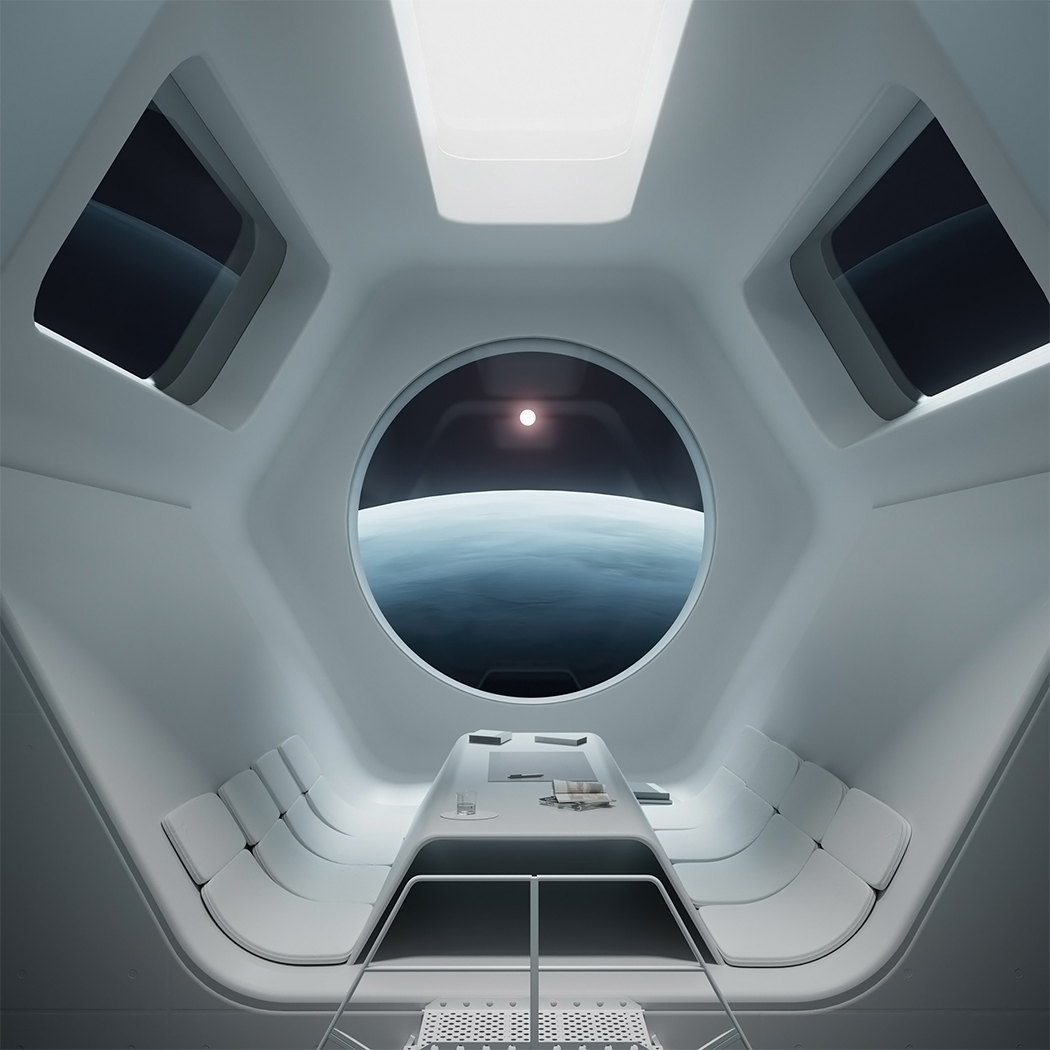
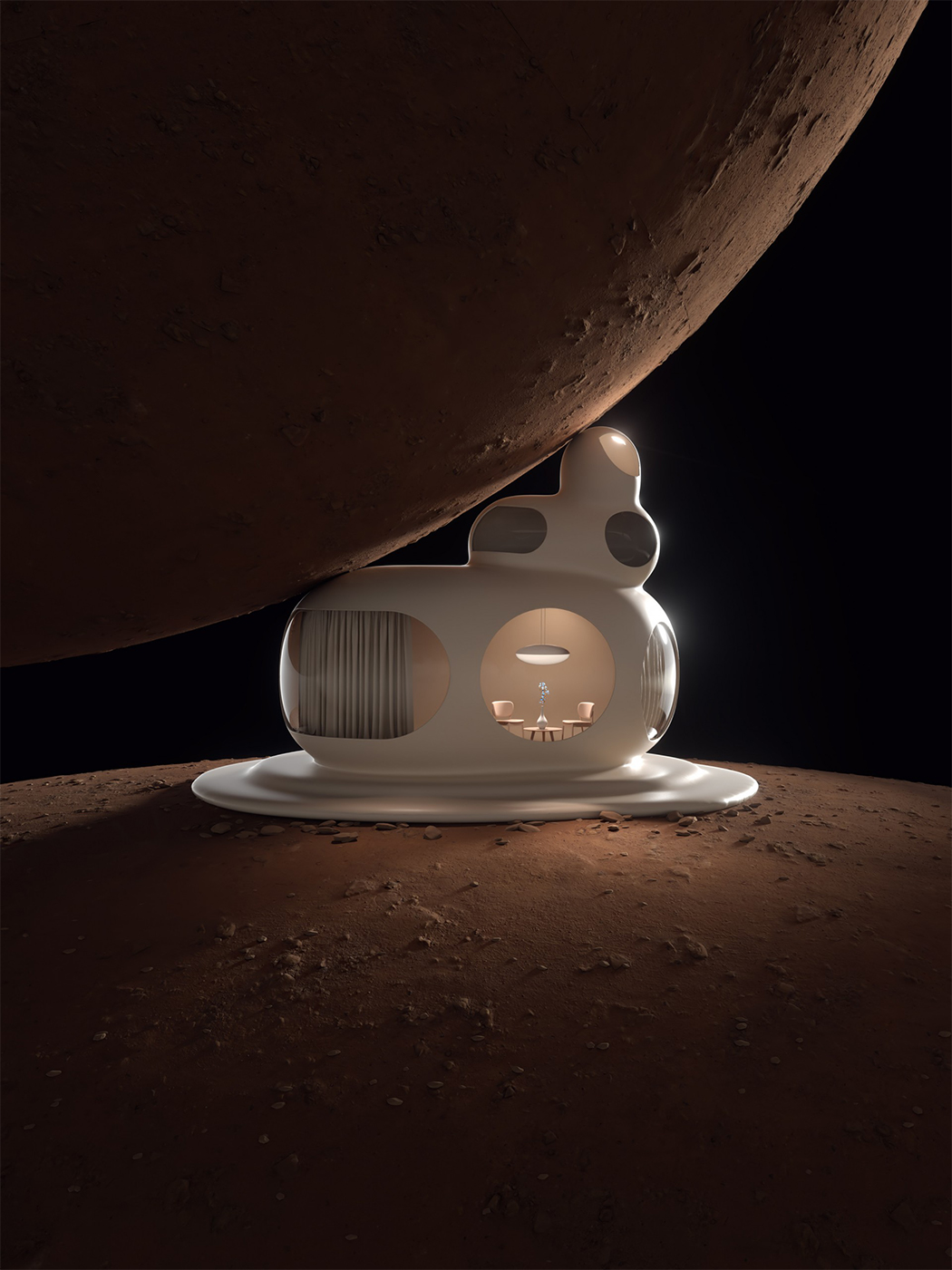
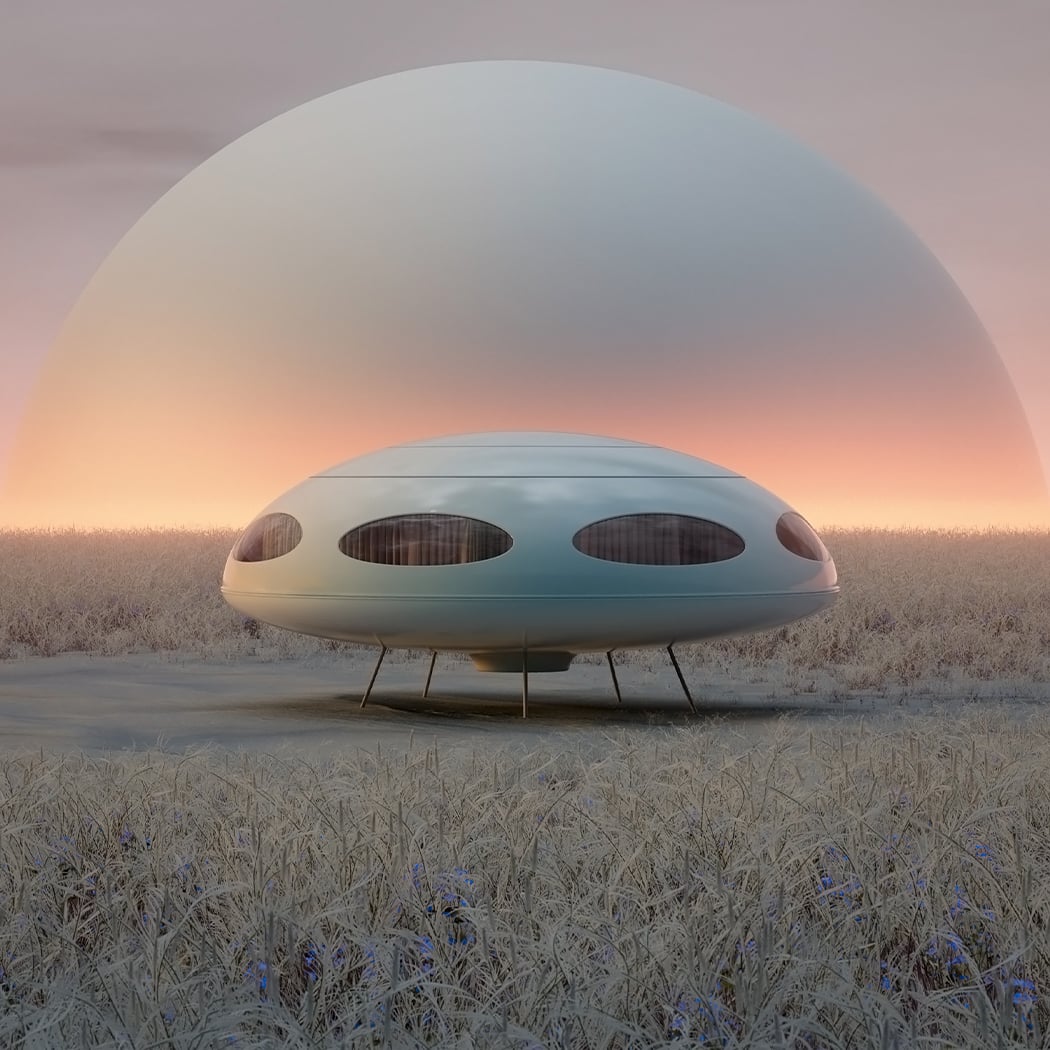
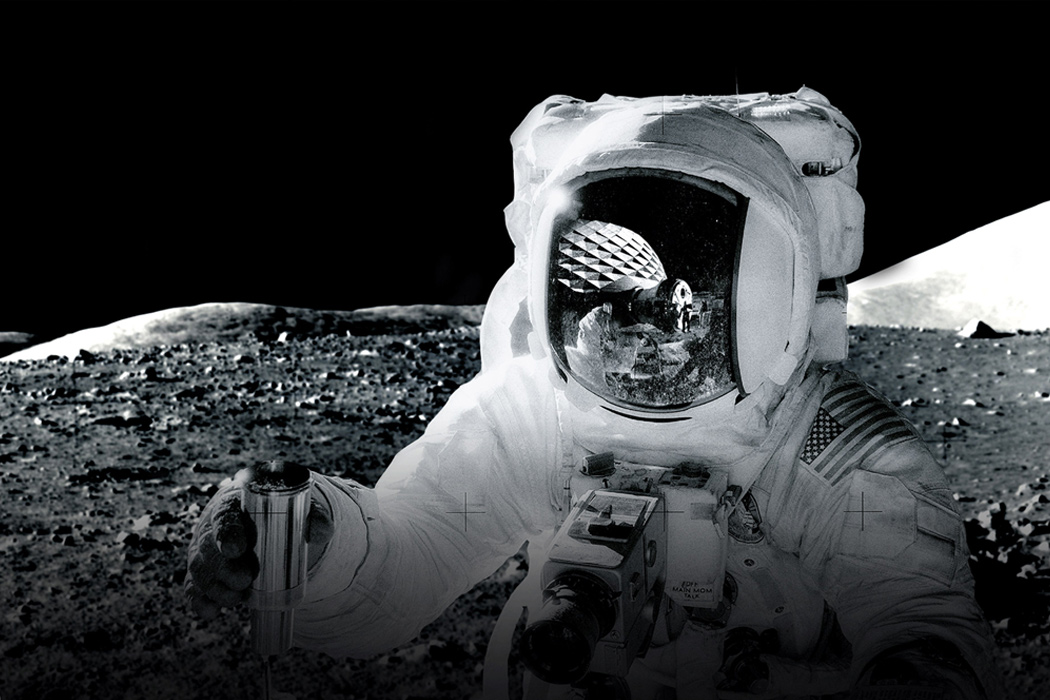
SpaceX Crew Dragon’s successful return from the space station has added a new dimension in humanity’s plans for space travel. Granted we have been sending spaceships out for a while, but the successful entry of Elon Musk to this space (literally!) promises a new direction or energy that our plans for living on Mars probably need! While NASA figures out the logistics to get us there, we want to focus more on the quality of life at the red planet and the architecture that will be used to house the people. After all, they promise a great view from any window we get!



