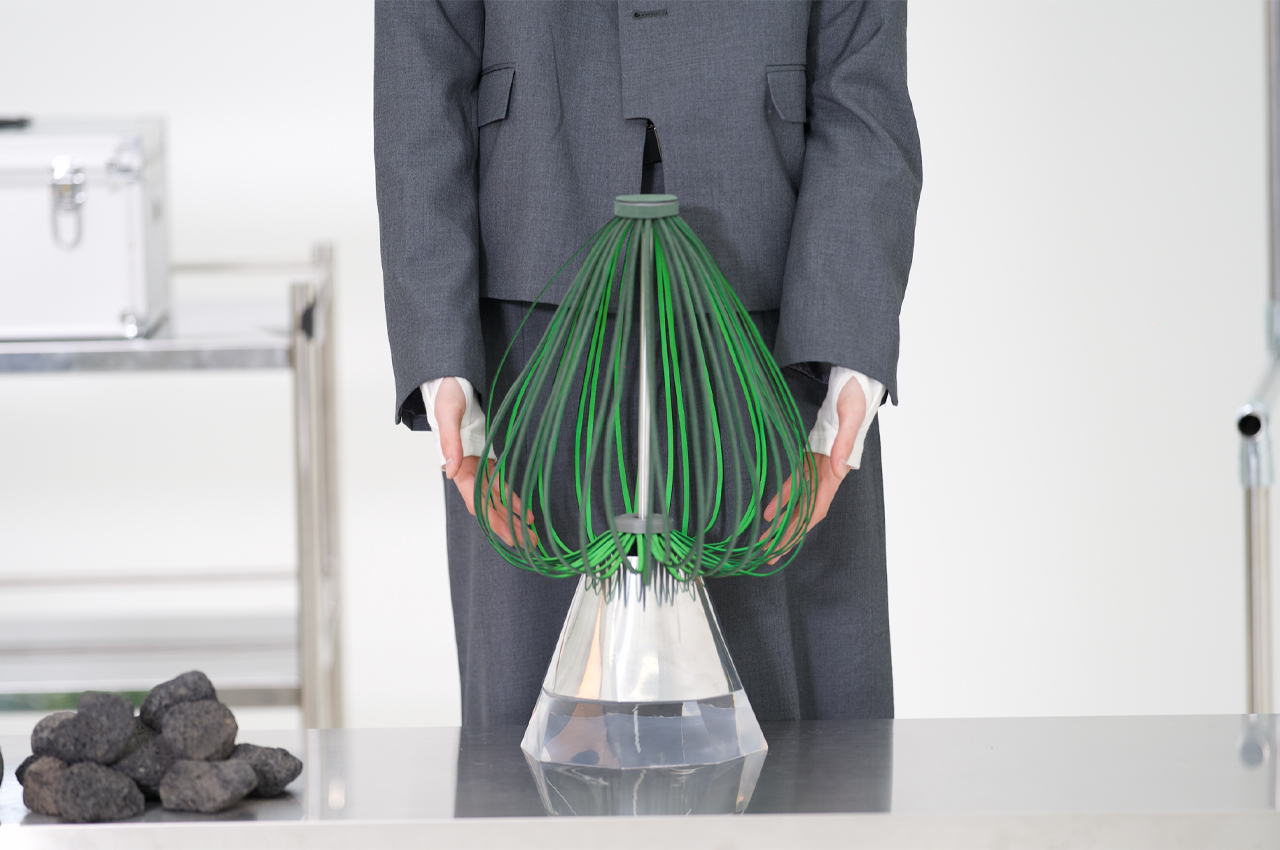
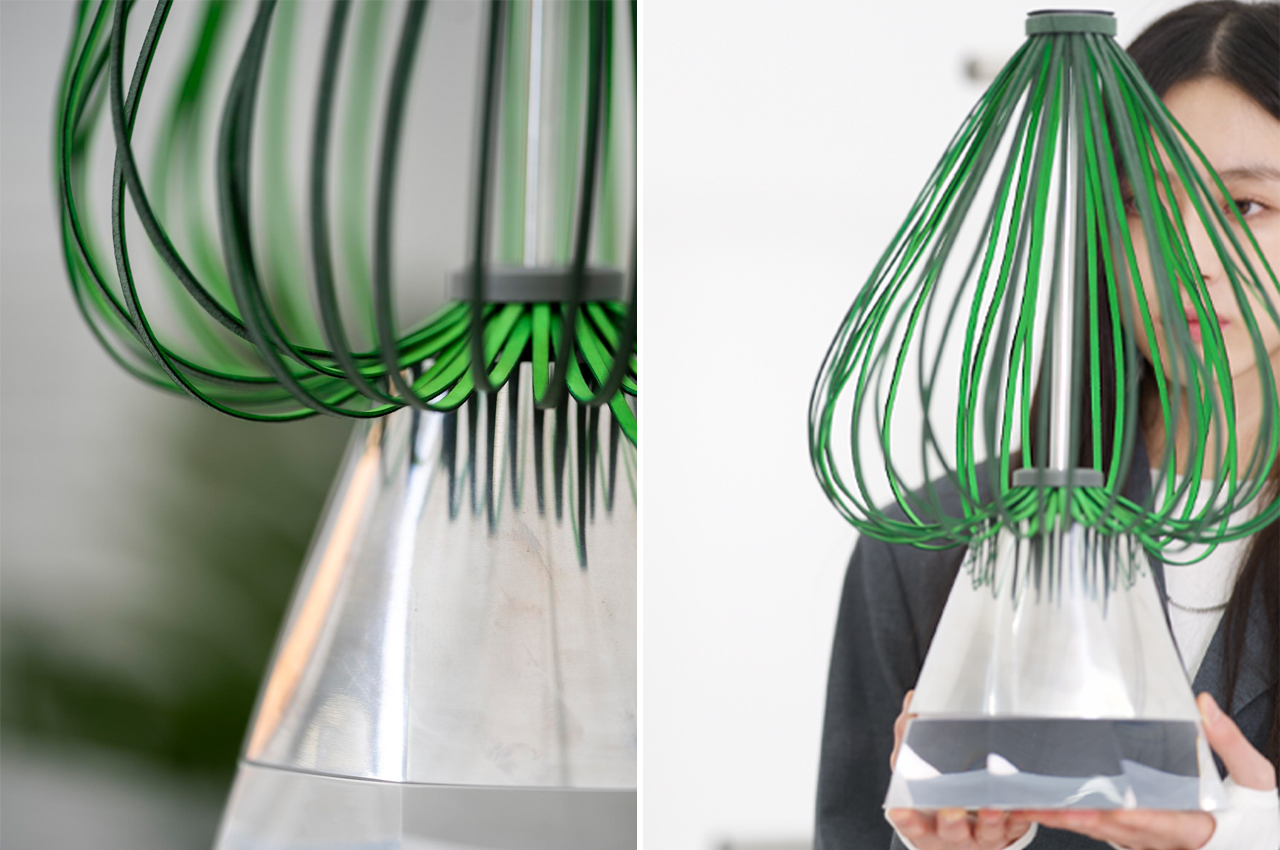


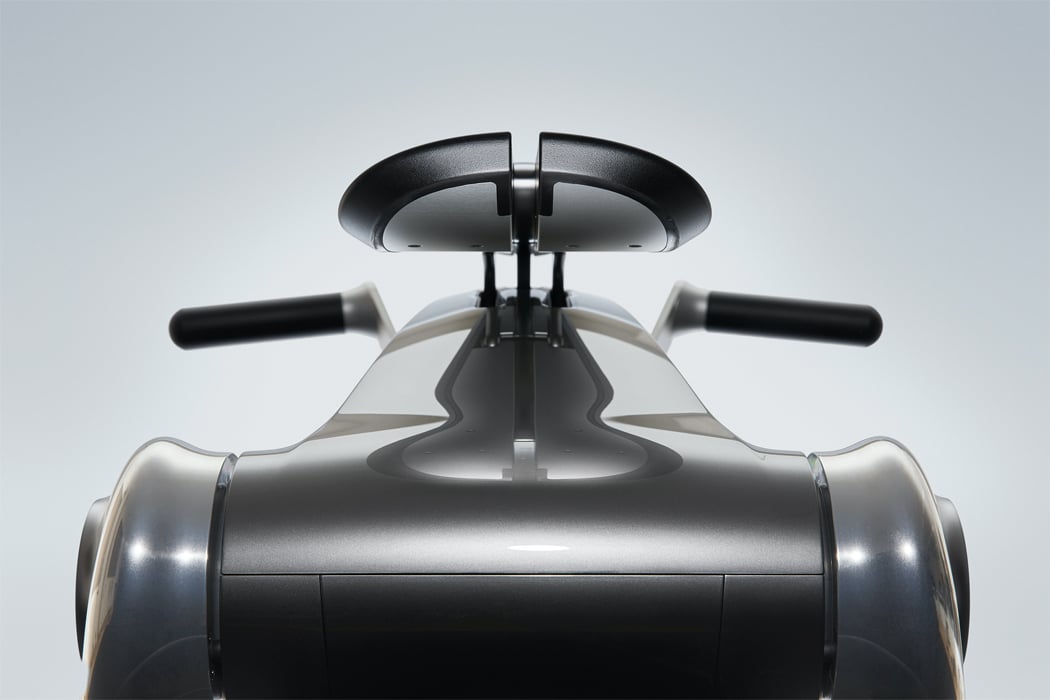
