
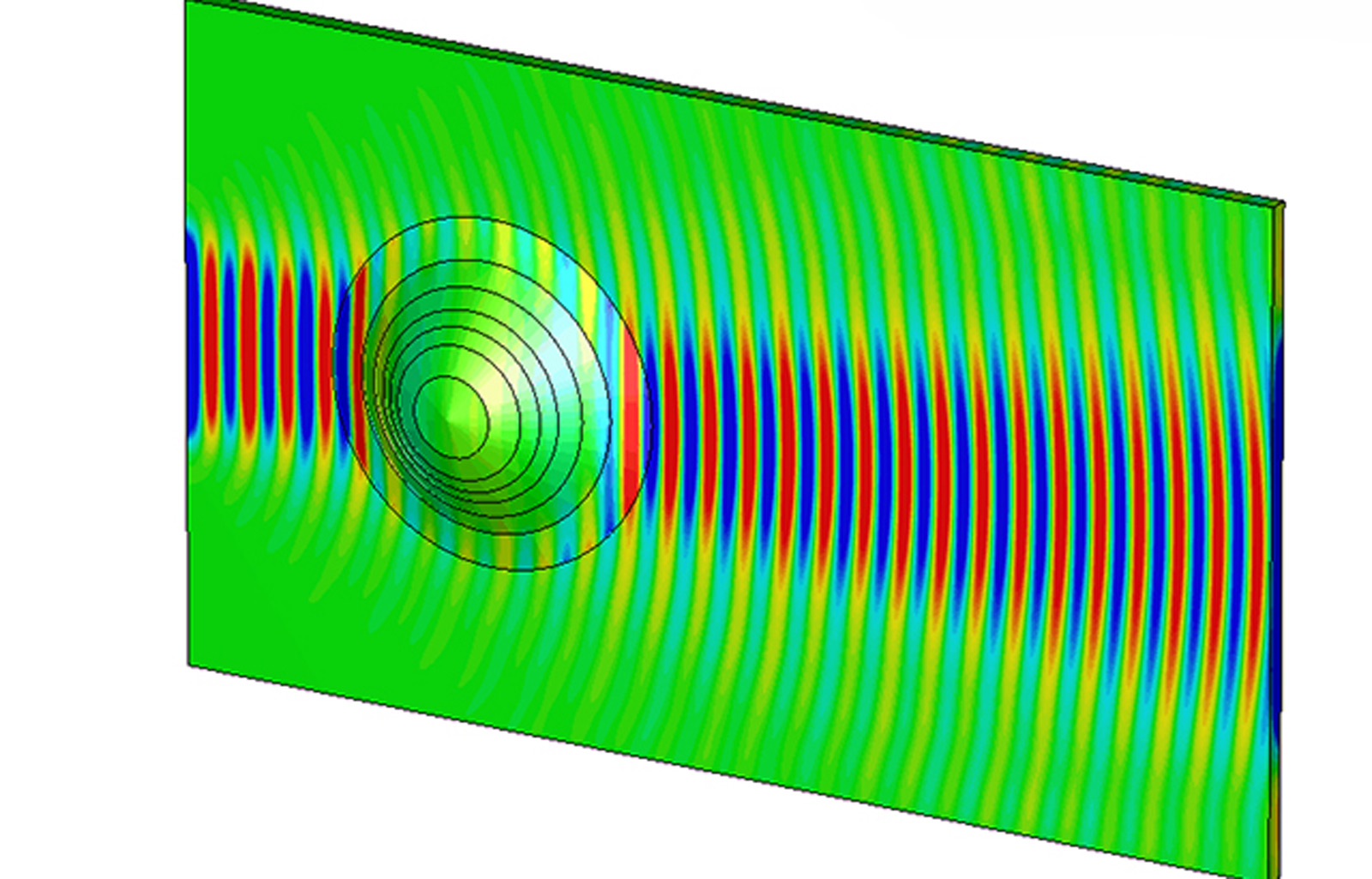
Grab your Marauder's Map and get ready to roll. Researchers at Zhejiang University in China have pioneered a new, time-efficient method of producing real world invisibility cloaks made out of Teflon. While it isn't the first time we've come across an invisibility cloak, it is the first to make use of an innovation called topology optimization. Thus far, physicists working on invisibility have largely relied on metamaterials -- synthetic materials that alter the behavior of light as it interacts with objects -- but the cost and difficulty of manufacturing them has made them an impractical option. The Zhejiang team has circumvented those obstacles by creating a so-called "eyelid" out of Teflon, the computer-altered topology of which minimizes the distortion of light as it moves past a cloaked object -- and it only took 15 minutes to produce. Since the Teflon eyelid is only invisible to microwaves, it won't enable you to roam the halls of Hogwarts unseen, but the technology could potentially open up new avenues in exploring invisibility on other wavelengths. To learn more, read the full paper at the source link below.
