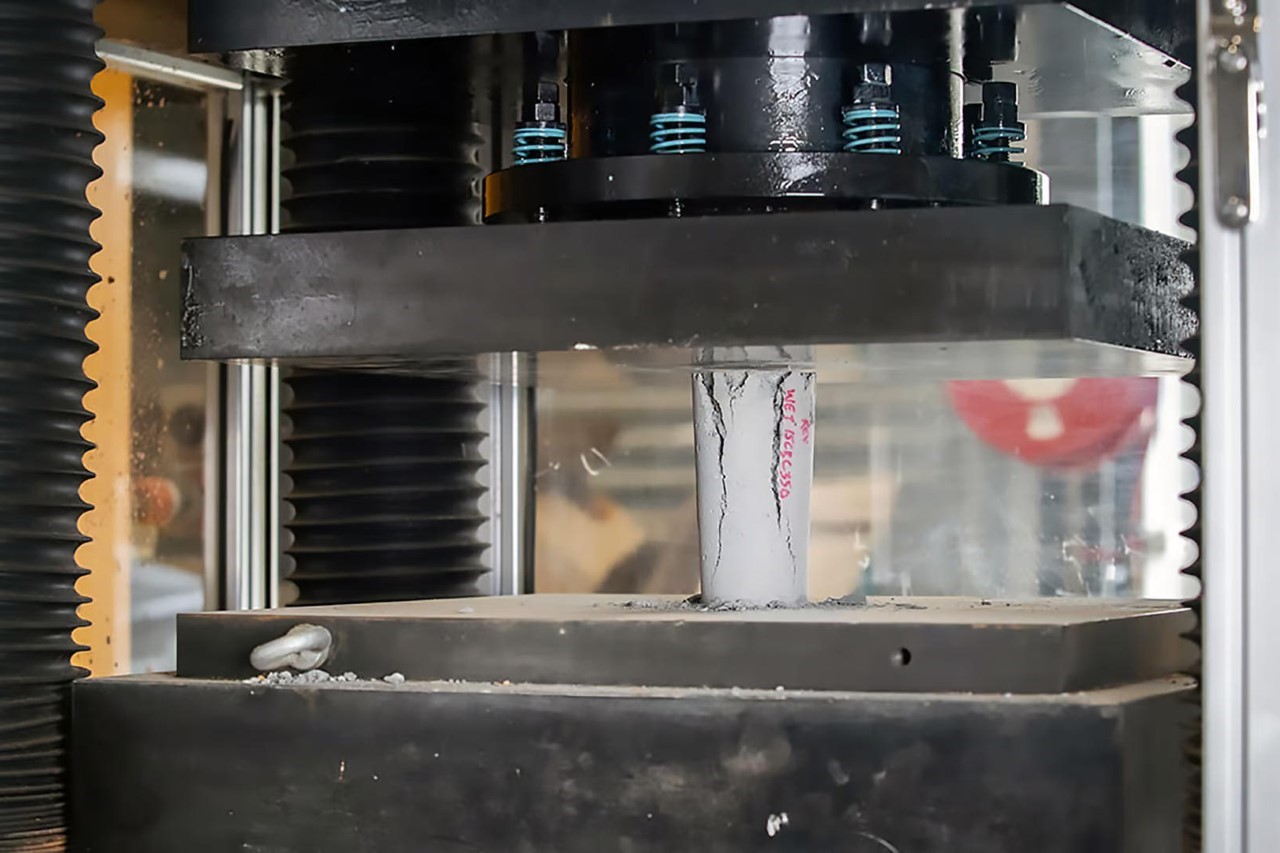
Did you know that the most widely used substance in the entire world, after water, is concrete?? You’d think it was paper or plastic or wood even, but more concrete is used every single day across the world than any of those materials… and for what it’s worth, it’s considered one of the least nature-friendly materials ever, but researchers at RMIT University of Melbourne are working on a concrete that uses an unlikely recycled material – coffee! The researchers have developed a new type of concrete that incorporates waste coffee grounds in a way that not just makes the concrete more sustainable, but also makes it 30% stronger than regular concrete!