To express positive valence, this Post-Plant robot rotates freely.
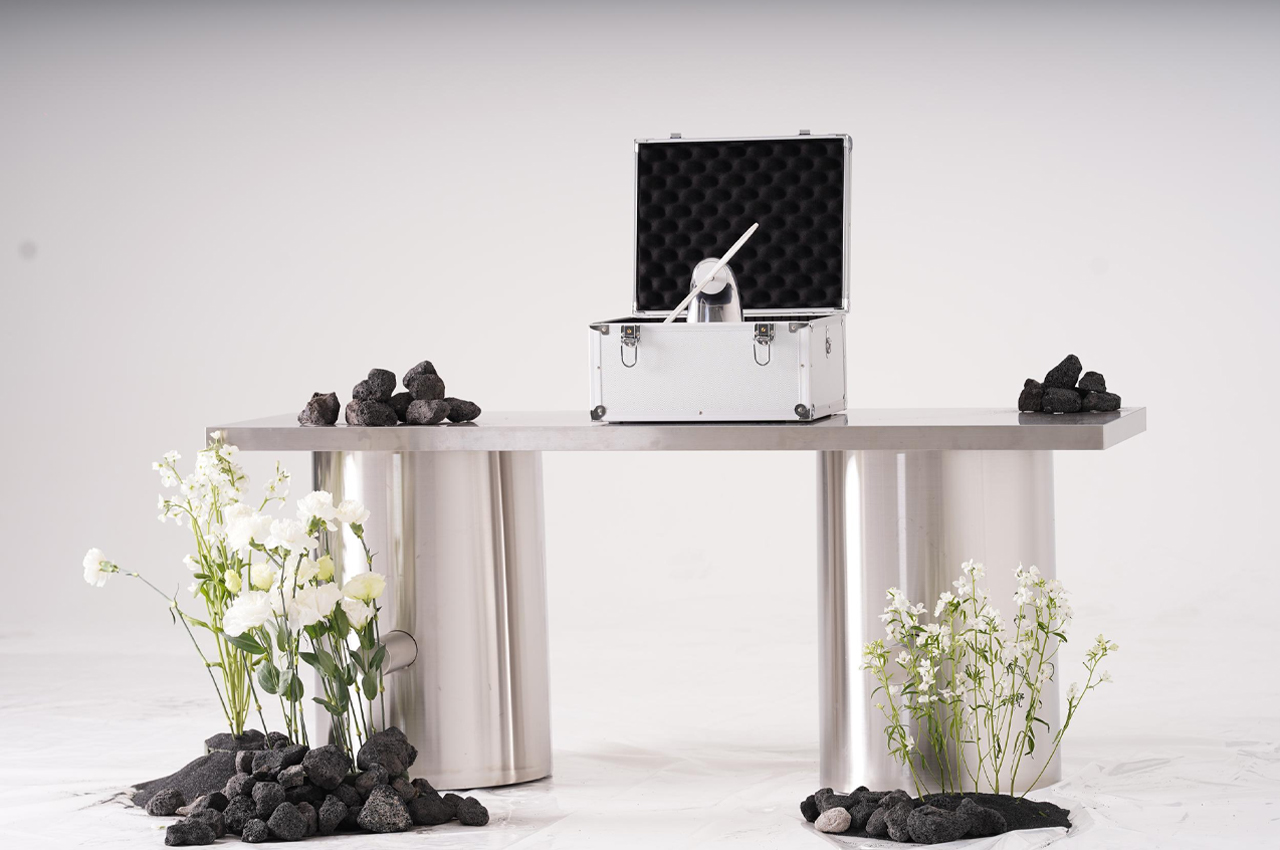