Filed under: Science, Alt
Comments
Via: MIT Technology Review
Source: arXiv (PDF)
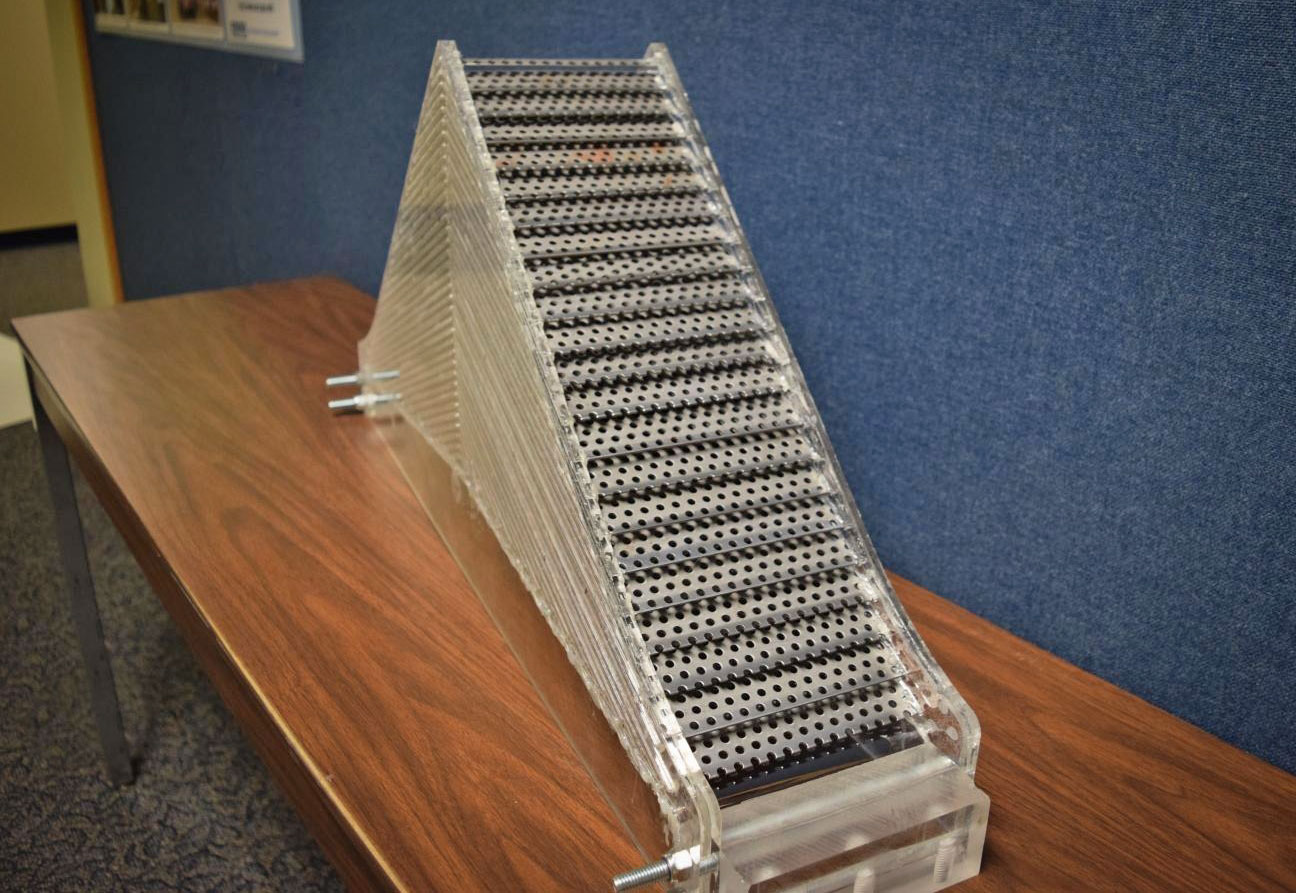 The concept of a cloaking device has a lot of appeal and though we're far from being able to make 3D objects invisible to the human eye, researchers continue to develop new ways in which to shield objects from other sorts of detection. At the Meeting...
The concept of a cloaking device has a lot of appeal and though we're far from being able to make 3D objects invisible to the human eye, researchers continue to develop new ways in which to shield objects from other sorts of detection. At the Meeting...
 The concept of a cloaking device has a lot of appeal and though we're far from being able to make 3D objects invisible to the human eye, researchers continue to develop new ways in which to shield objects from other sorts of detection. At the Meeting...
The concept of a cloaking device has a lot of appeal and though we're far from being able to make 3D objects invisible to the human eye, researchers continue to develop new ways in which to shield objects from other sorts of detection. At the Meeting...
 Humanity is still some distance away from a real, honest-to-goodness invisibility cloak, but British scientists are that much closer to making it practical. They've developed a coating that uses graded refractive index nanocomposite materials (just r...
Humanity is still some distance away from a real, honest-to-goodness invisibility cloak, but British scientists are that much closer to making it practical. They've developed a coating that uses graded refractive index nanocomposite materials (just r...