The secret ingredient? Biochar. By heating coffee grounds in a low-oxygen environment at 350°C (662°F), researchers transform them into this charcoal-like material. Biochar doesn’t decompose over time, making it a perfect candidate for concrete reinforcement. This innovative method tackles two environmental concerns simultaneously. It reduces reliance on sand, a finite resource that’s increasingly strained by demand, and diverts coffee grounds from landfills, where they decompose and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Designer: RMIT Australia
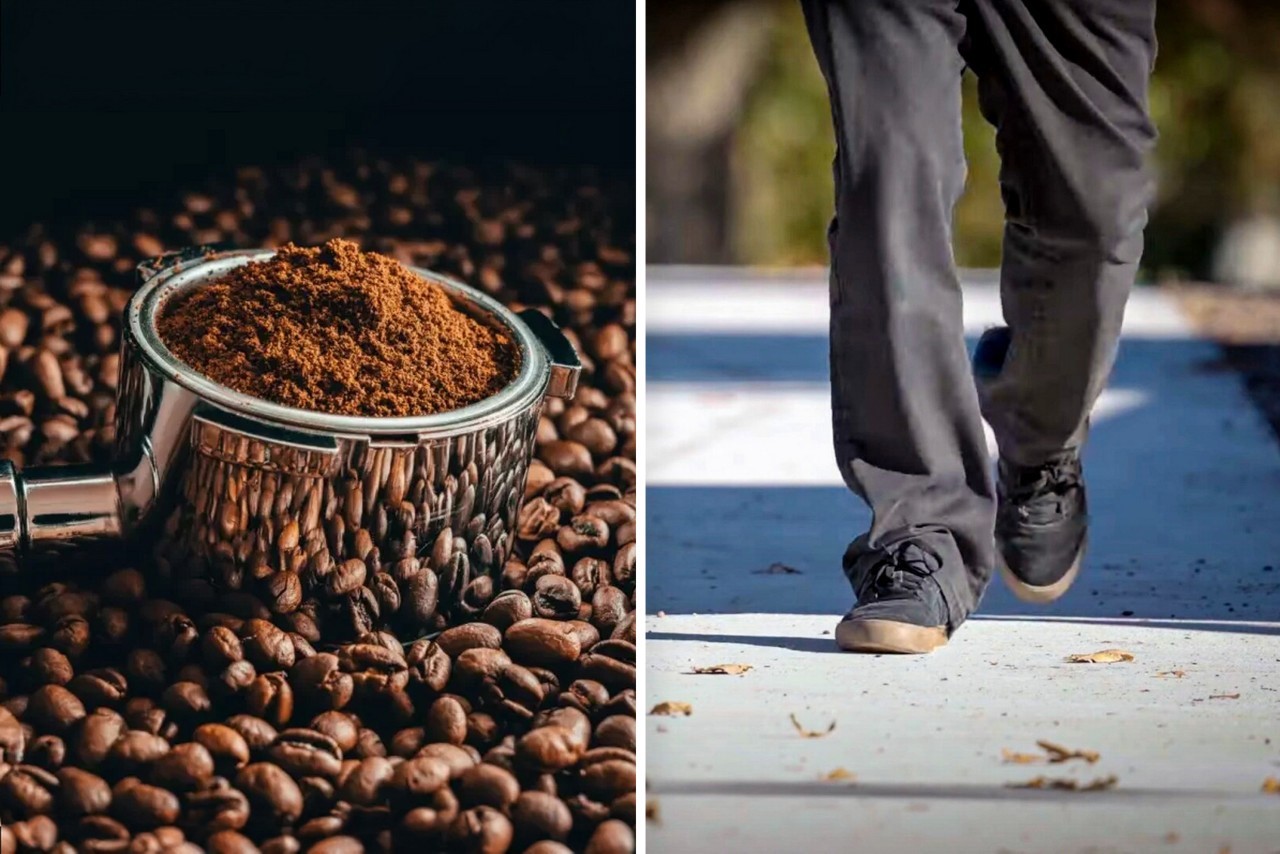

The project is now taking a crucial step from the lab to real-world testing. The researchers have partnered with a local council to lay down sections of sidewalk made with coffee biochar concrete alongside standard concrete for comparison. This side-by-side trial will provide valuable insights into how the new material performs under everyday wear and tear from foot traffic.