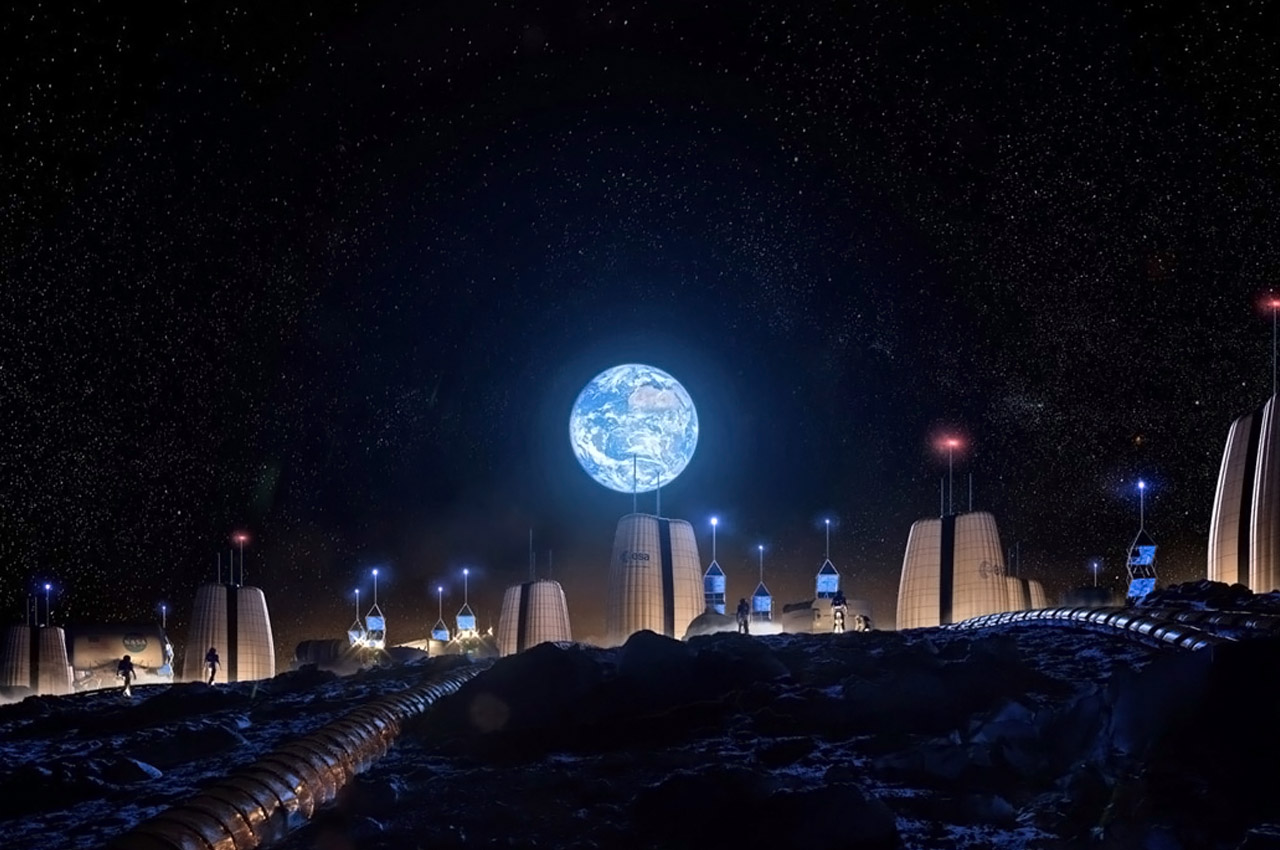
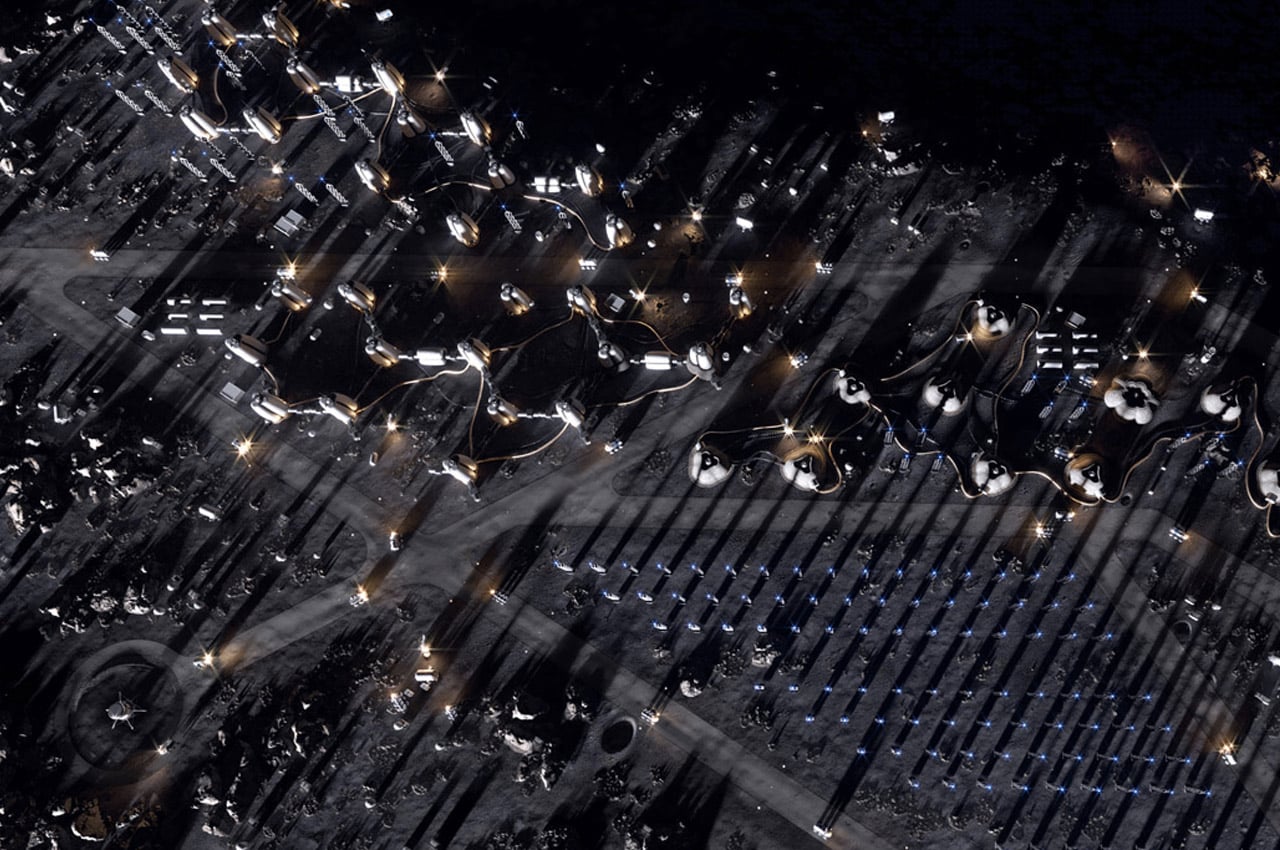
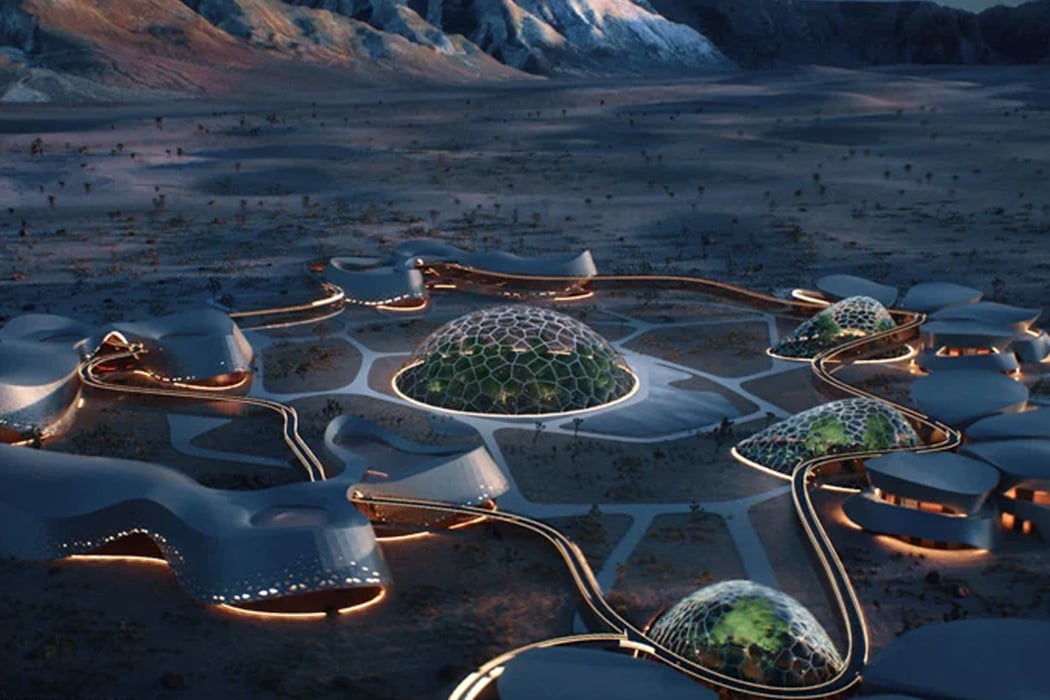
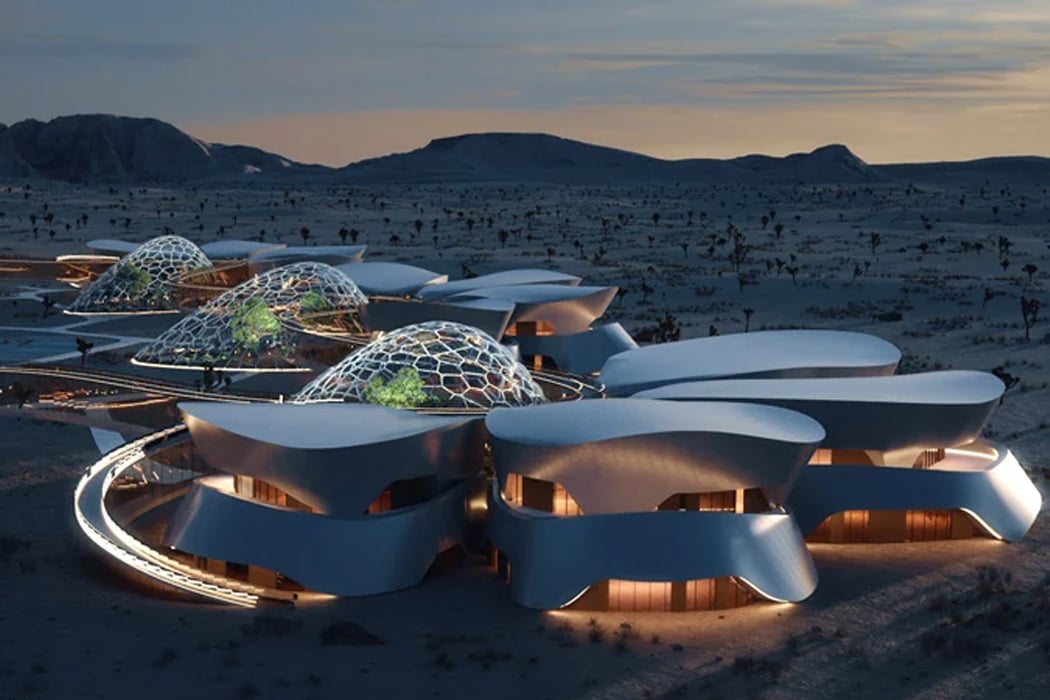
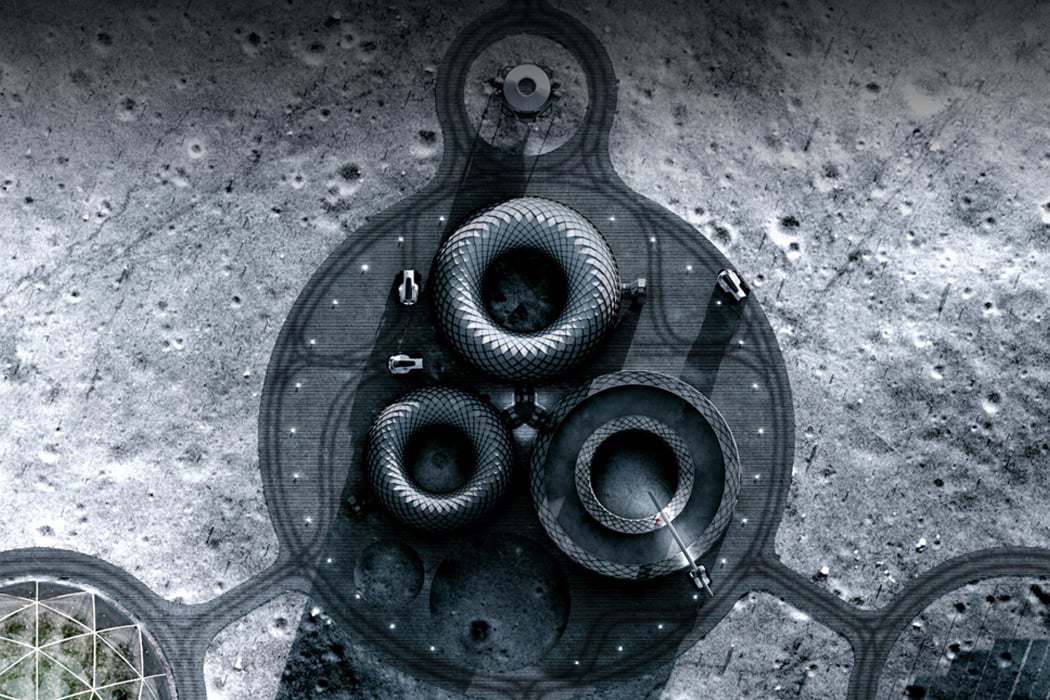
Paris-based Interstellar labs have planned to build a network of biomes in the Mojave desert in California to create and study the future of human settlement on Mars. Named EBIOS (experimental bio-regenerative station) the design is a circular village (enclosed on itself) with ‘regenerative life support technologies’. “Sentient life is likely very rare in our universe — complex life may be rare in our solar system,” said founder and CEO Barbara Belvisi. “At Interstellar lab we are building technologies to help its preservation and regeneration on earth now and in the future on other planets. What we need to bring on mars for life is what we need to protect on earth right now. The only path to becoming a multiplanet species is to join our energy in the same direction.” Following this philosophy, Interstellar is working closely with NASA to create the ideal habitat to help humans start the next leg of our journey across the Milky Way. After all, once we settle on Mars, who is to stop us from finding new planets!

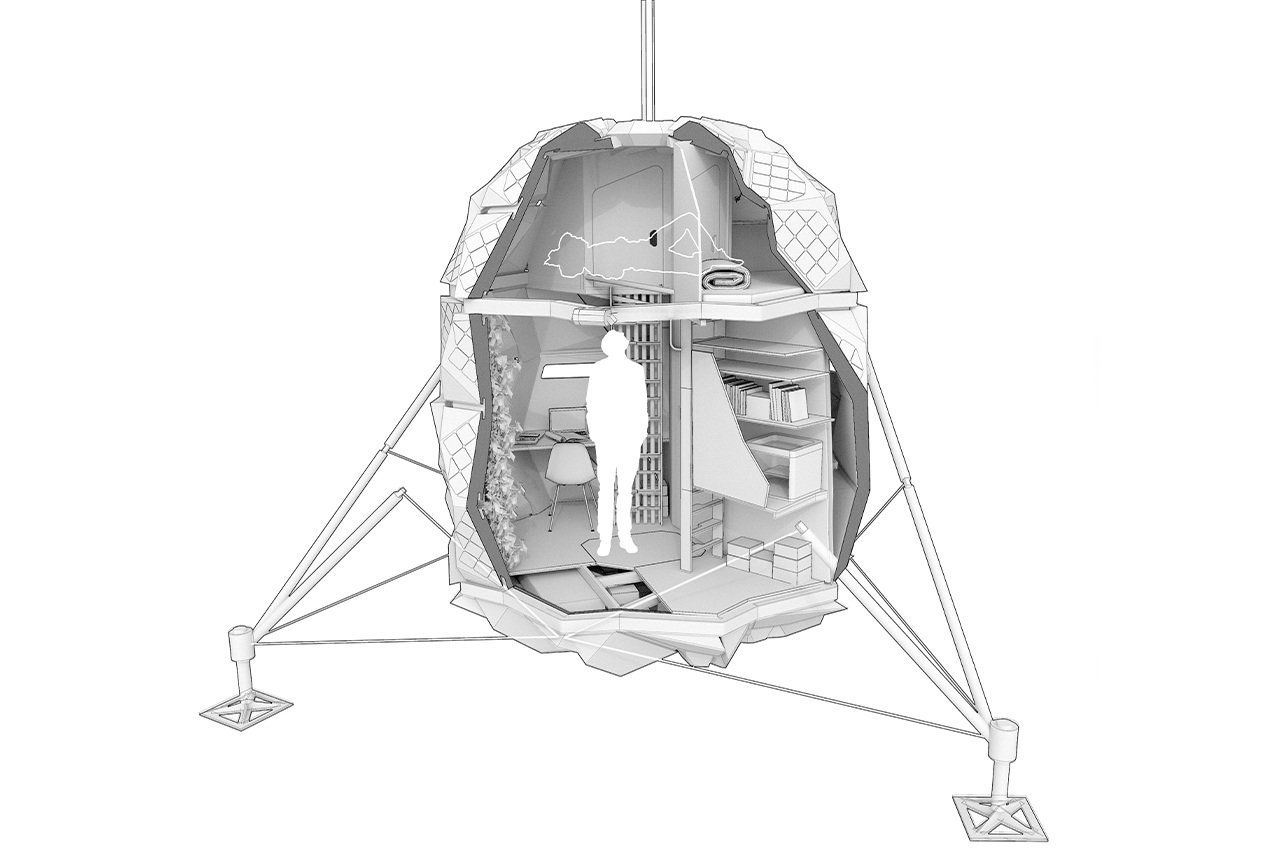
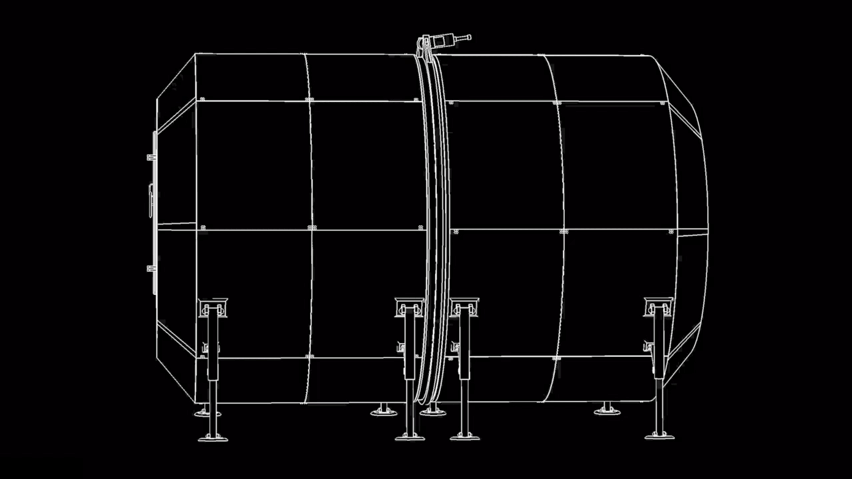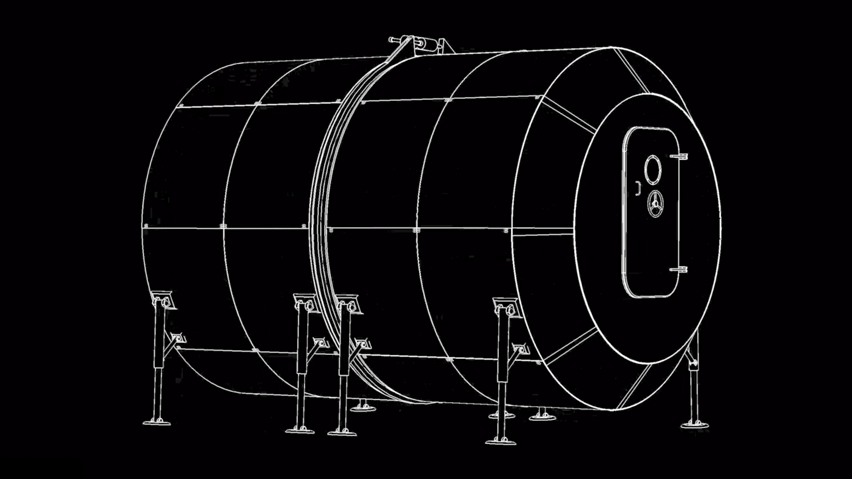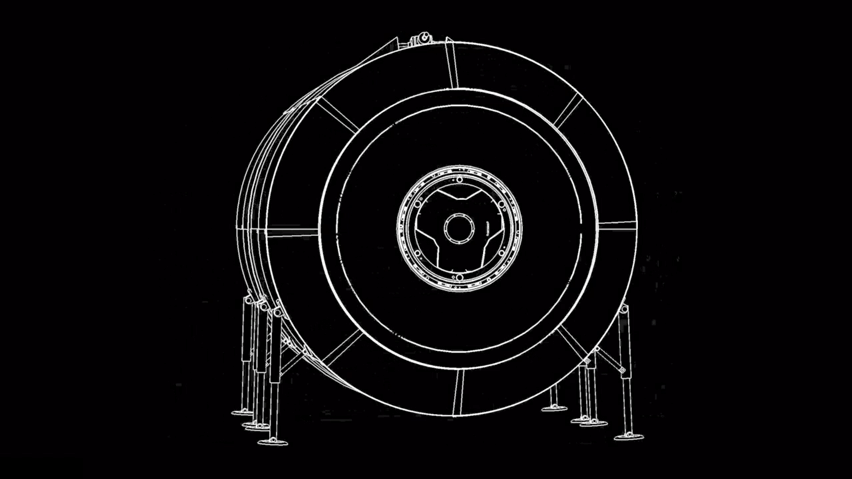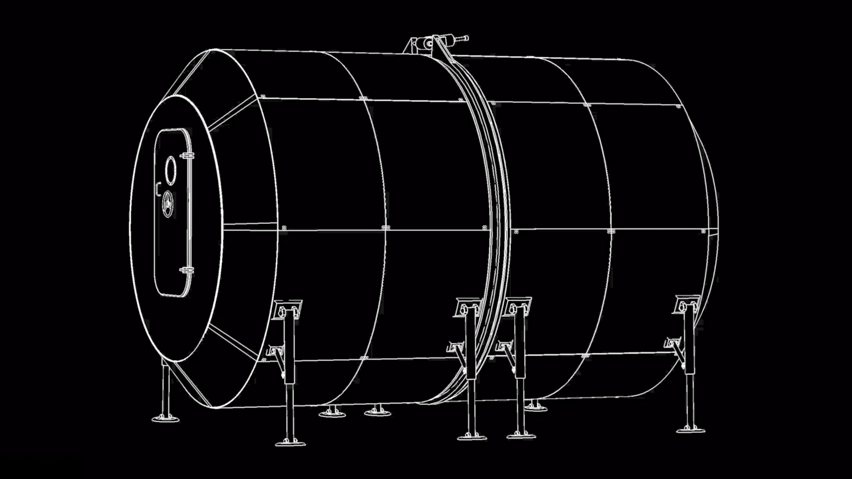
SpaceX got their rocket to the space station and back successfully. So it’s only logical the next step for them is to build us a solar-friendly housing there (after all the roadster is already orbiting in space!) and we even have a date for it! The Dragon Crew included a crew of two, whereas rehabilitation requires mass transportation with SpaceX’s 100-passenger reusable rocket design (named Starship) preparing to get us there. Elon Musk has said it would take 1,000 of SpaceX’s starship rockets 20 years to transport the cargo. A series of tweets by Musk outlines how many rockets he thought it would need to carry the necessary cargo to set up a base on Mars. “A thousand ships will be needed to create a sustainable mars city… as the planets align only once every two years,” he said. Musk also stated a full ‘Mars base alpha’ – a preliminary city on the red planet – could be completed as soon as 2028. SpaceX intends to use the BFR to build a base on the moon and for return trips to and from mars. the most recent images of the mars base photo include the updated BFR design, which this year added bigger fins.