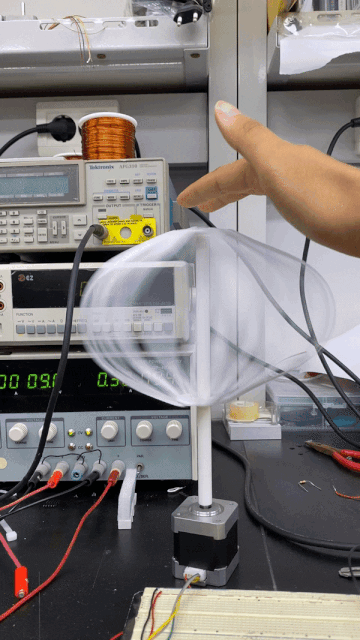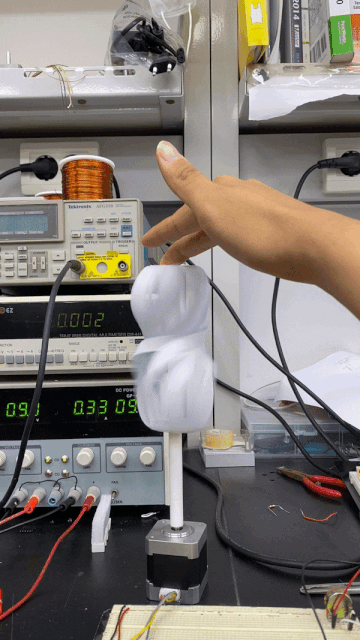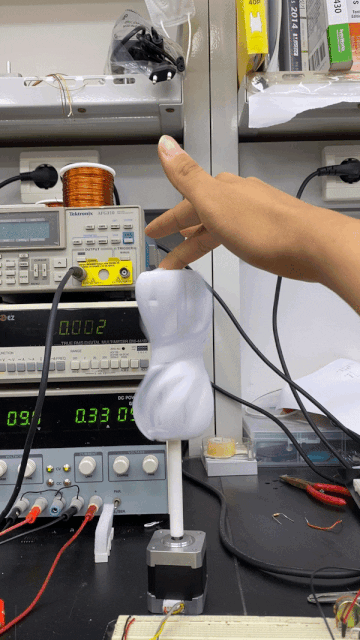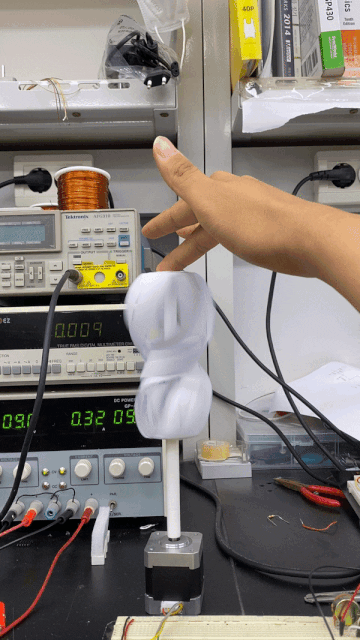


Spinning its propeller, this robot expresses general contentedness.