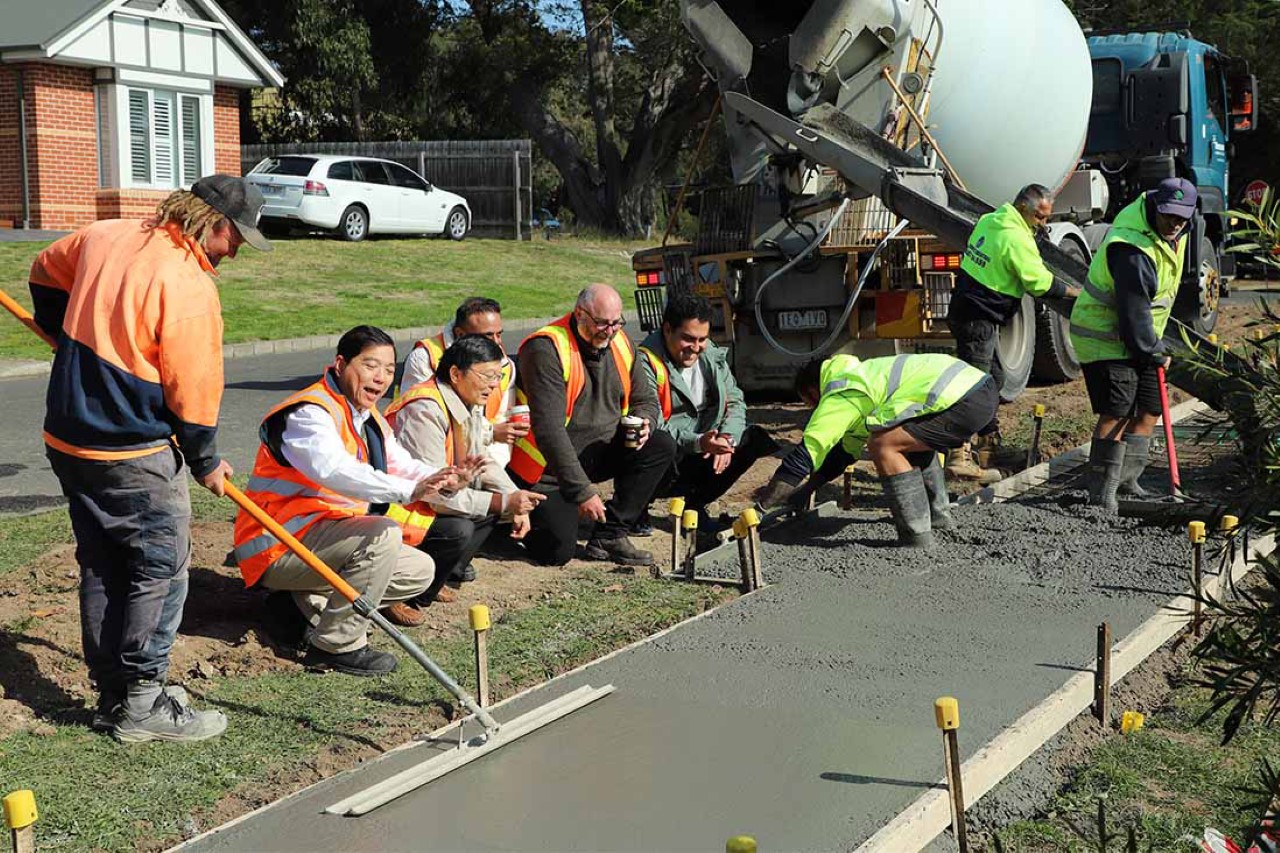

The potential benefits extend beyond environmental sustainability. The increased strength of coffee concrete could lead to reduced construction costs. The researchers believe that the higher strength might allow for a decrease in the amount of cement needed in the mix, potentially by up to 10%. This translates to lower material costs and a smaller environmental footprint from cement production.