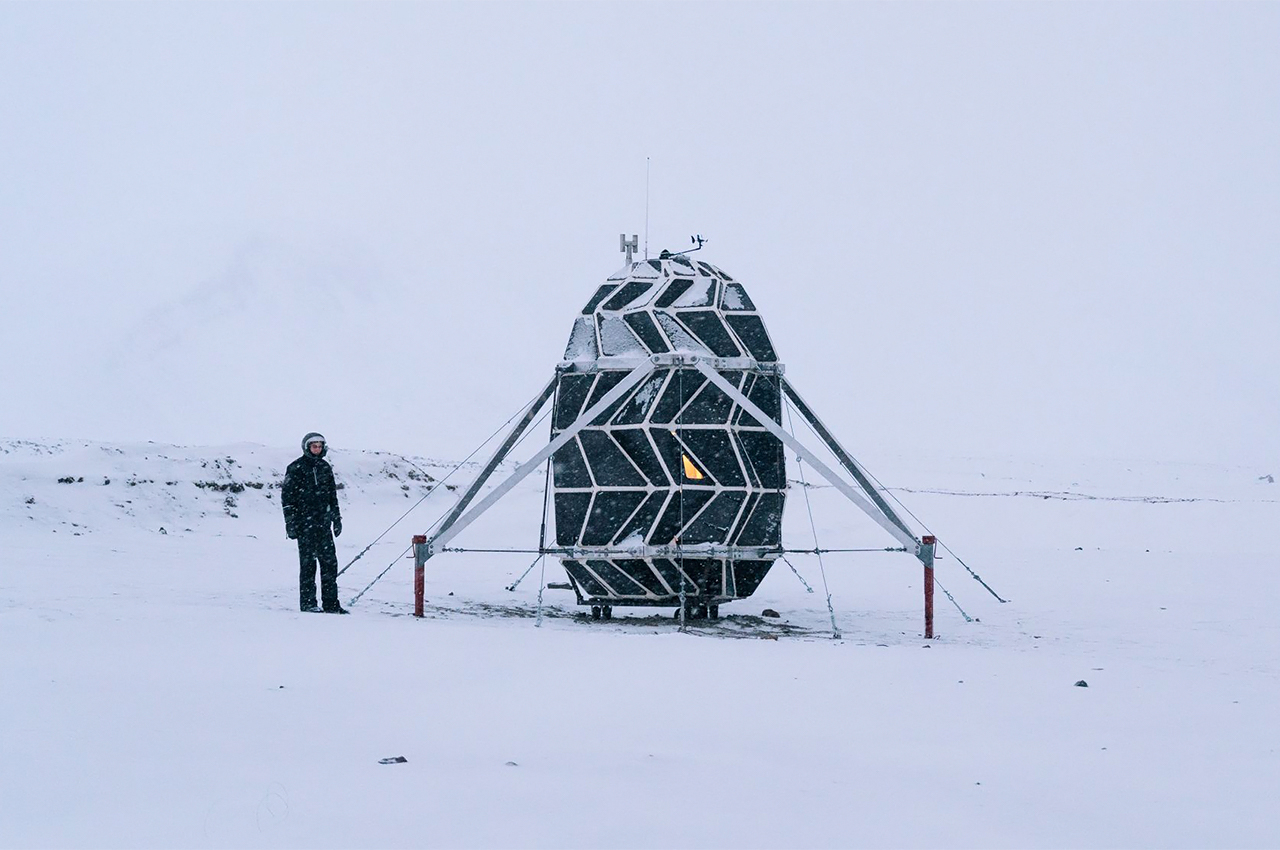
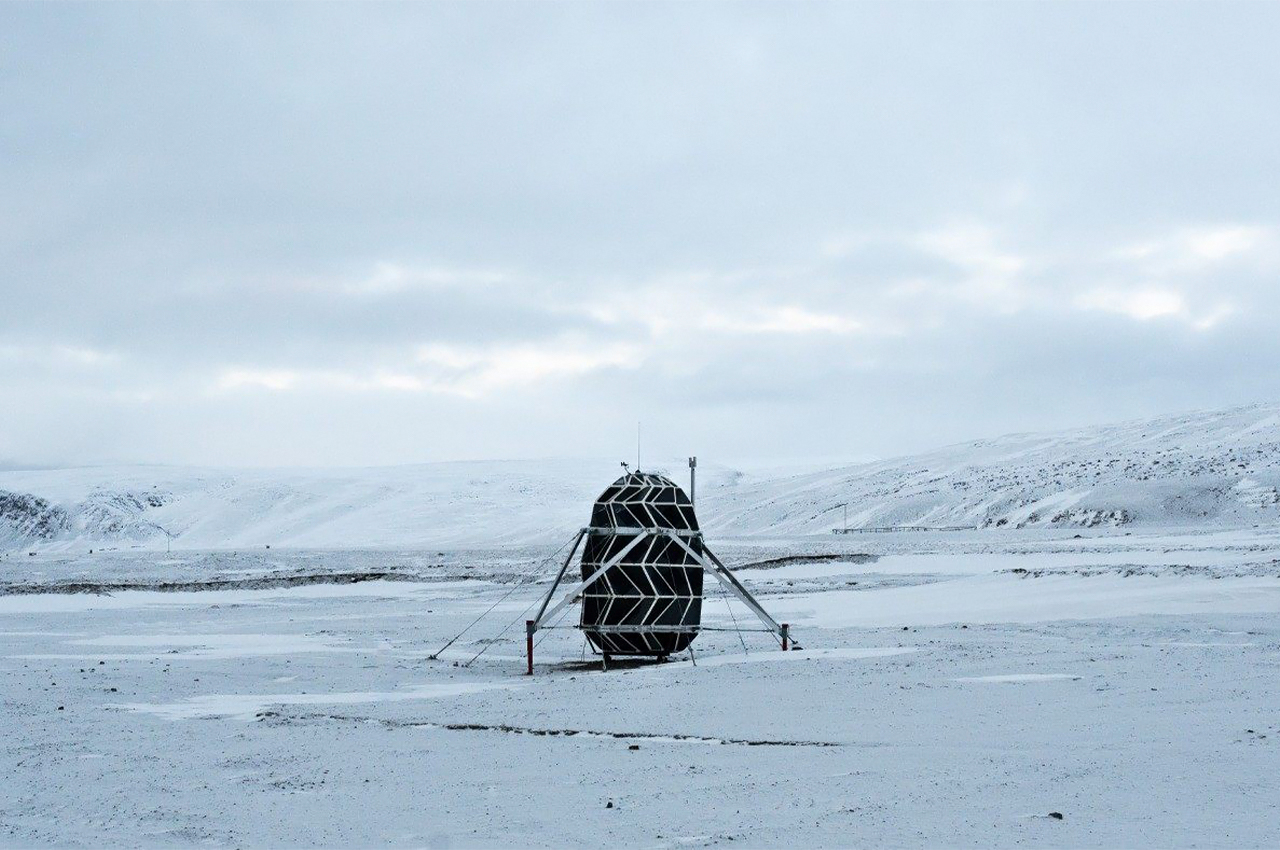
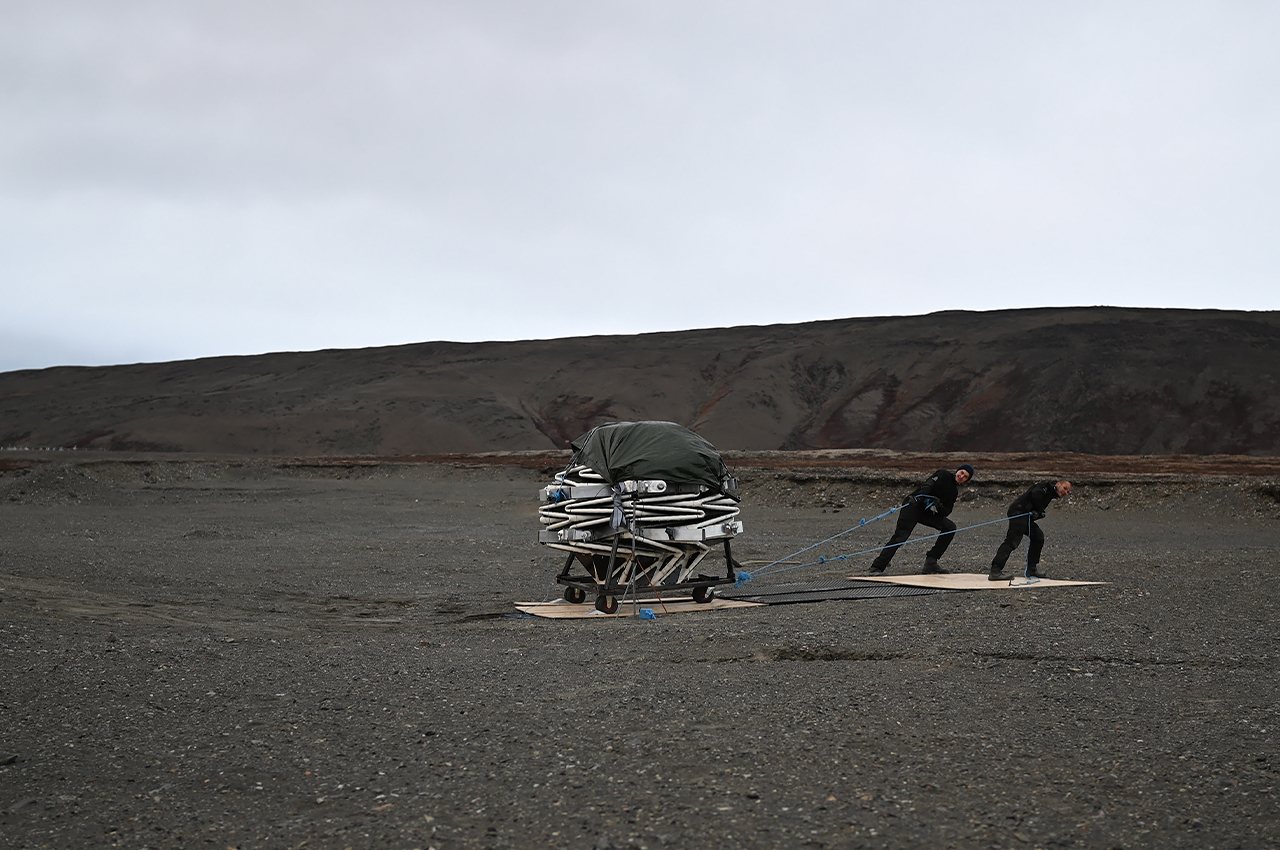
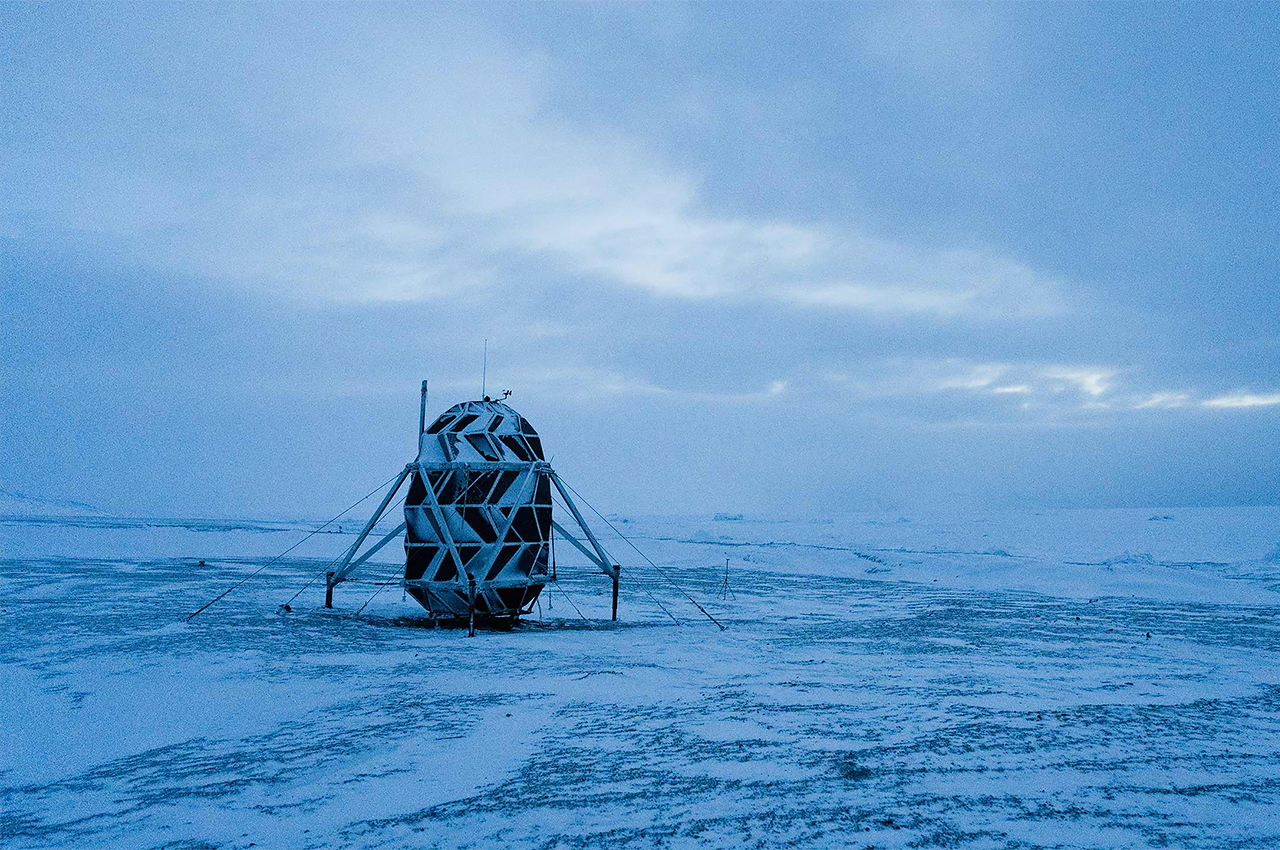
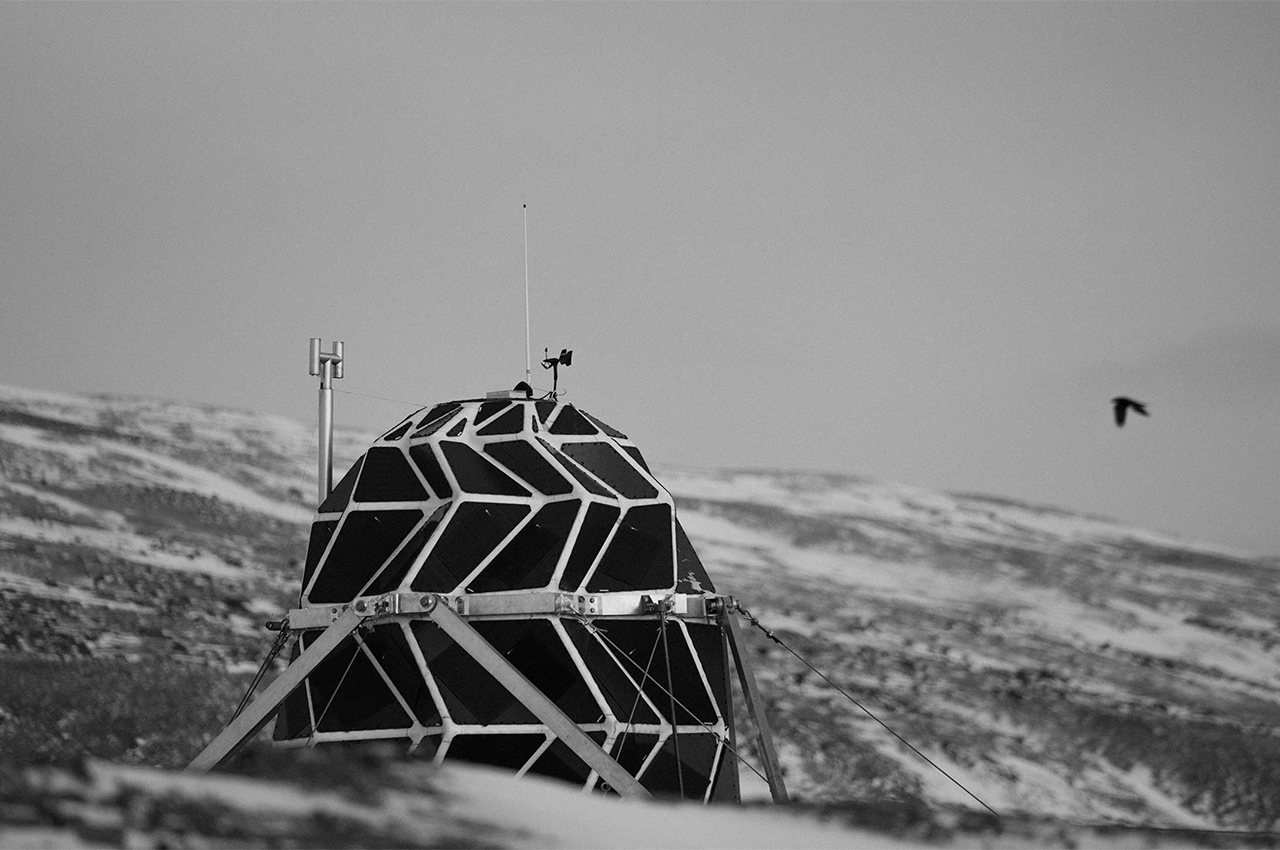
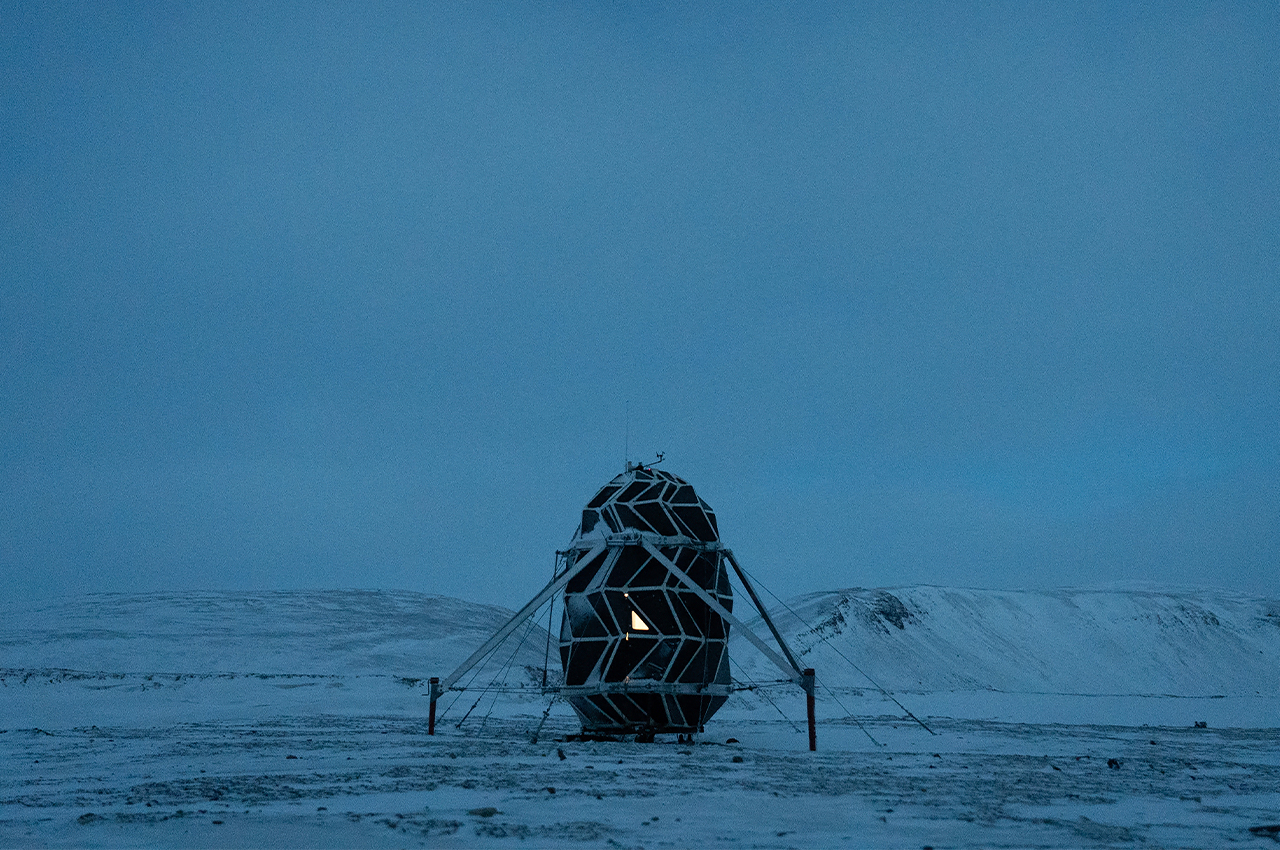
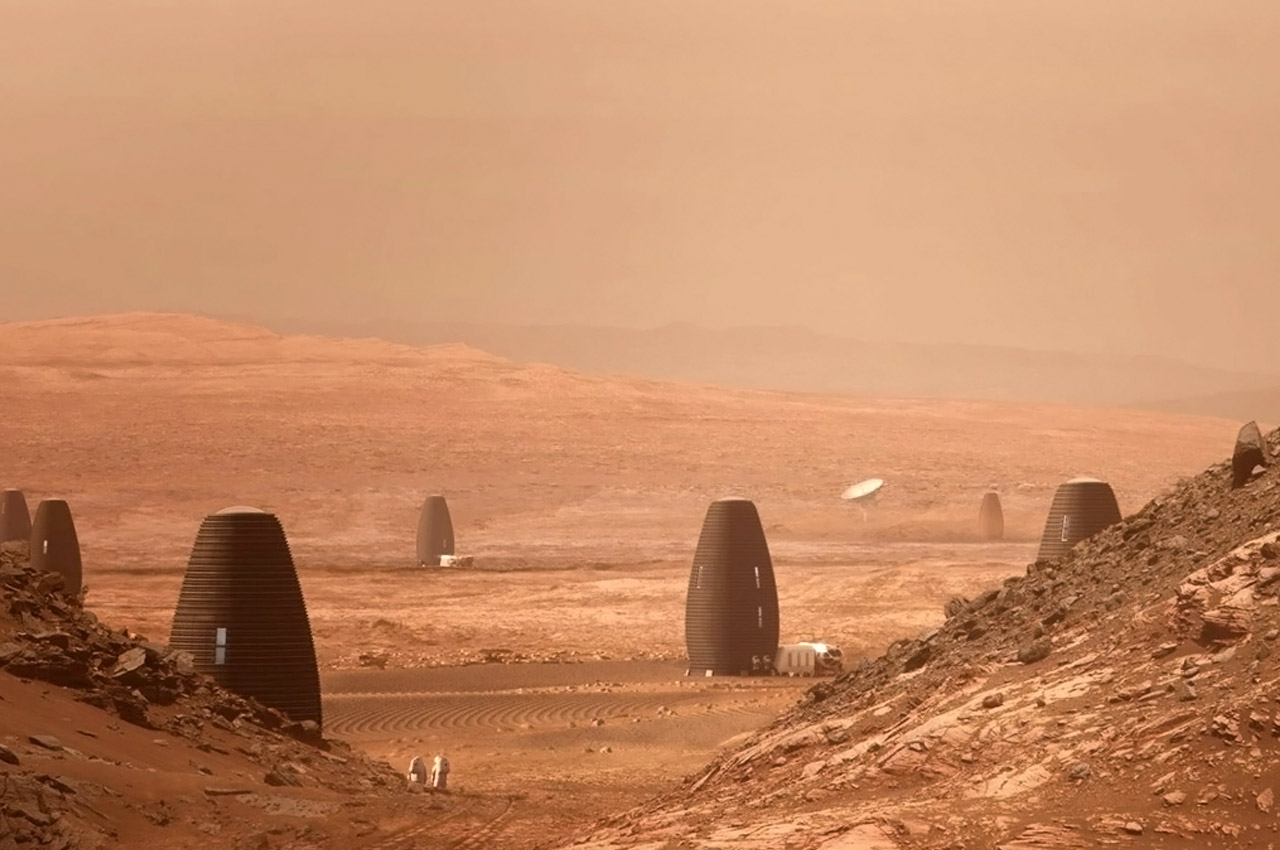
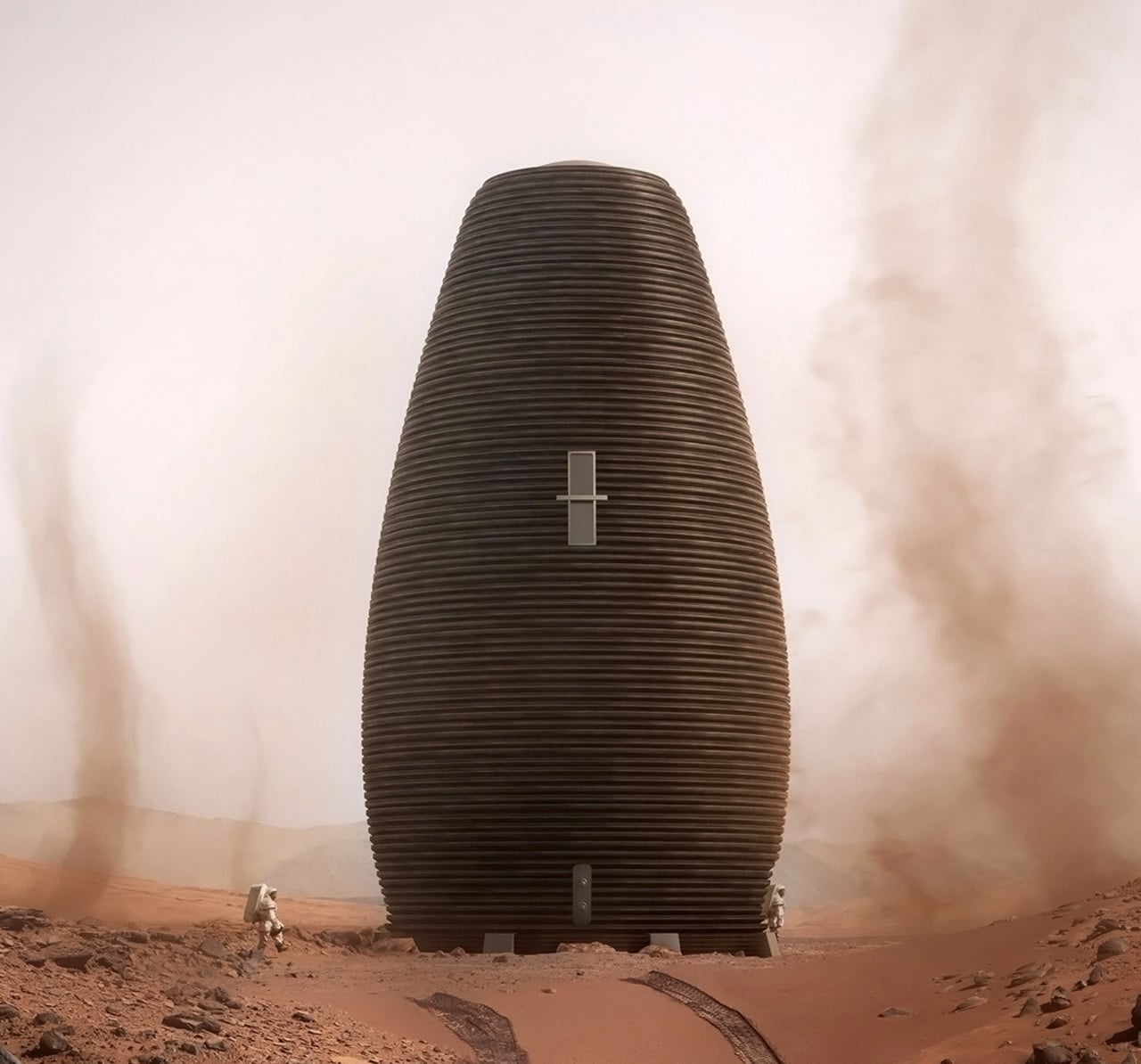
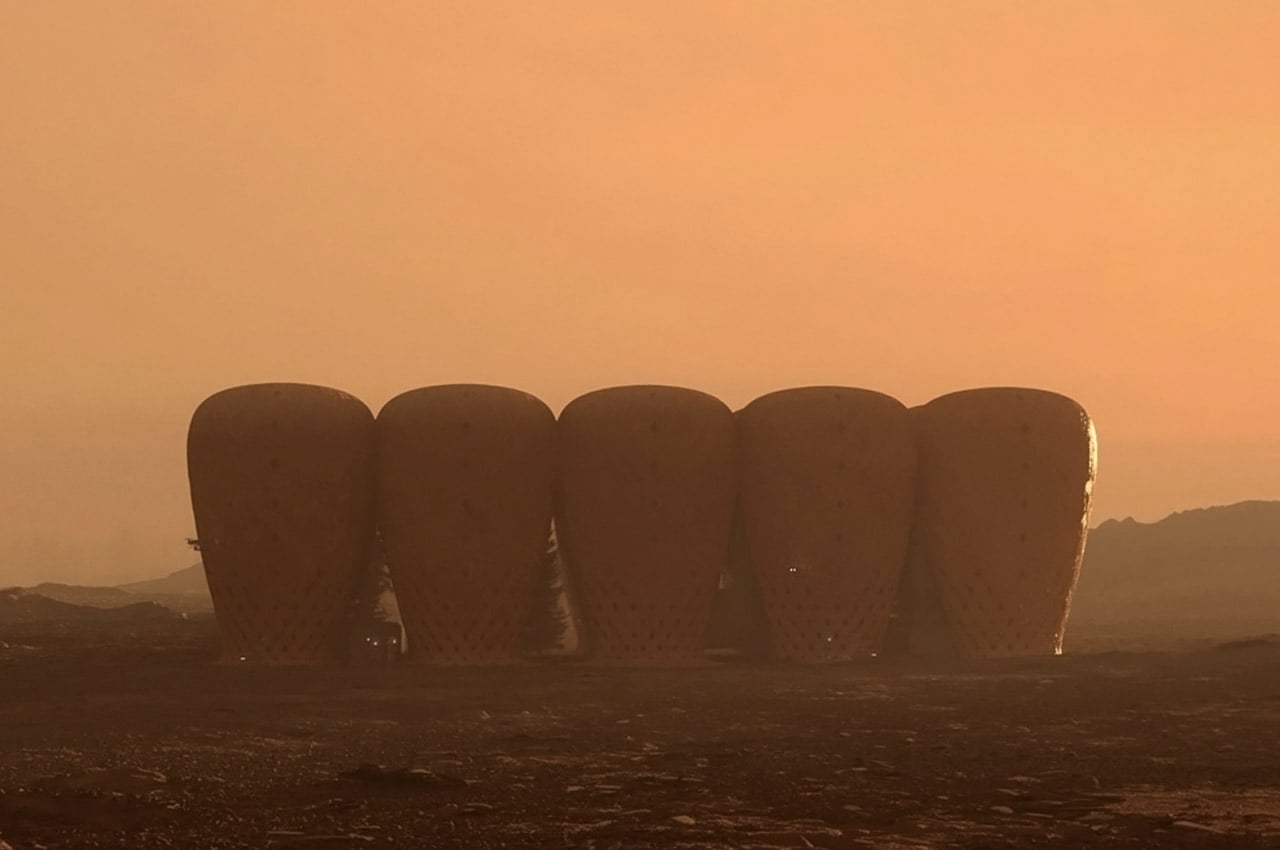
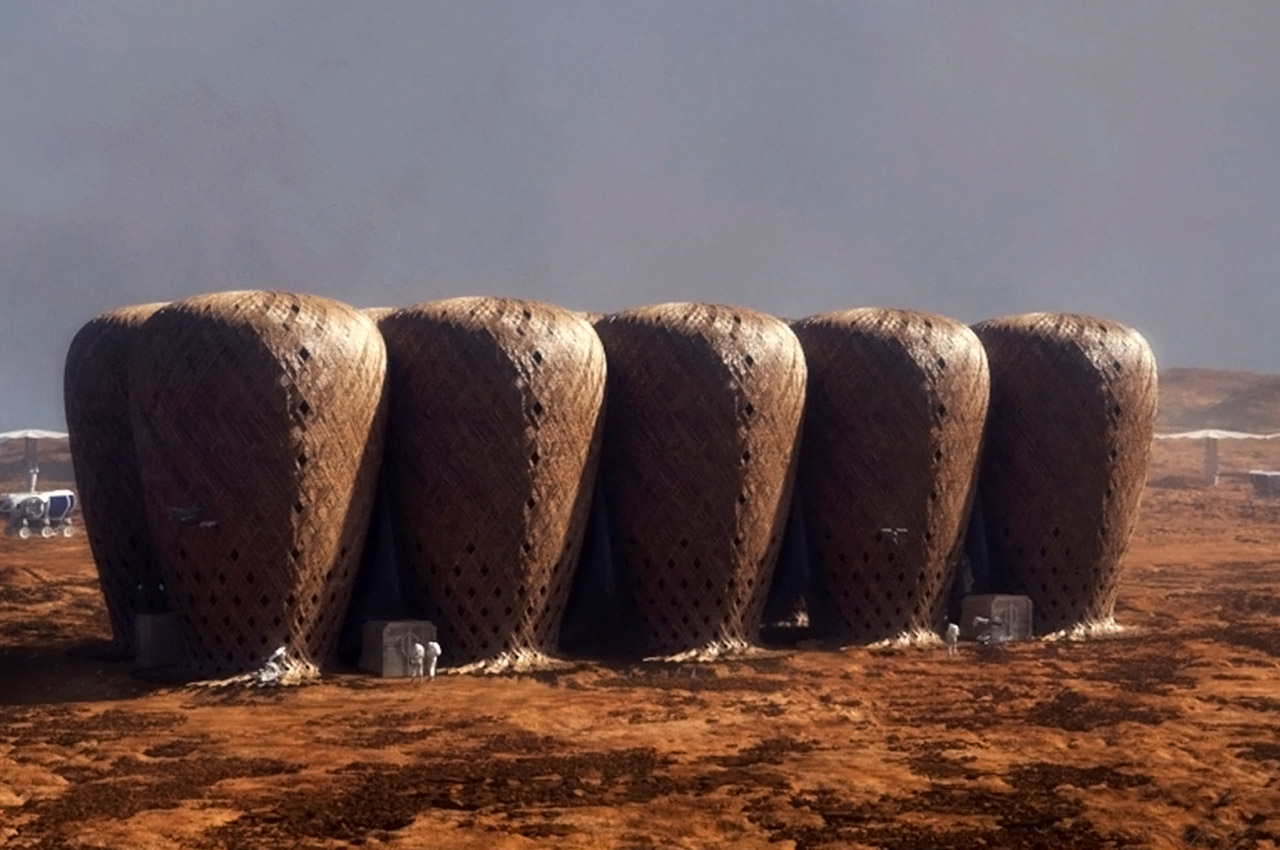
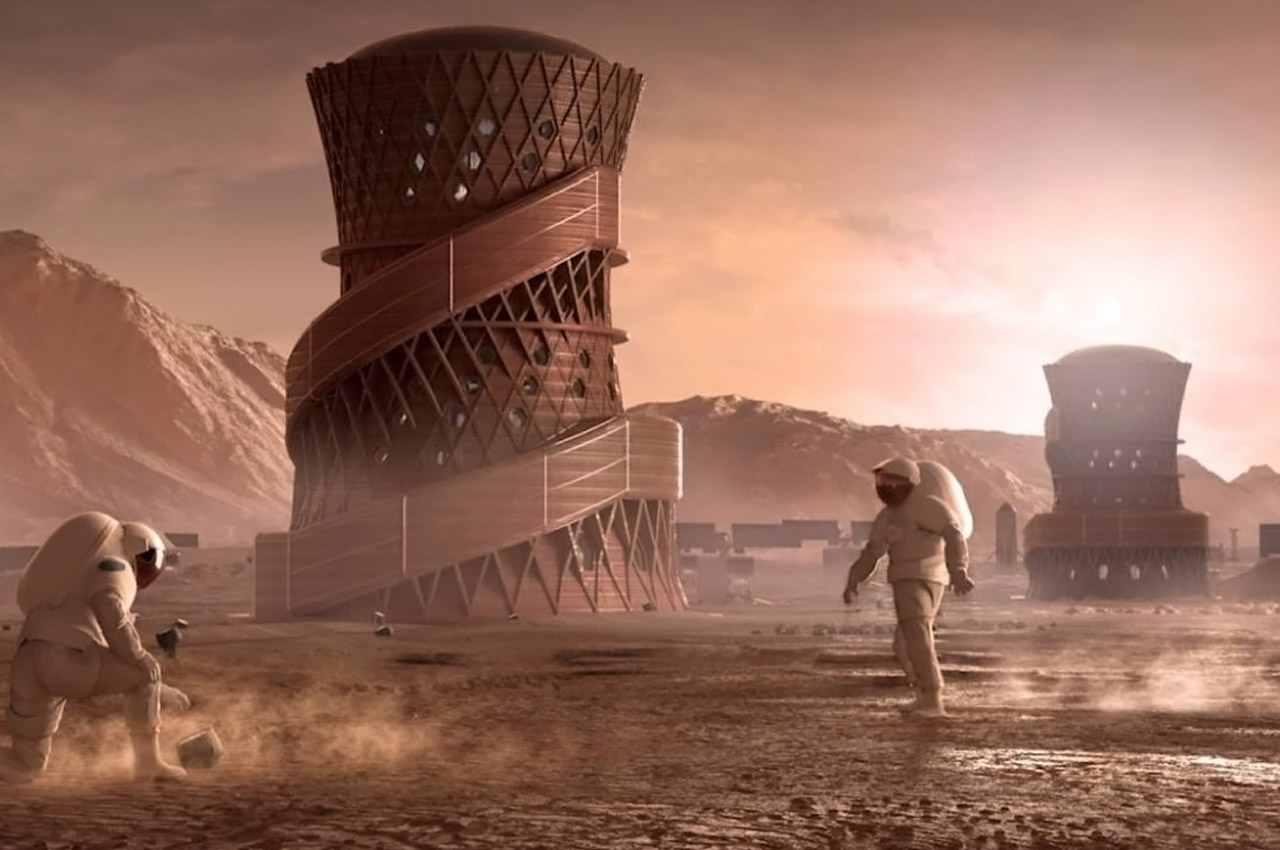
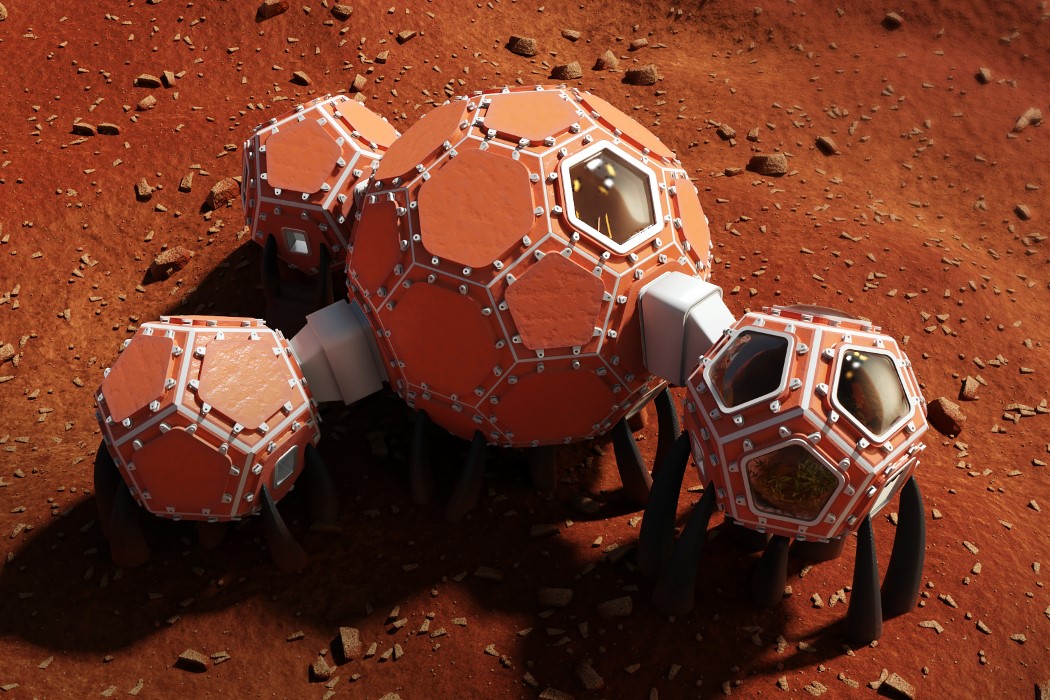
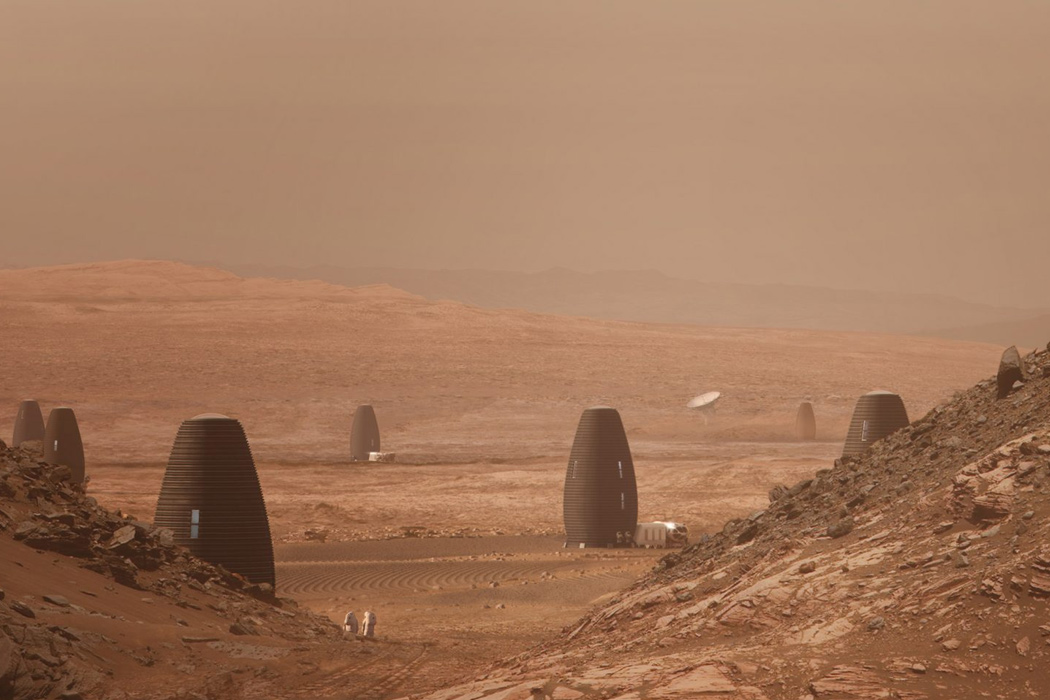
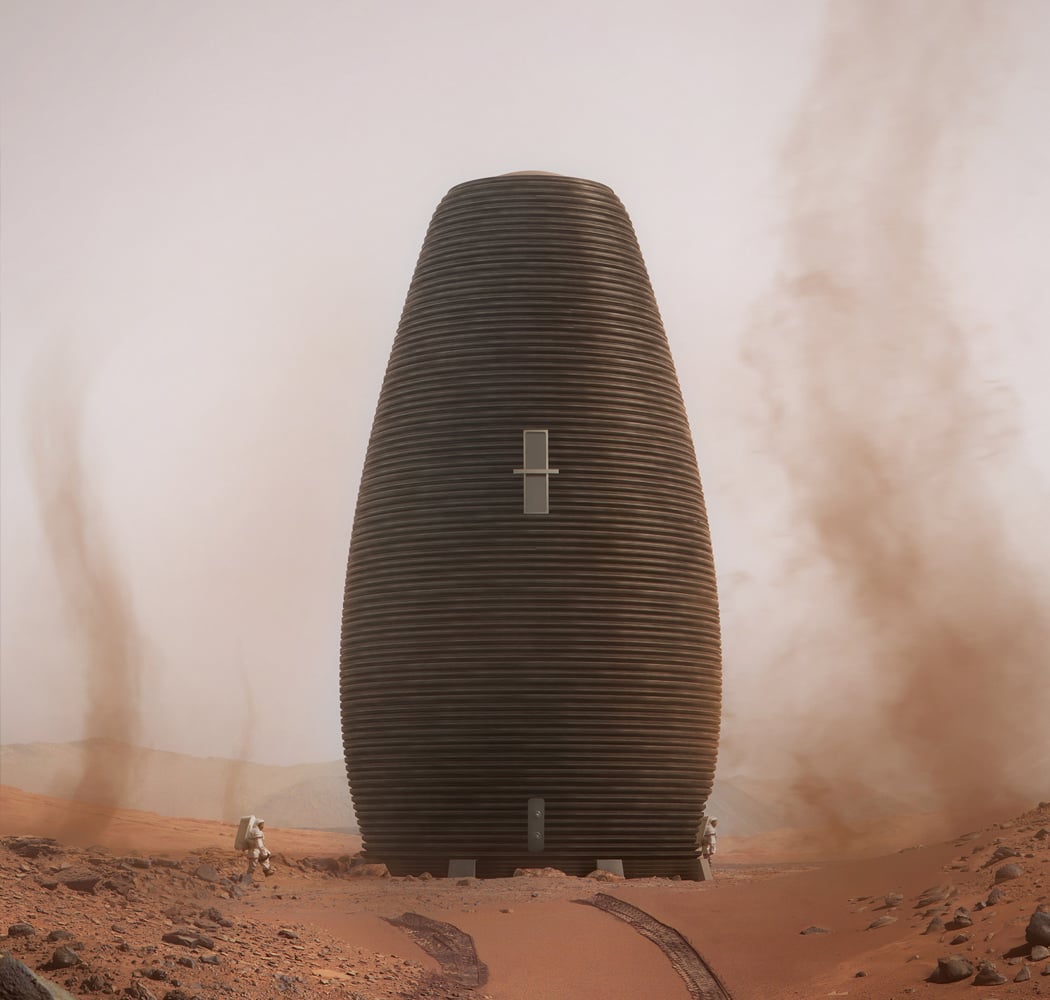
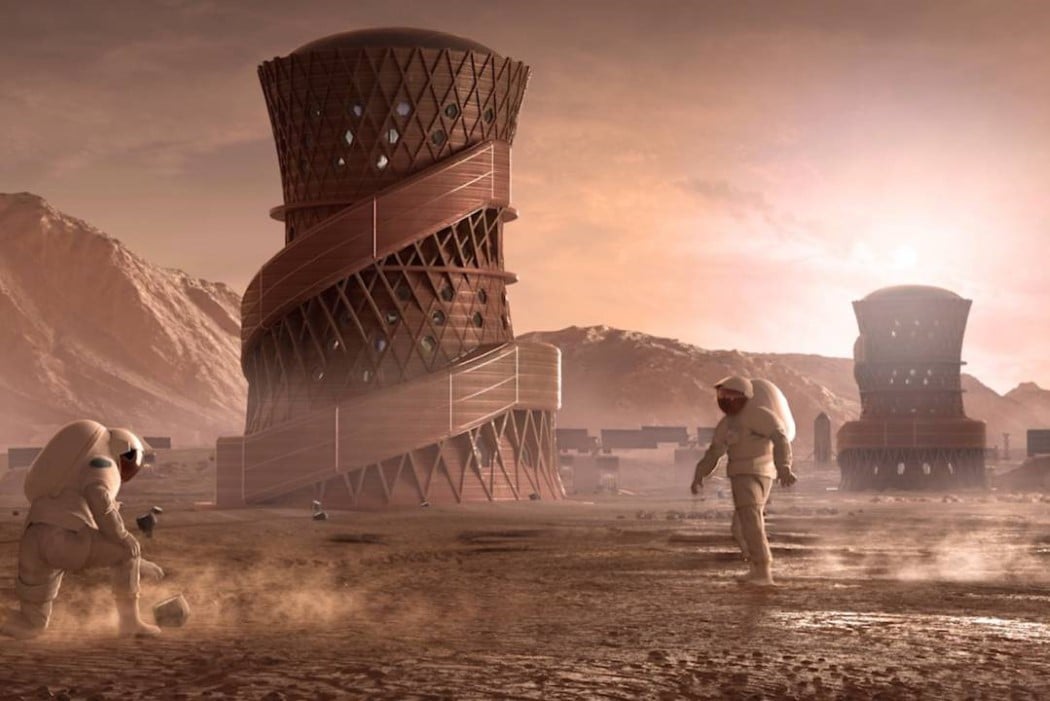
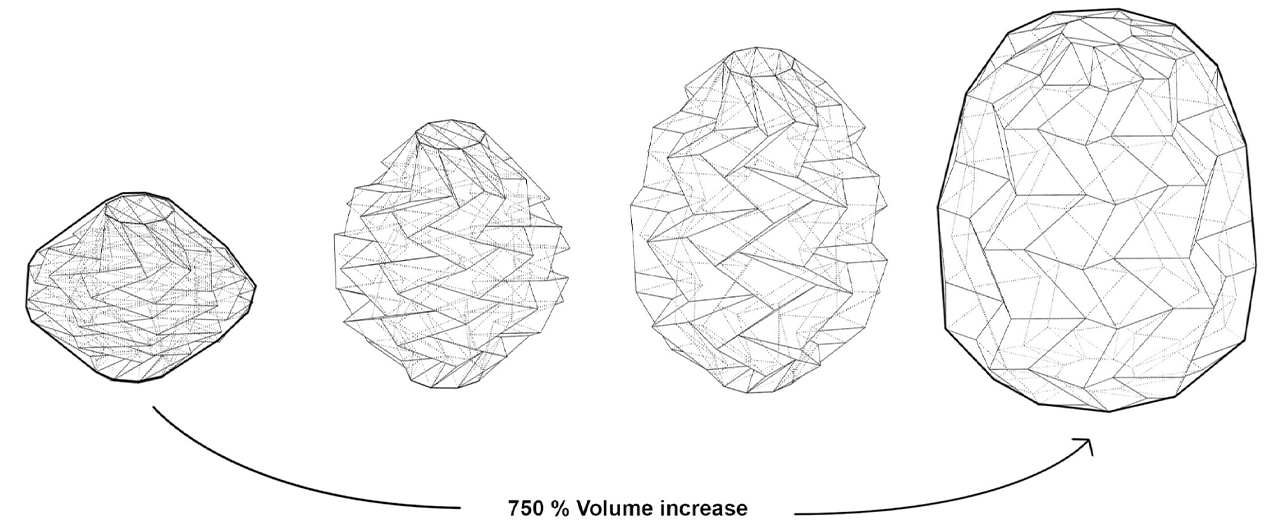
