
Metamaterials are proving to be quite useful for toying with the electromagnetic spectrum, whether for technology previously thought to be the stuff of science fiction, or for boring real-world applications. Engineers at Duke University have come up something that falls more into the latter category: a metamaterial imaging sensor that doesn't require a lens to generate a picture. The sensor is a flexible copper-plated sheet patterned with small squares that capture various light frequencies all at once, functioning like one big aperture. Add a few circuits with a pinch of software and the sensor-only camera can produce up to ten images per second, but the catch is Duke's only works at microwave frequencies. Microwave imaging is used plenty, however, and due to its flexibility and lack of moving parts, the sensor could be used to build better integrated, cheaper airport scanners and vehicle collision avoidance technology -- making you safer however you choose to travel. Unless you take the train. Then you're on your own.
Filed under: Misc, Transportation, Science, Alt
Comments
Via: Phys.org
Source: Science, Duke University
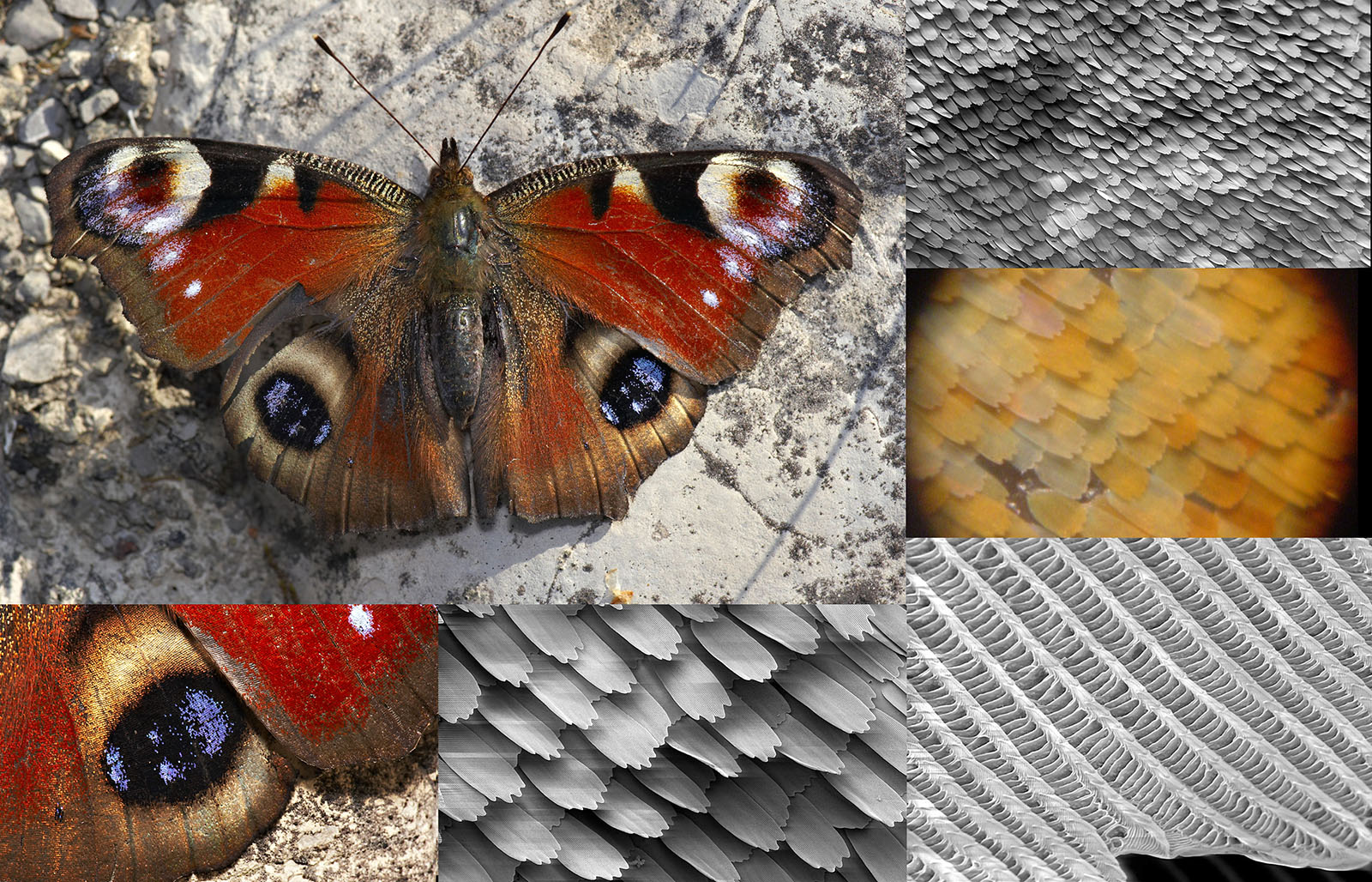 Mixed reality company Magic Leap is cagey with its tech, to say the least. However, it recently released a research paper in conjunction with Berkeley Lab that some hints on what it's doing. The team developed new materials that can take in light fro...
Mixed reality company Magic Leap is cagey with its tech, to say the least. However, it recently released a research paper in conjunction with Berkeley Lab that some hints on what it's doing. The team developed new materials that can take in light fro...
 Mixed reality company Magic Leap is cagey with its tech, to say the least. However, it recently released a research paper in conjunction with Berkeley Lab that some hints on what it's doing. The team developed new materials that can take in light fro...
Mixed reality company Magic Leap is cagey with its tech, to say the least. However, it recently released a research paper in conjunction with Berkeley Lab that some hints on what it's doing. The team developed new materials that can take in light fro...