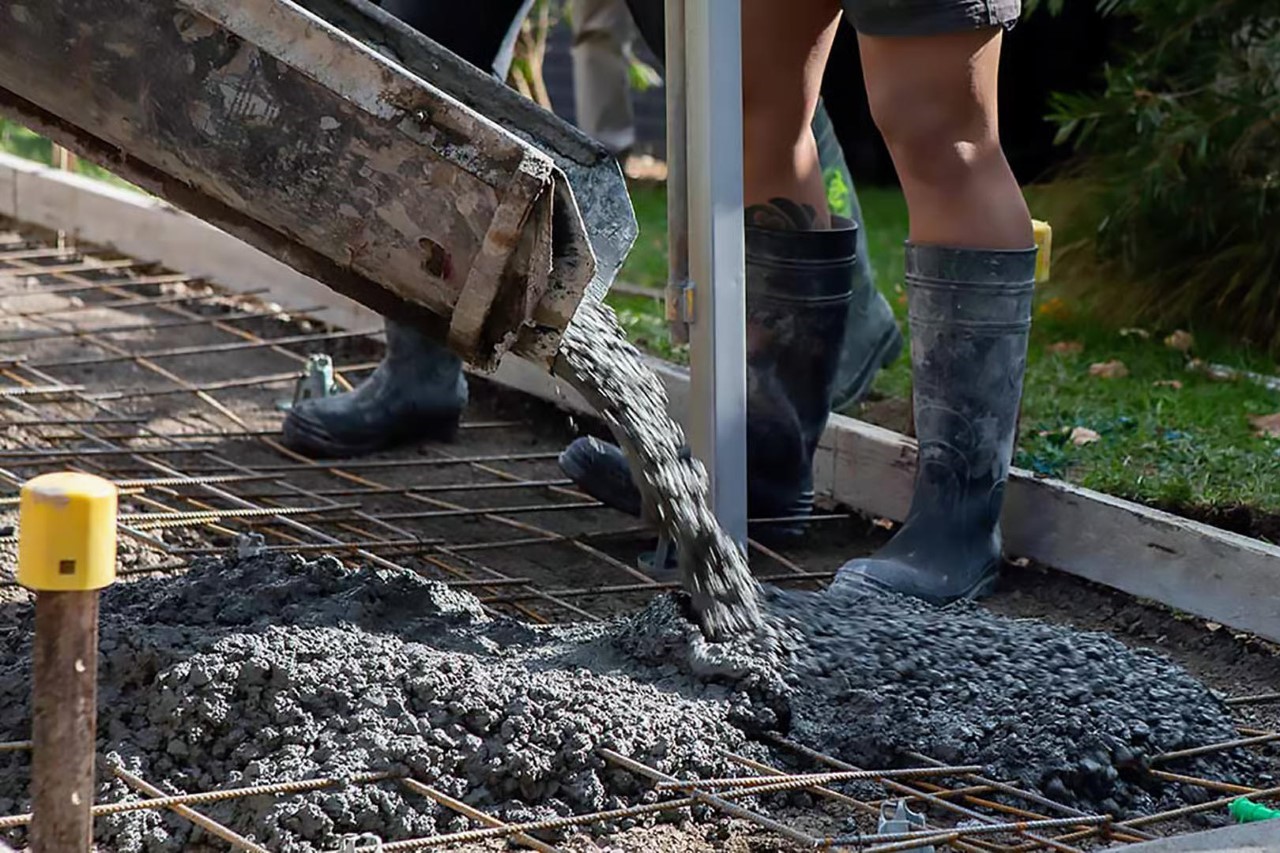

“We’re taking those experiments and putting them in ground and in the field today, we’re going to have people walking across the concrete that includes these products, and RMIT is going to be coming back and doing testing to see how they stand up,” said Shane Walden, the Council’s Director of Assets and Operations. “This not only helps improve the knowledge level of our contractors and our staff, but it also has lots of other benefits and benefits that are important to our community. This includes helping the environment, acting sustainably and, most importantly, reducing waste to landfill and having a circular economy.”