When NASA announced a competition to design the best Martian habitation design, AI SpaceFactory came in second place with its vertical, egg-shaped structure that holds a double shell system to handle the internal atmospheric pressure and the structural stress the design may have to endure. Designed to be constructed on Mars, the design keeps in mind using elements already present on the planet, reducing the dependency of construction materials to be carried from Earth. The team developed an innovative mixture of basalt fiber, extracted from Martian rock, and renewable bioplastic (polylactic acid) derived from plants that would be grown on Mars. The design envisions individual structures instead of a communal habitat but given the area it covers, it should comfortably house more than one Martian at a time!


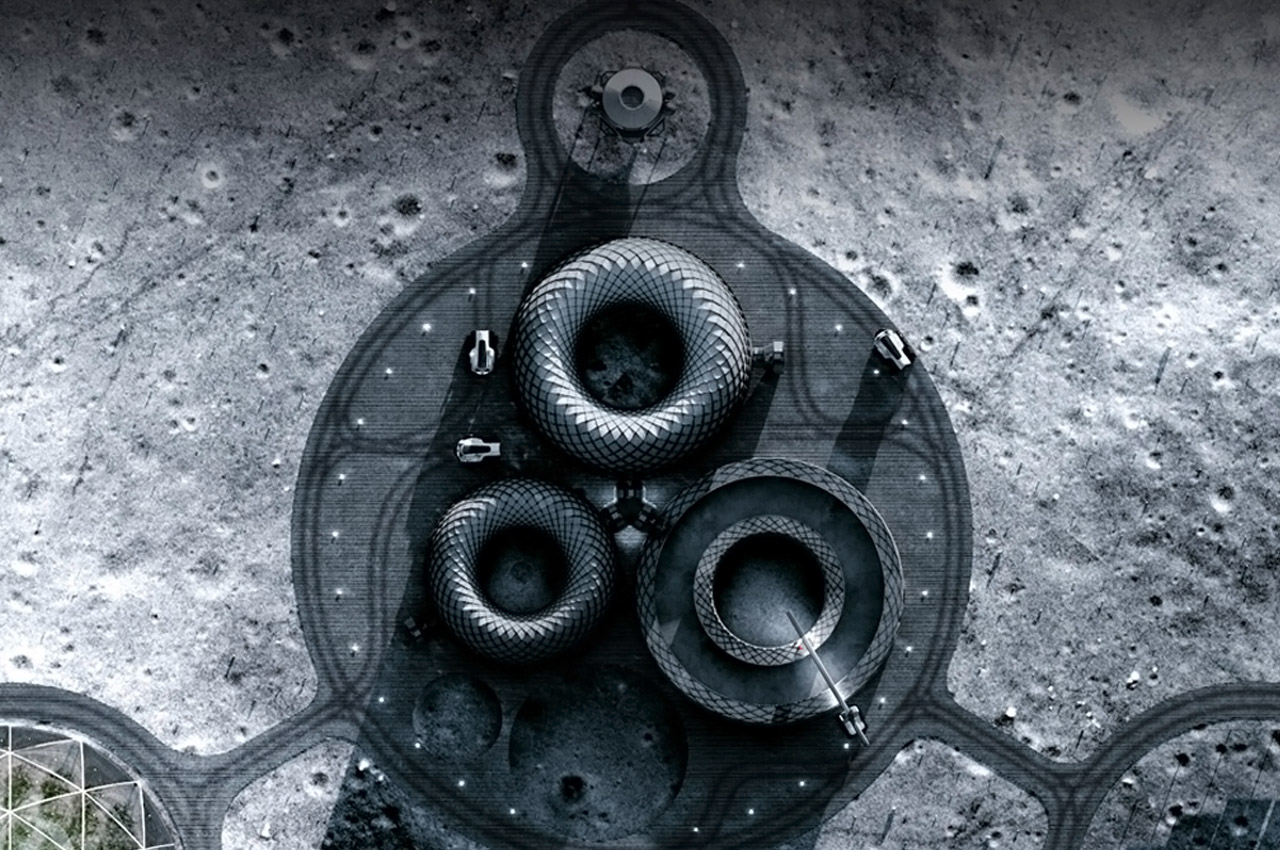
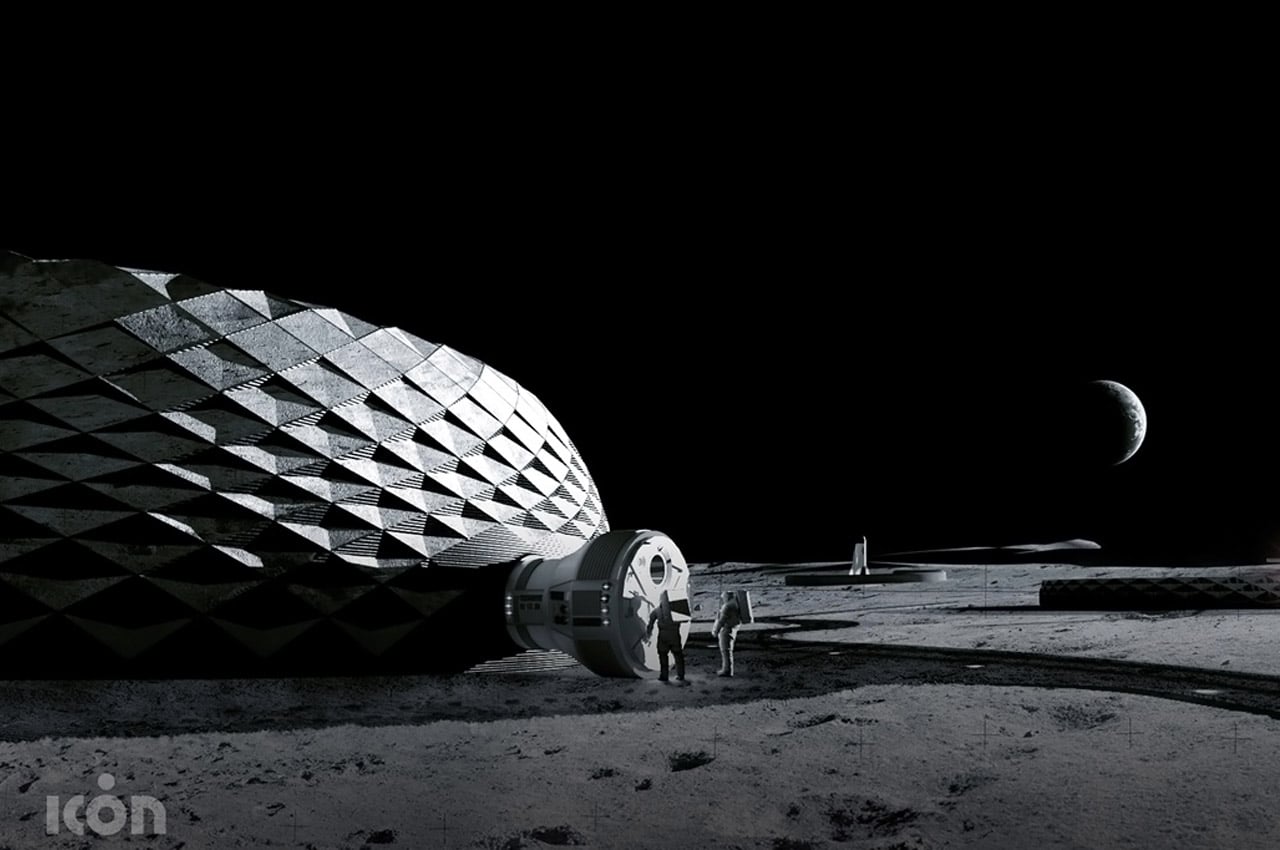
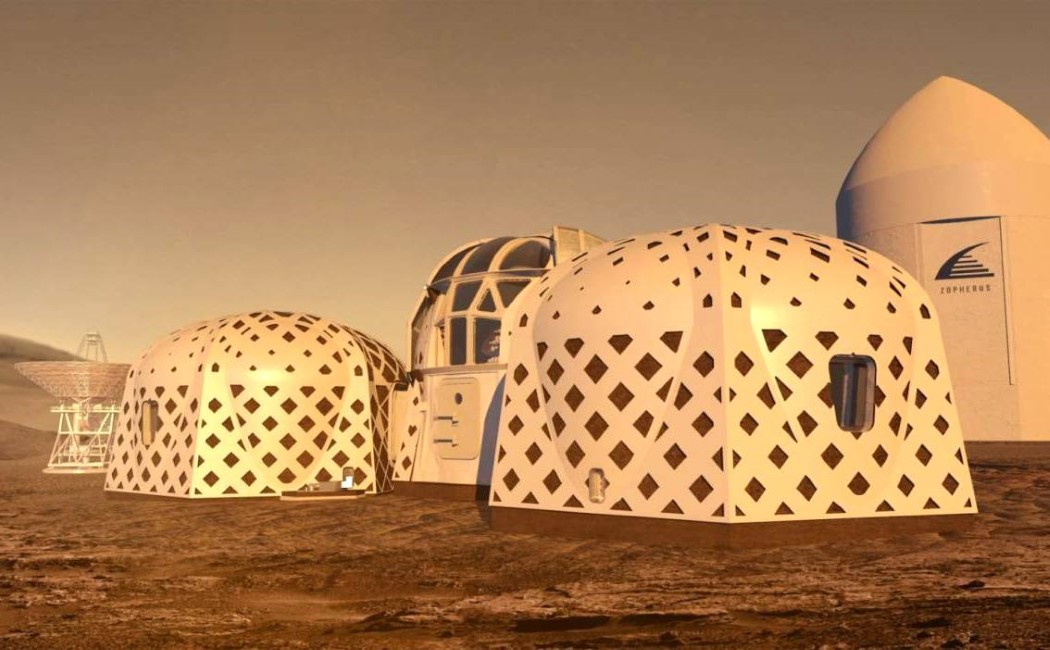
The winner of NASA’s competition to design 3D-printed habitat for Mars is the Zopherus designed by an Arkansas-based team. The design is envisioned to be built from the materials available on the planet and showcases a settlement with rounded hut-like structures. The construction is designed to be 3D printed, without any human intervention to keep the place ready for the humans before they arrive. The process starts with a lander who settles and looks for a suitable area to start building the settlement, the lander deploys autonomous robots who gather the material for the process to start.