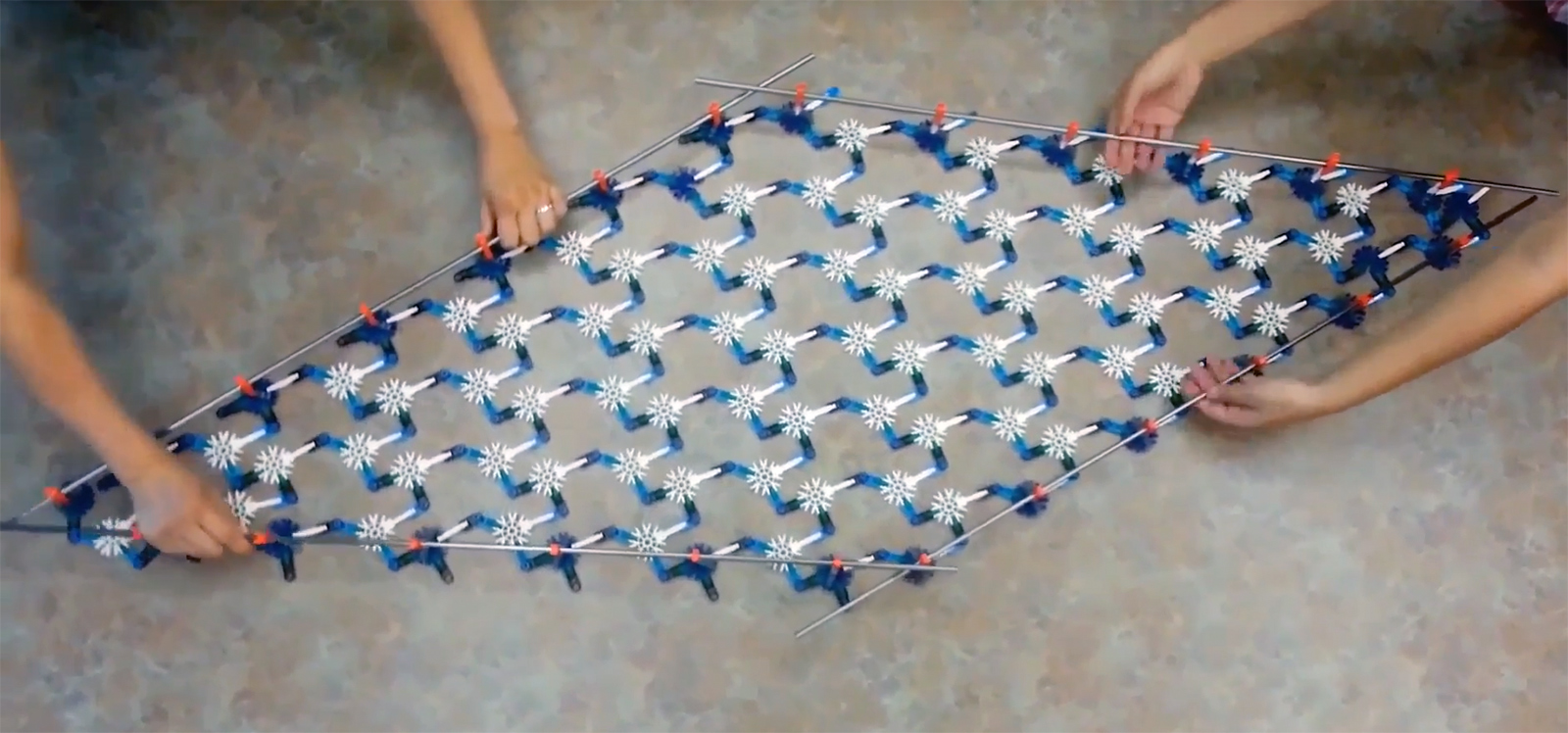 University of Michigan researchers have developed a technique for a new 'metamaterial' that can change its level of solidness, but without damaging or changing the material itself. Metamaterials are man-made materials whose properties come from the w...
University of Michigan researchers have developed a technique for a new 'metamaterial' that can change its level of solidness, but without damaging or changing the material itself. Metamaterials are man-made materials whose properties come from the w...

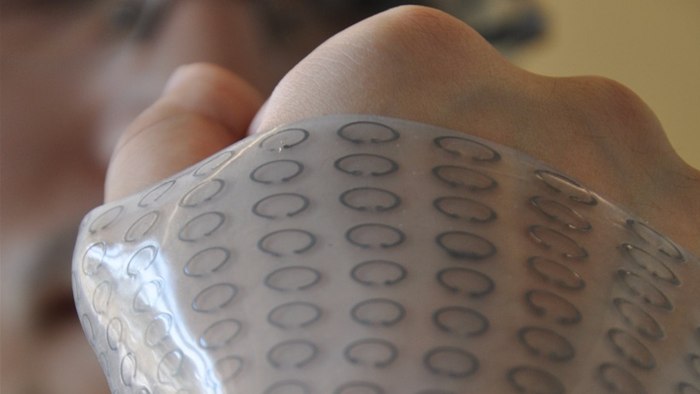 We've been inching closer to real-life invisibility cloaks for a bit now, but going full on Harry Potter in the Hogwarts library is probably still a ways off. The latest advancement in metamaterial-based vanishing tech from Iowa State University guar...
We've been inching closer to real-life invisibility cloaks for a bit now, but going full on Harry Potter in the Hogwarts library is probably still a ways off. The latest advancement in metamaterial-based vanishing tech from Iowa State University guar...