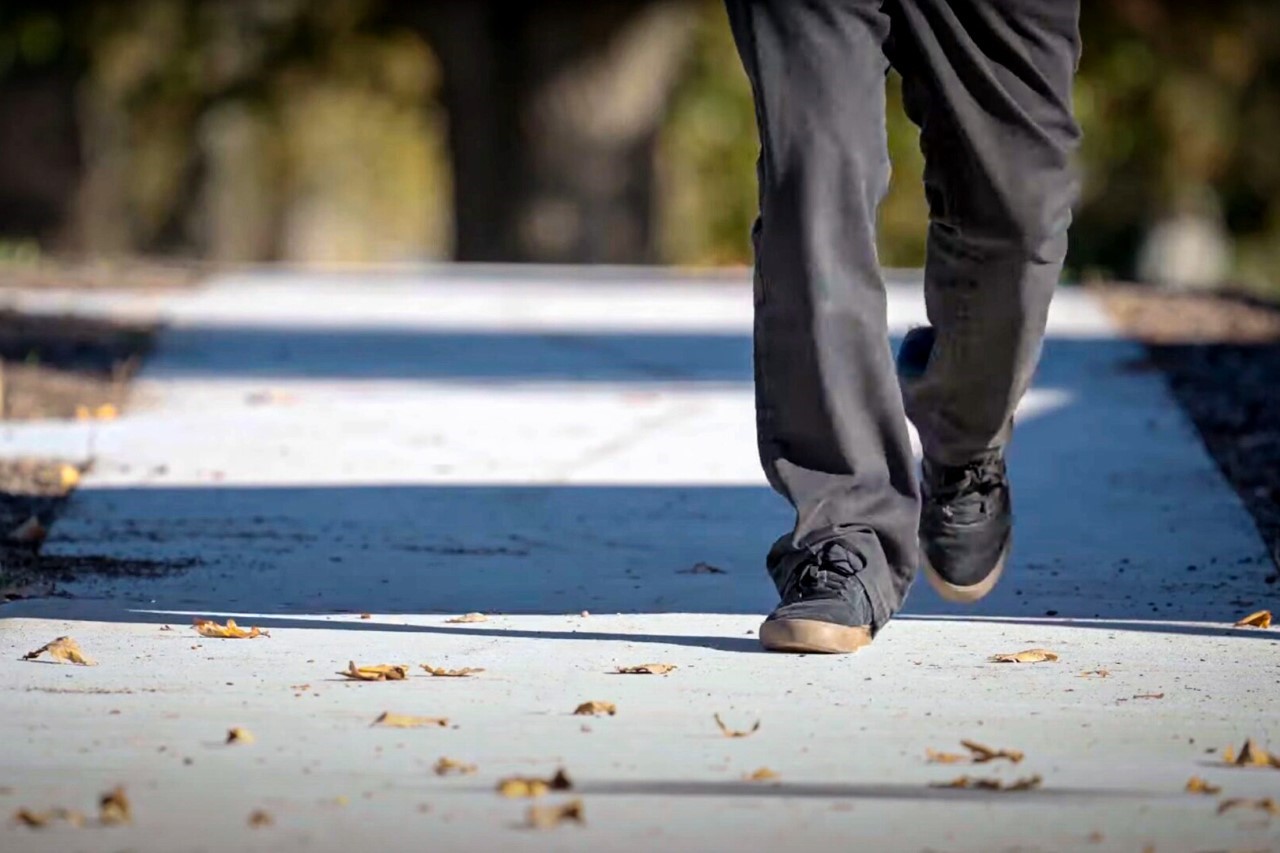

However, coffee isn’t the only contender. The researchers are exploring the use of biochar derived from other organic waste materials as well. Each type of biochar has unique properties that could influence the performance of the concrete in different ways. By understanding these variations, researchers can tailor the biochar type to achieve specific desired qualities in the final concrete product.