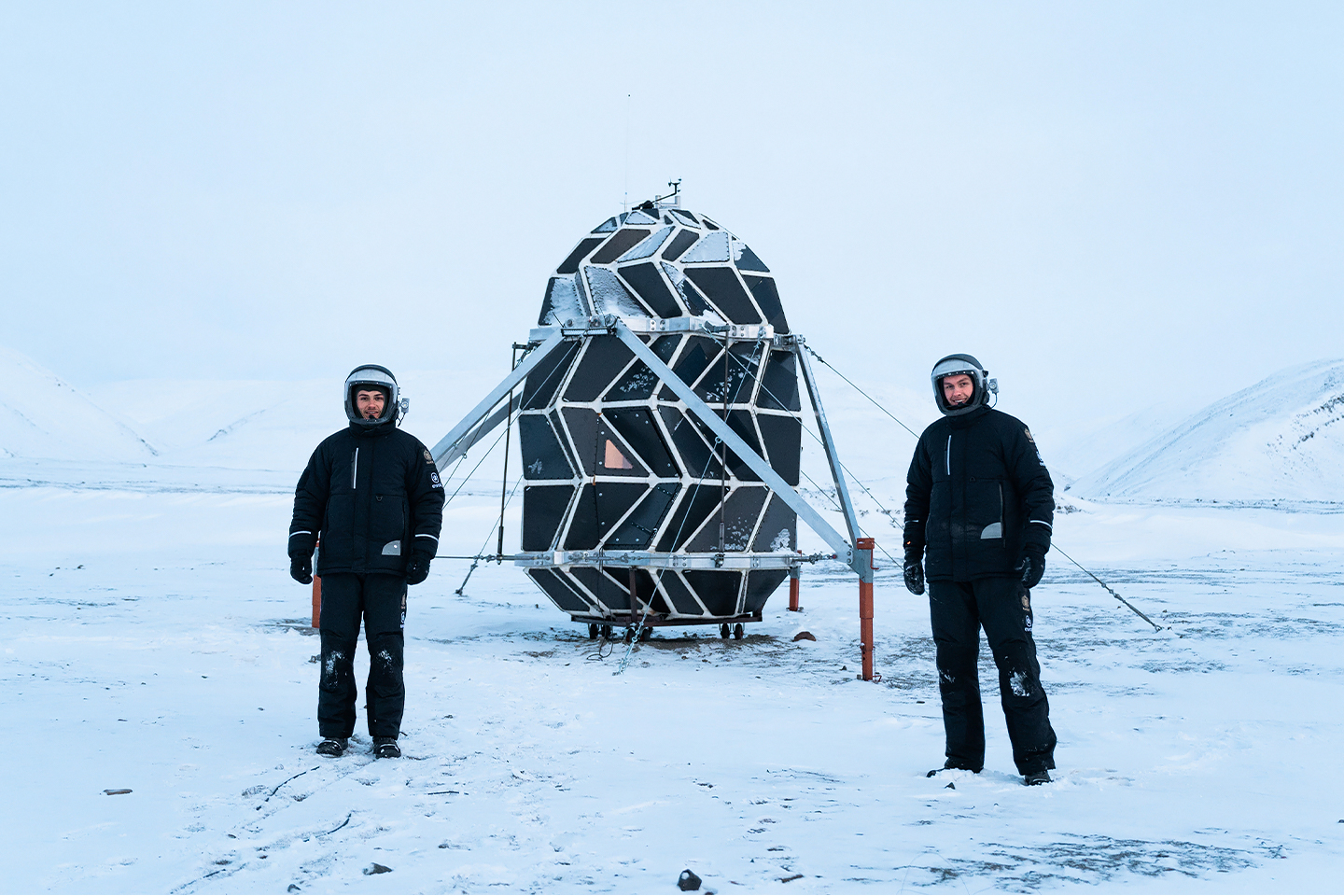
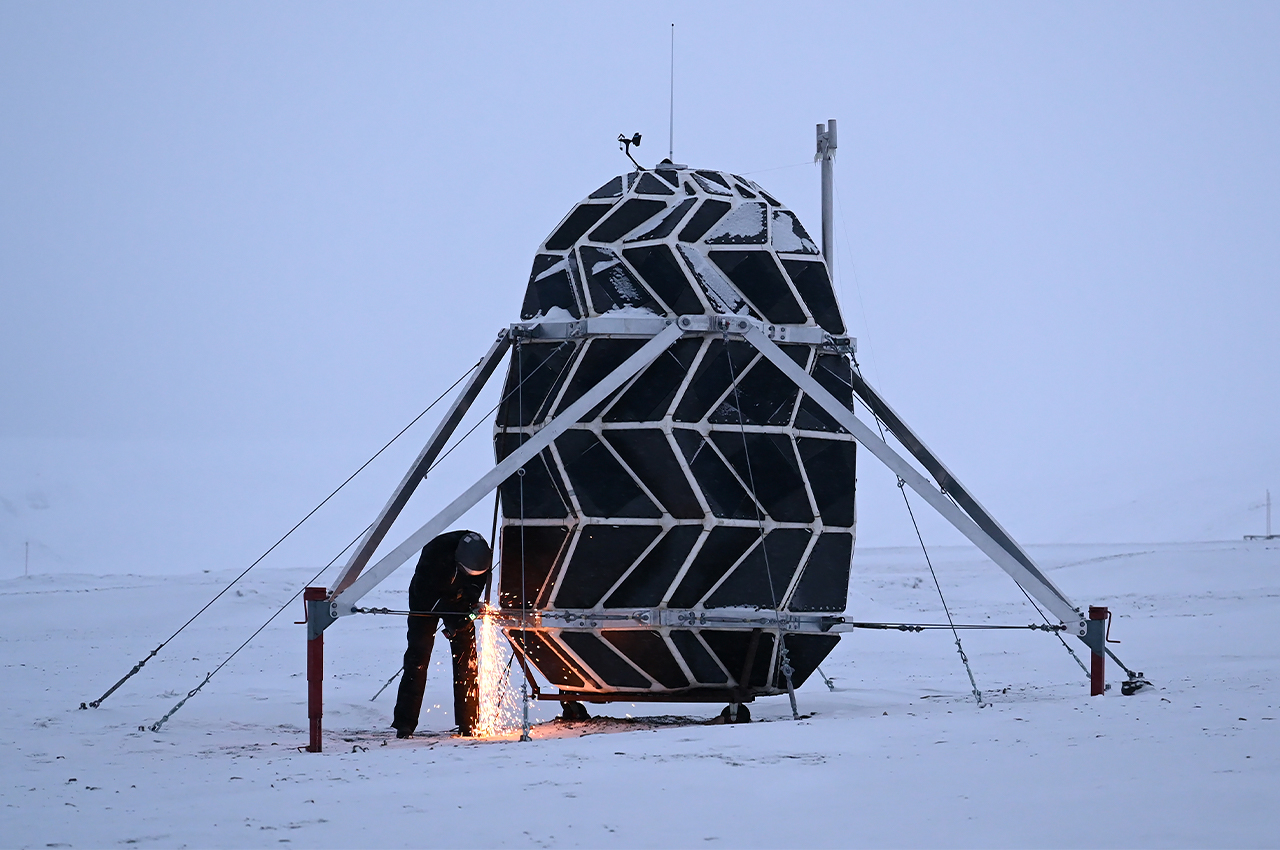
Danish architect Bjarke Ingels’s Mars Science City is designed to operate as a space simulation campus for scientists to understand “humanity’s march into space”. Located in Dubai, the experimental city is built to hold a team for a year which will recreate the conditions expected on Mars. The laboratories are dedicated to investigating self-sufficient forms of energy, food and water for future life on Mars. Ingels, the founder of Danish firm BIG, will work on the AED 500 million (£101 million) project with a team of Emirati scientists, engineers, and designers led by the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre and the Dubai Municipality. “The UAE seeks to establish international efforts to develop technologies that benefit humankind, and that establishes the foundation of a better future for more generations to come,” said Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid, vice president and prime minister of the UAE, and ruler of Dubai.



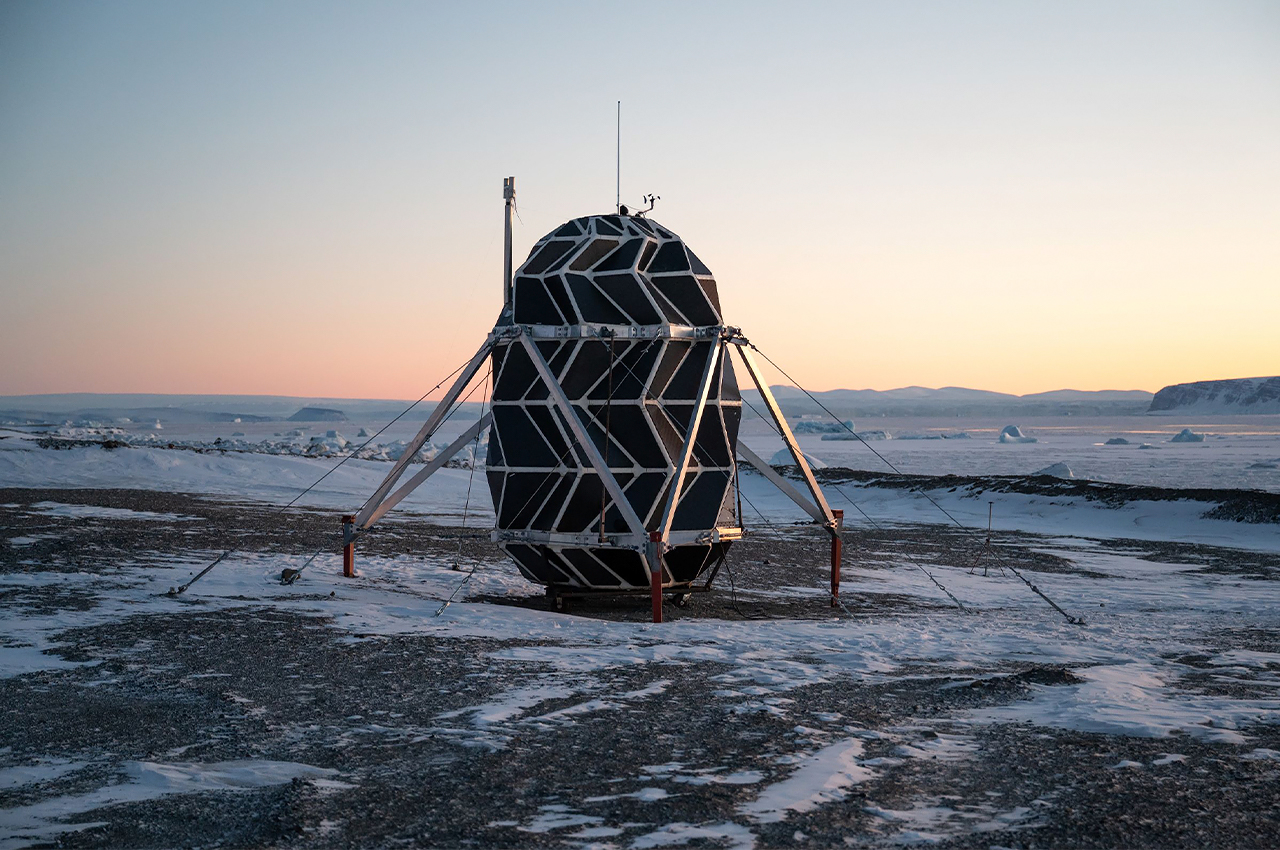
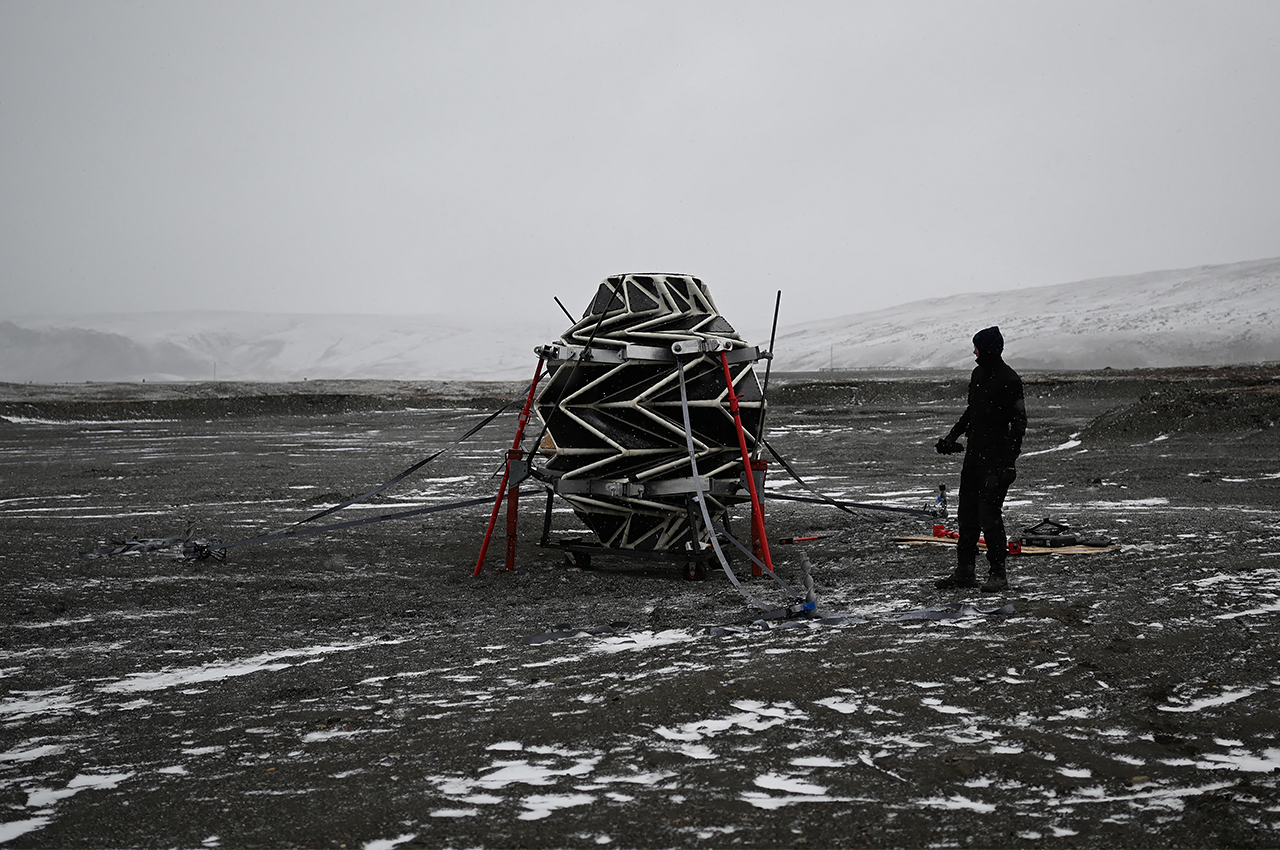
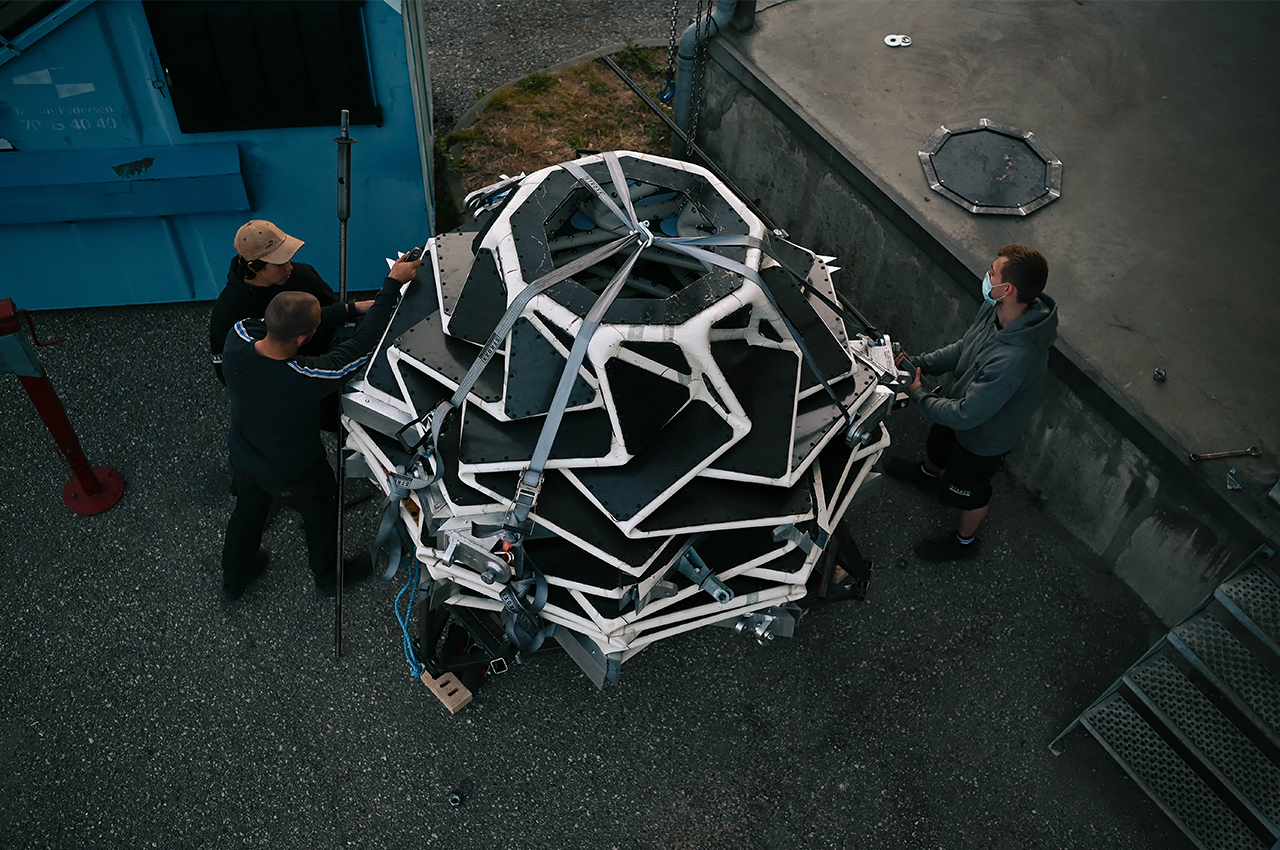
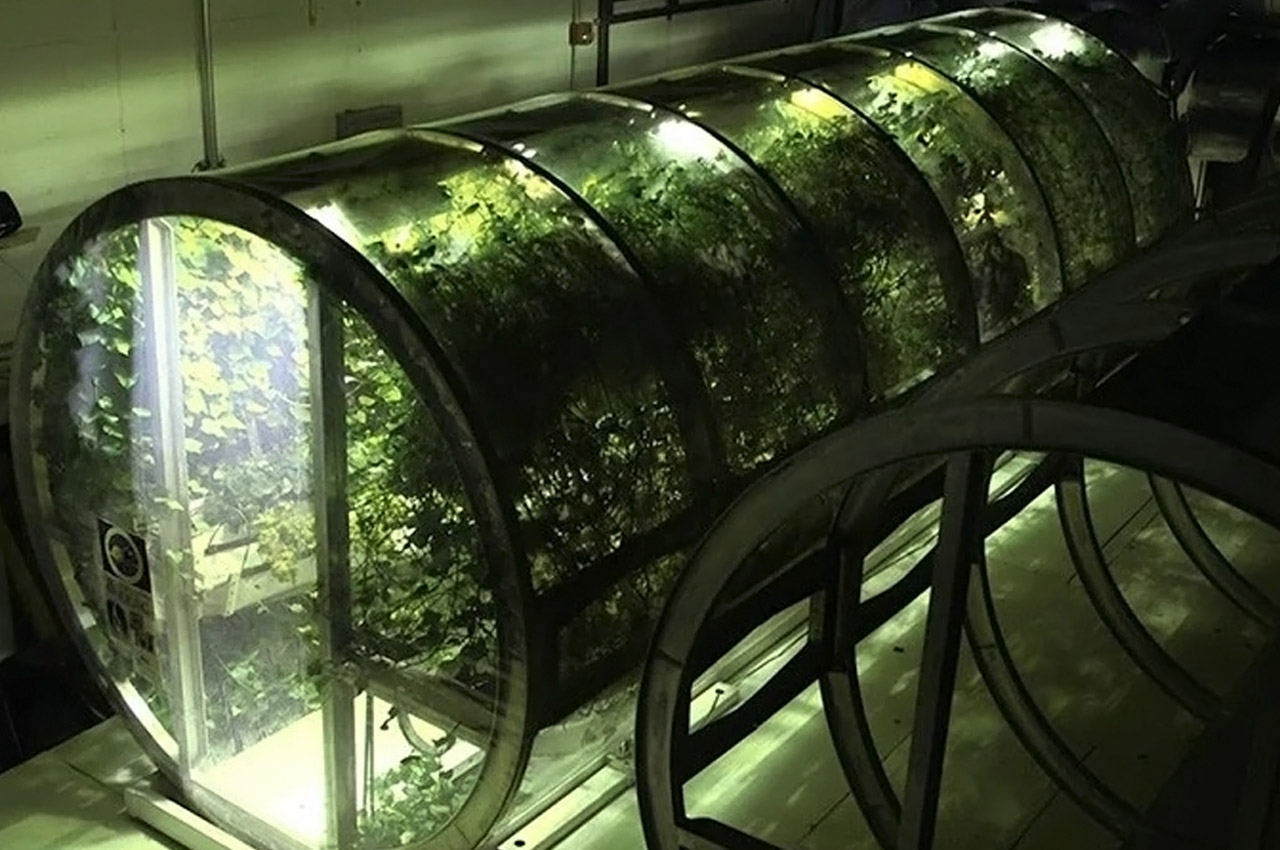
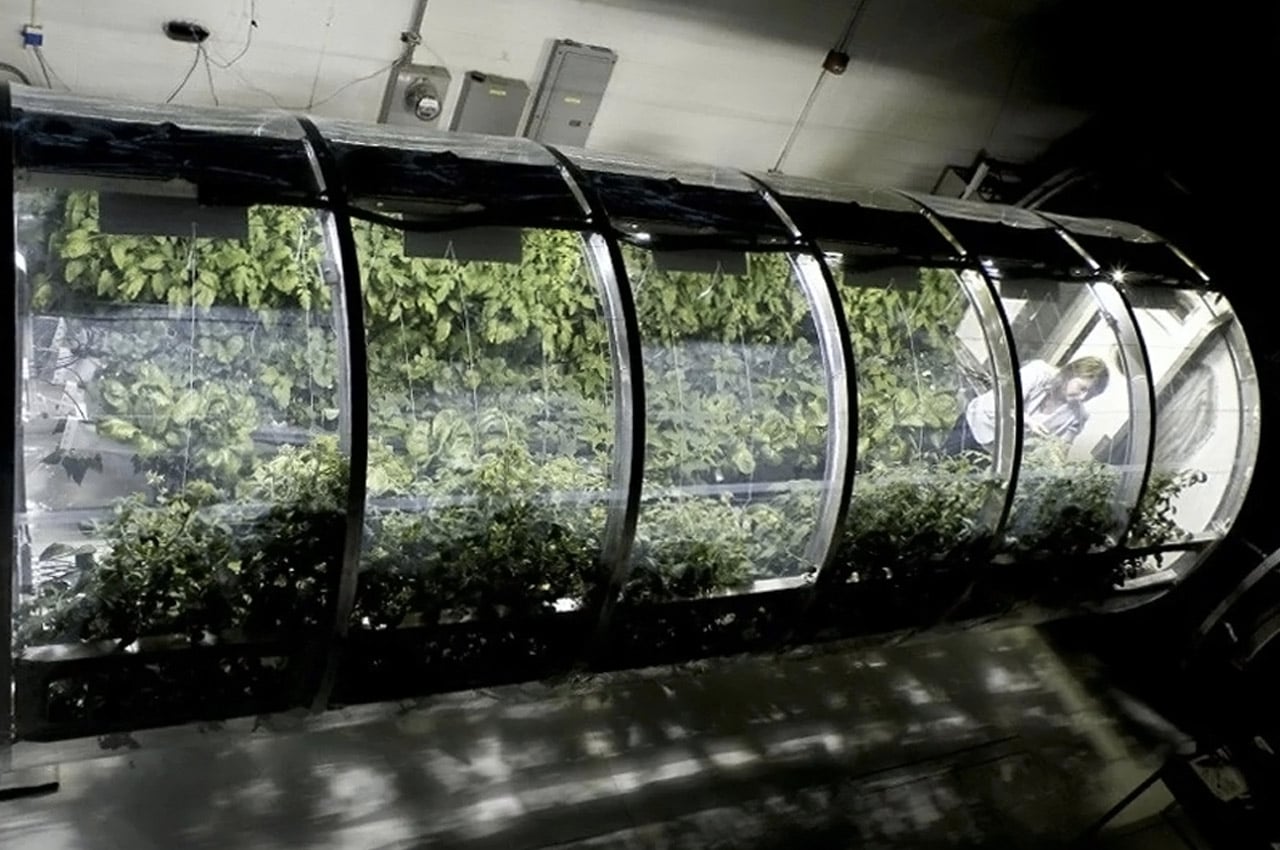
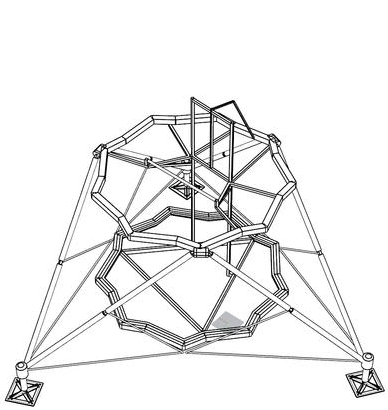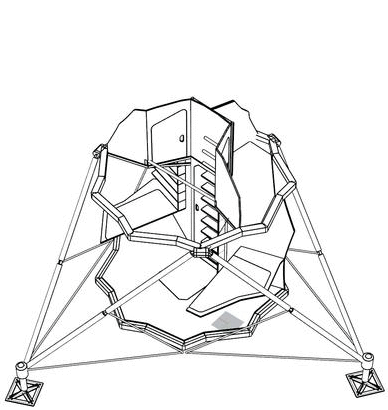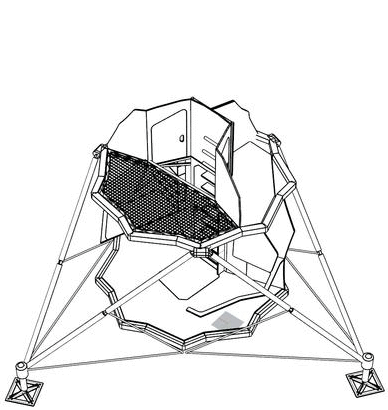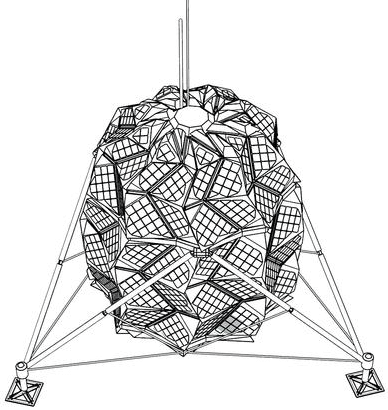
NASA scientists and the University of Arizona’s agricultural department have teamed up to develop this inflatable greenhouse that can be used to grow vegetables in deep space. The result of this experiment is to sustain astronauts on a vegetarian diet while staying for long term on the Moon or Mars. While NASA scientists have been growing crops in the International Space Station, this 18×7 feet design can be used for air revitalization, water recycling, or waste recycling and also repurposing the carbon dioxide exhaled by the astronauts. R. Gene Giacomelli, director of the controlled environment agriculture center at the University of Arizona states “We’re mimicking what the plants would have if they were on earth, and using of these processes for life support. The entire system of the lunar greenhouse does represent, in a small way, the biological systems that are here on earth.”



Warith Zaki and Amir Amzar plan to use the bamboo grown on Mars to actually build the first colony, named Seed of Life, on Mars. The conceptual colony design is actually a series or cluster of structures woven by autonomous robots from bamboos. The aim of the project is to create structures that do not rely on construction materials being shipped from Earth or to use 3D printing. “After doing a lot of research on Mars colonization, we