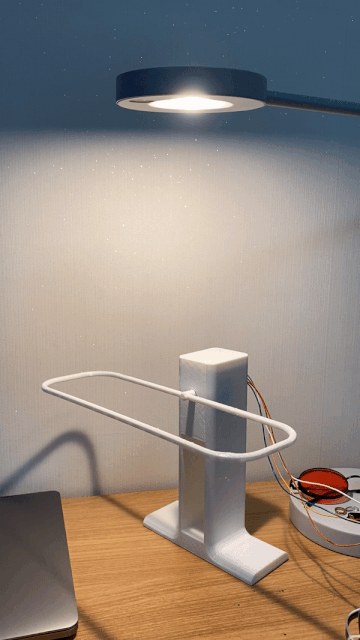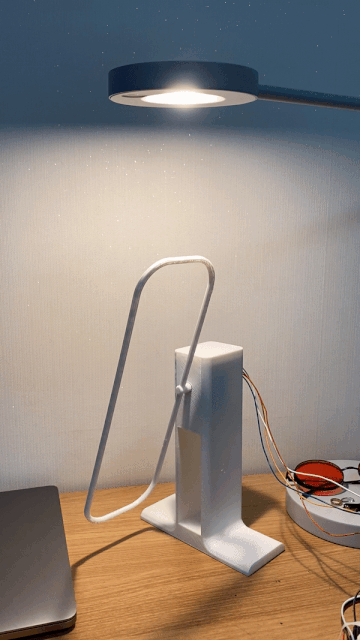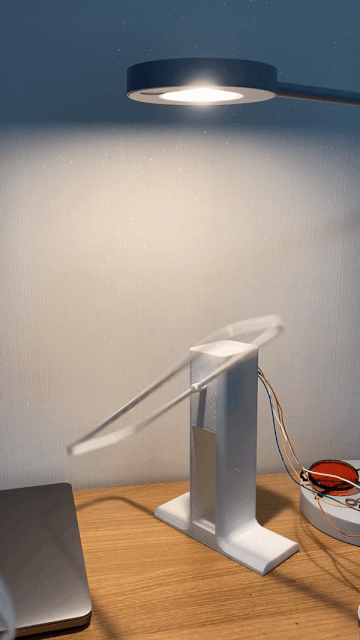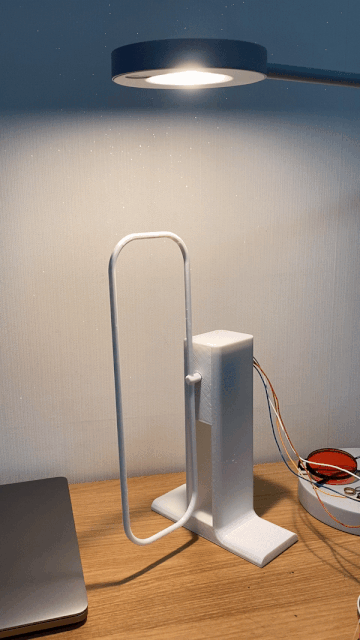