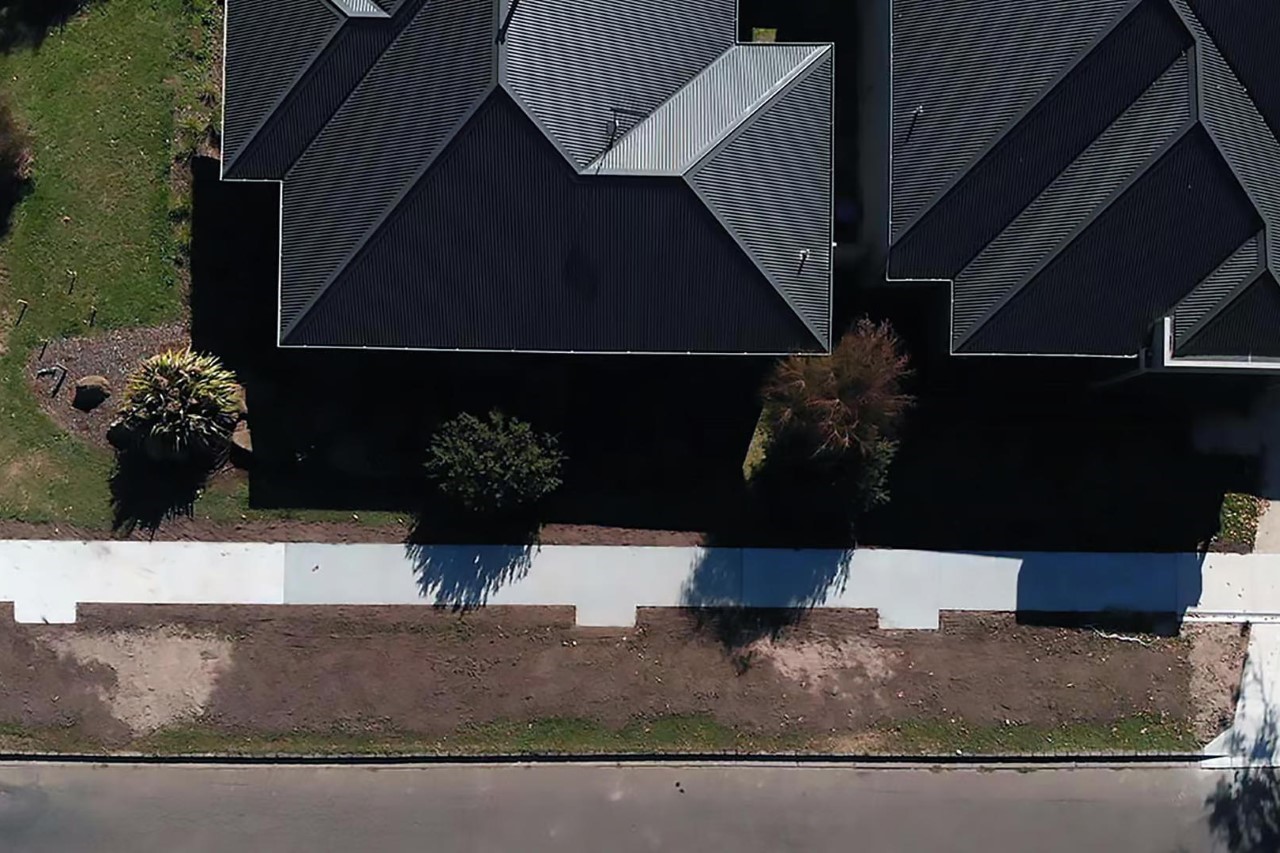

This first-of-its-kind trial ‘paves’ the way for a more sustainable future in construction. By incorporating waste materials into building materials, we can lessen our environmental impact and potentially create stronger, more durable infrastructure. The success of this trial could lead to a future where our daily walks contribute not just to our health but also to a greener planet. Now if only our pavements also smelled like coffee!
The post World’s First “Coffee-Concrete” Pavement in Australia is 30% Stronger and uses Recycled Coffee Grounds first appeared on Yanko Design.