realized that half of the ideas would go about deploying fully synthetic materials made on earth to build shelters, while the other half is about using the locally available regolith,” said Zaki and Amzar. “Human civilization has yet to build anything on any other planet outside of Earth. That fact alone opens up infinite possibilities of what could or should be used. Sure, 3D printing seems to be a viable proposition, but with thousands of years worth of experience and techniques in shelter construction, why shouldn’t we tap on other alternatives too?”


The construction industry emits 4 times more CO2 than the aviation industry and that is enough proof they must focus on ecodesign to reduce their colossal impact especially when sustainable materials, like mycelium composites, already exist! This material is created by growing mycelium–the thread-like main body of a fungus–of certain mushroom-producing fungi on agricultural wastes. The mycelia are composed of a network of filaments called “hyphae,” which are natural binders and they also are self-adhesive to the surface they grow on. This mushroom material is biodegradable, sustainable, and a low-cost alternative to construction materials while also possessing thermal and fire-resistant properties. The Living has designed an organic 42 feet tall mycelium tower to show the potential of using mushrooms for stable structures which is just one of many such projects. Mycelium materials are also being tested for being acoustic absorber, packaging materials, and building insulation. Even NASA is currently researching using mycelium to build sustainable habitable dwellings on Mars – if we have to move into a mushroom house, might as well test it on Earth first, right?


23 shares Dezeen – Mars One
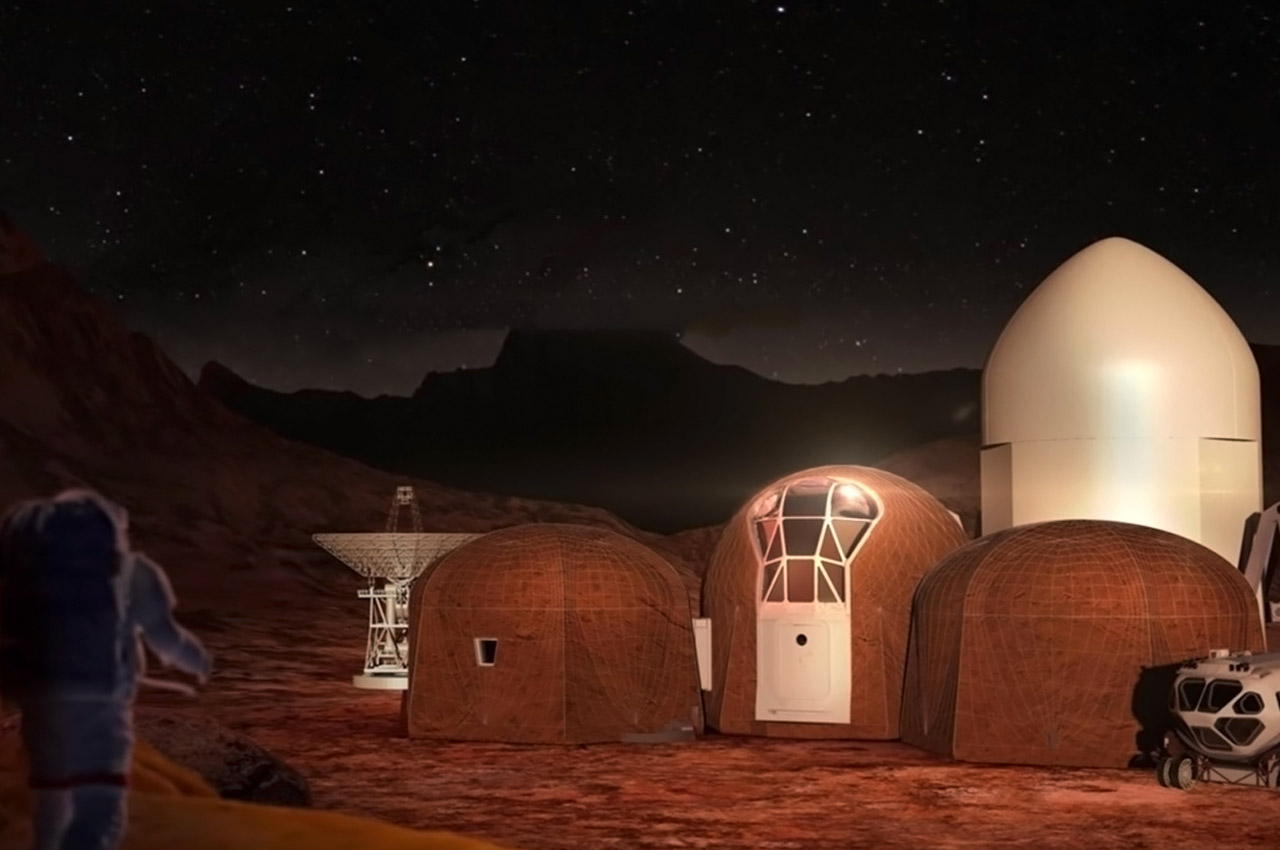
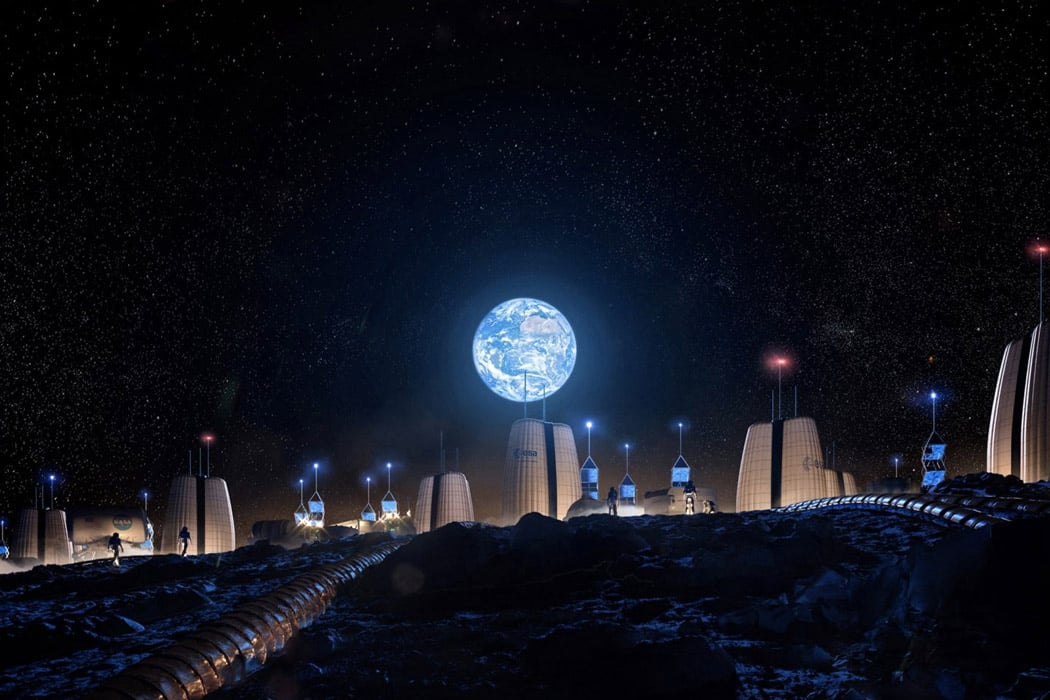
Would you be ready to move to Mars and establish the first civilization on Mars? Well, more than 200,000 people from 140 countries have applied for a one-way ticket to join such a human settlement. Established by non-profit organization Mars One, the £4 billion project, founded by Dutch entrepreneur Bas Lansdorp in 2012, plans to establish the first permanent human settlement on Mars in 2023 and has proposed that humans will live in a modular environment made up of multiple inflatable units. “As the habitat will be modular, and constructed using fully redundant systems, even if one inflatable unit is damaged beyond repair, the habitat will still be secure and fully functional,” said the organization. “The first footprint on Mars and lives of the crew thereon will captivate and inspire generations; it is this public interest that will help finance this human mission to Mars,” said Mars One.