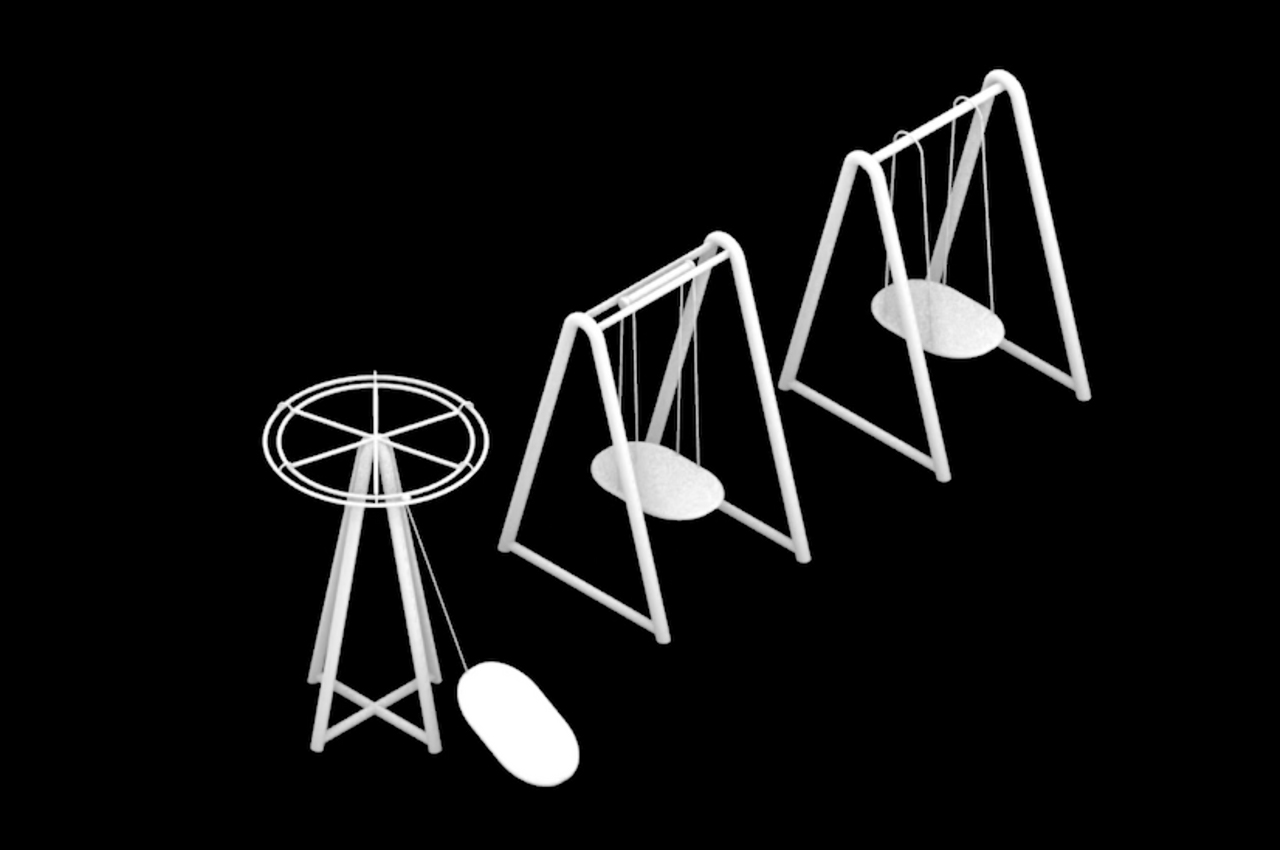
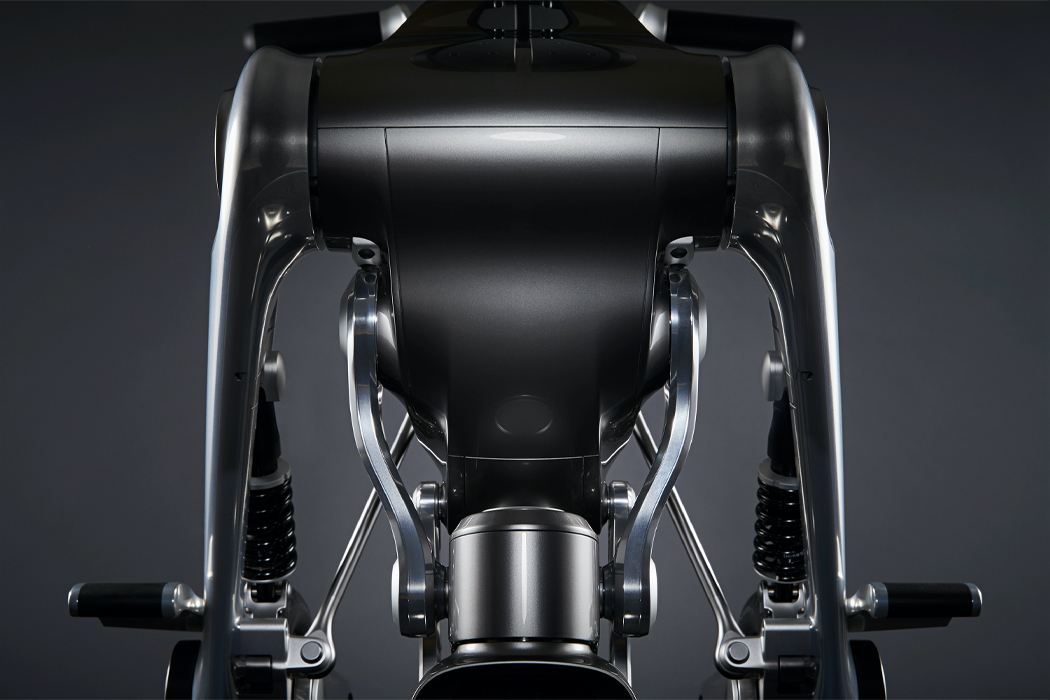
Inspired by everyday objects familiar to humans, Kim conceived the form of his non-humanoid robots.
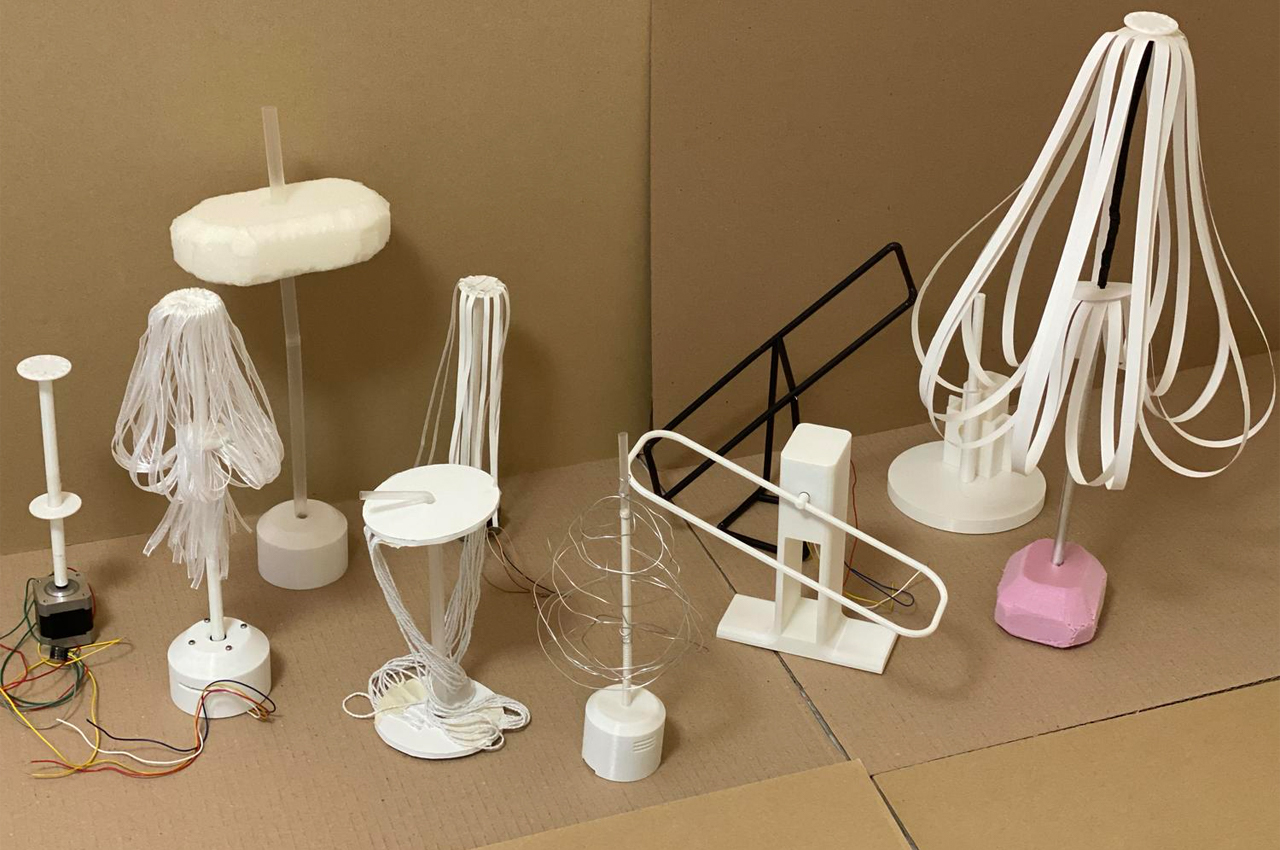

Following multiple iterations, Kim felt inspired by plant life to build the bodies of his robots.
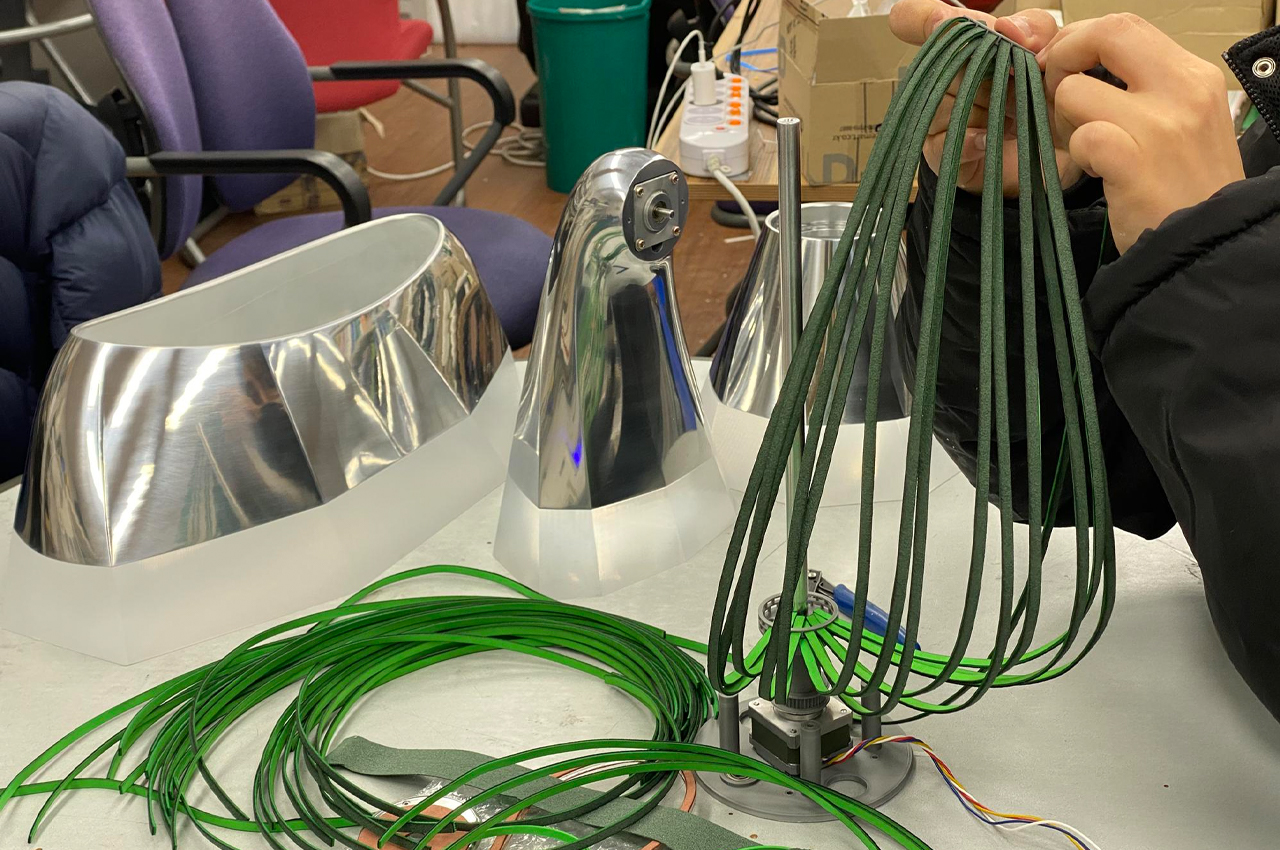

The leaves of this robot seem to be constructed from leather bands.



