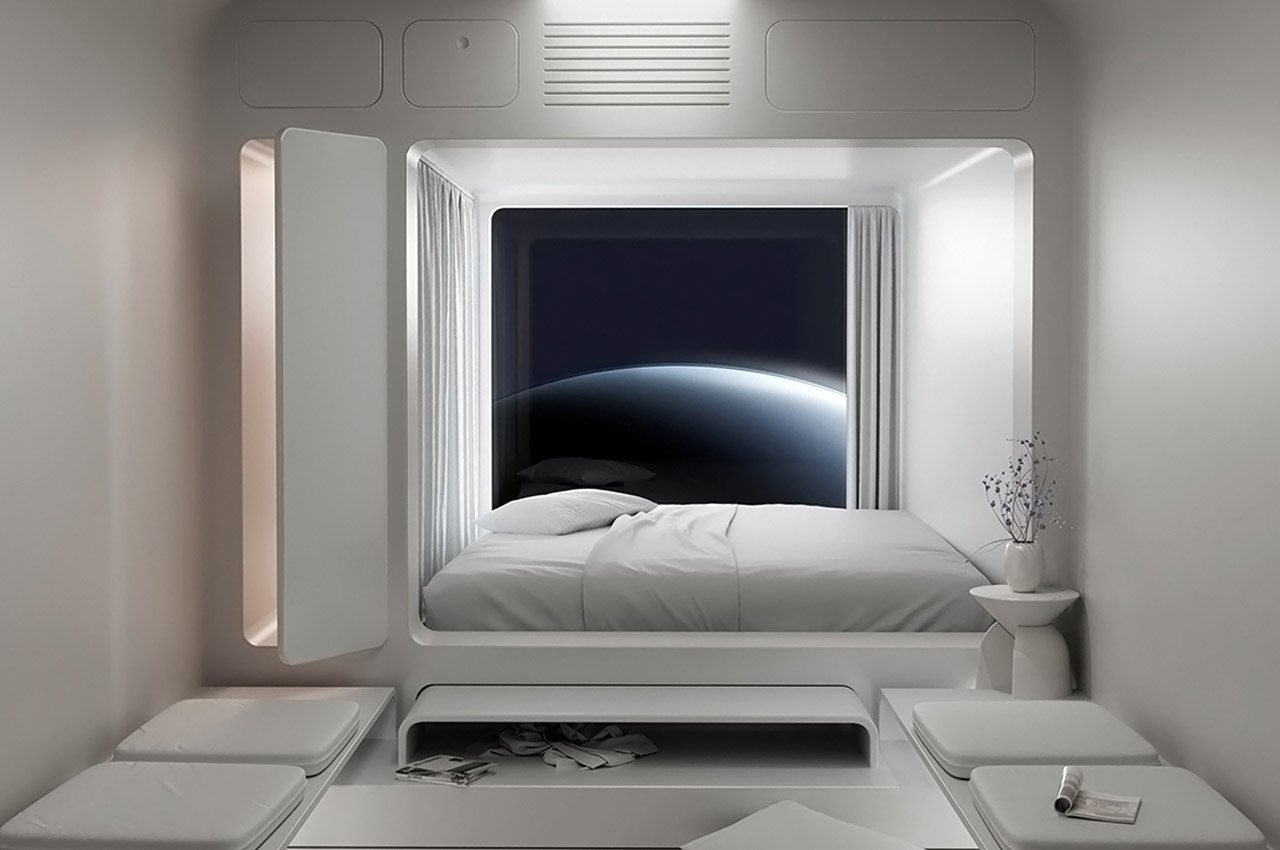
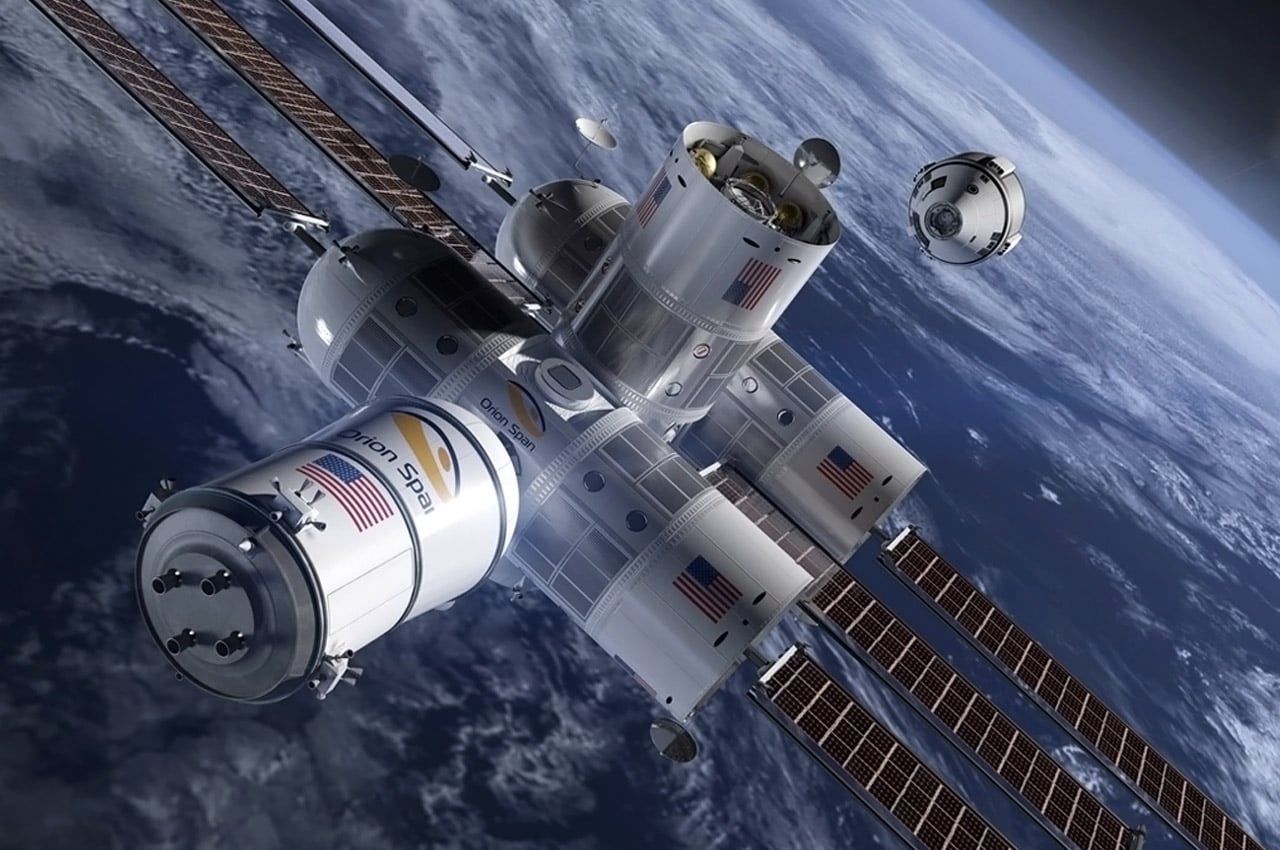
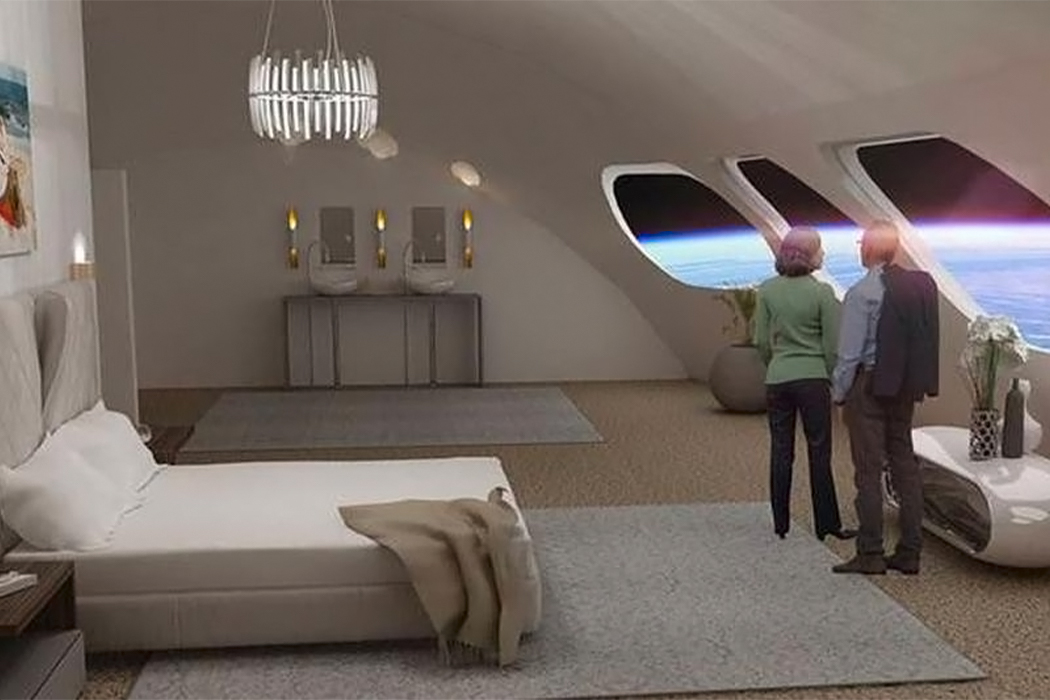
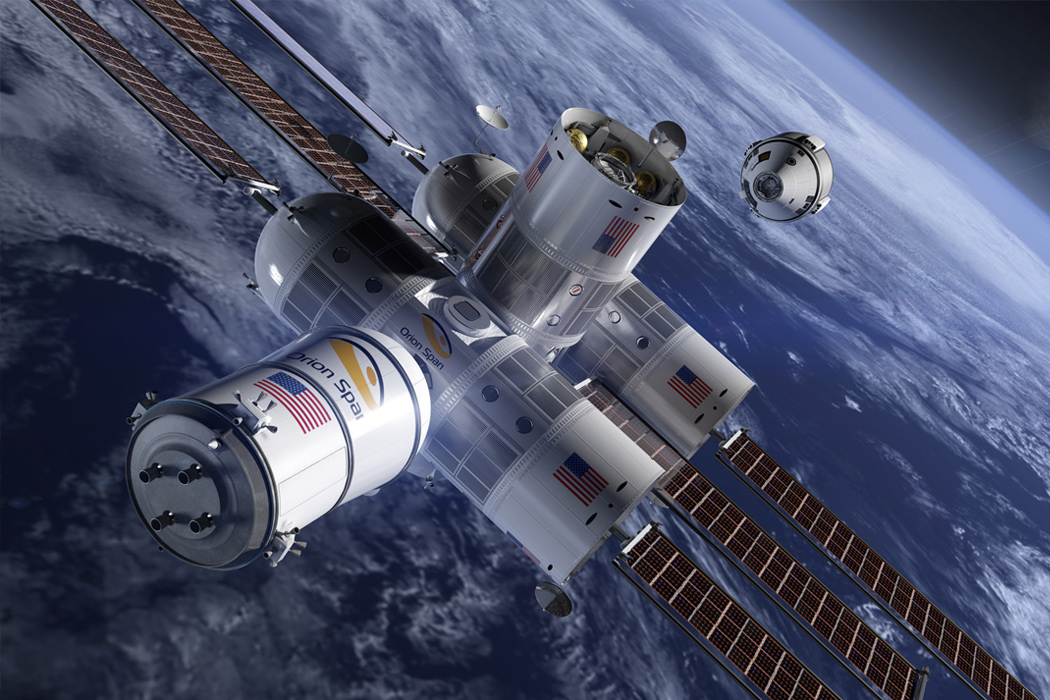
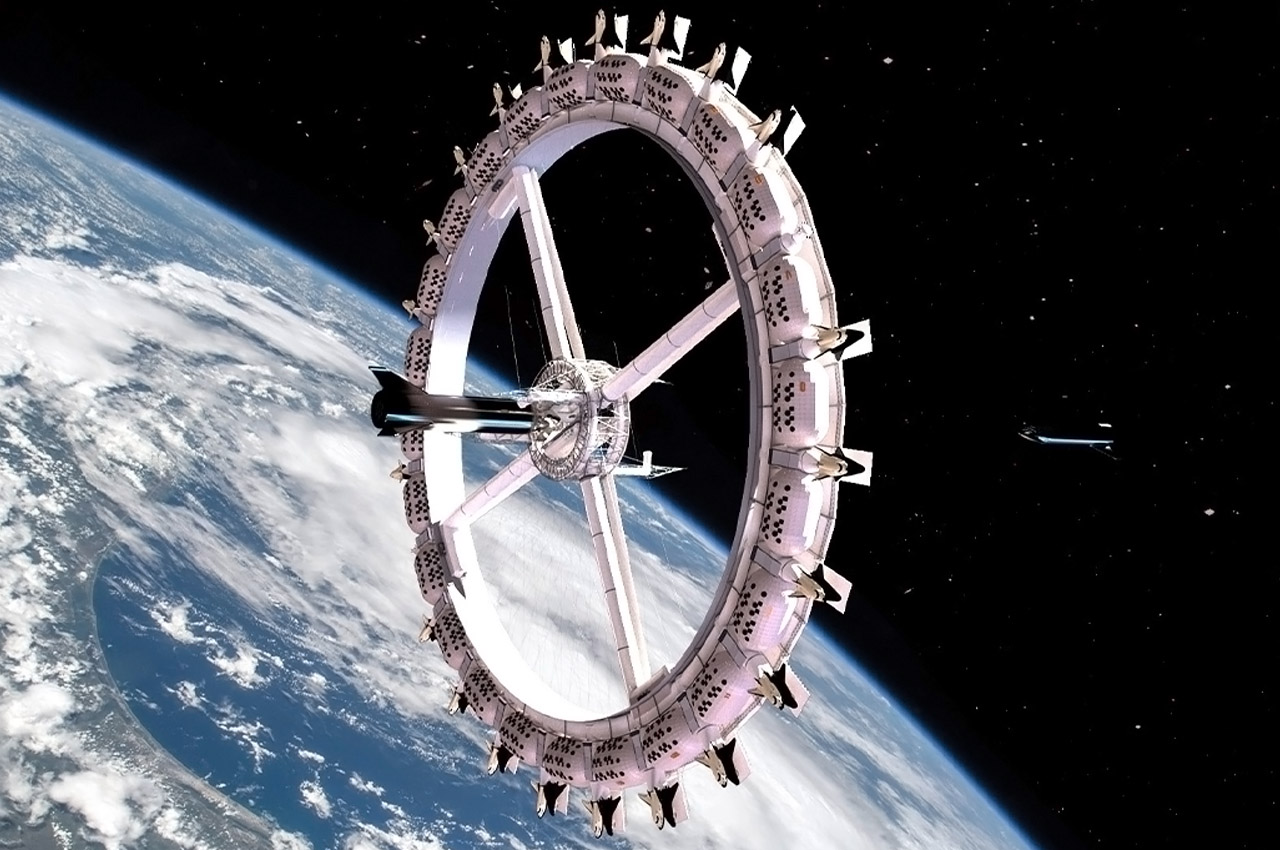
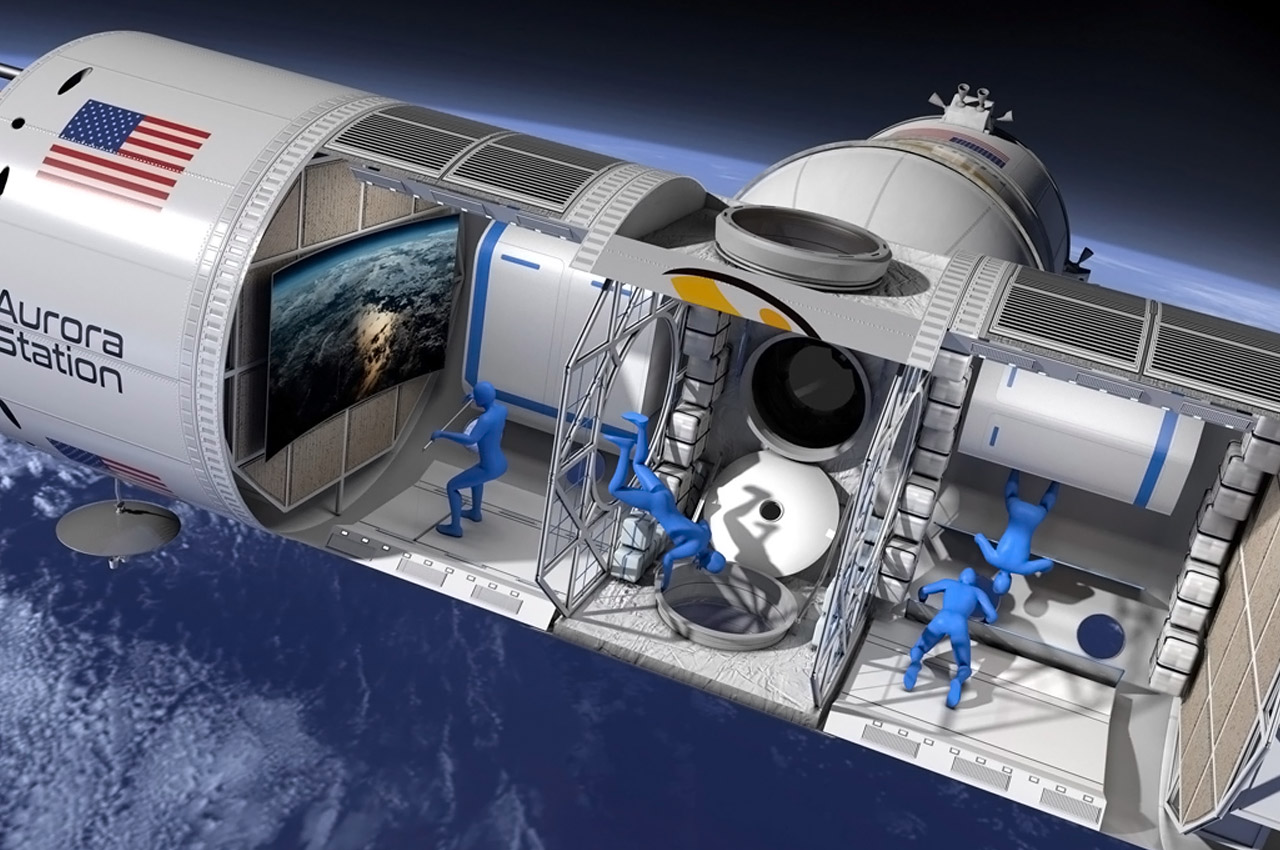
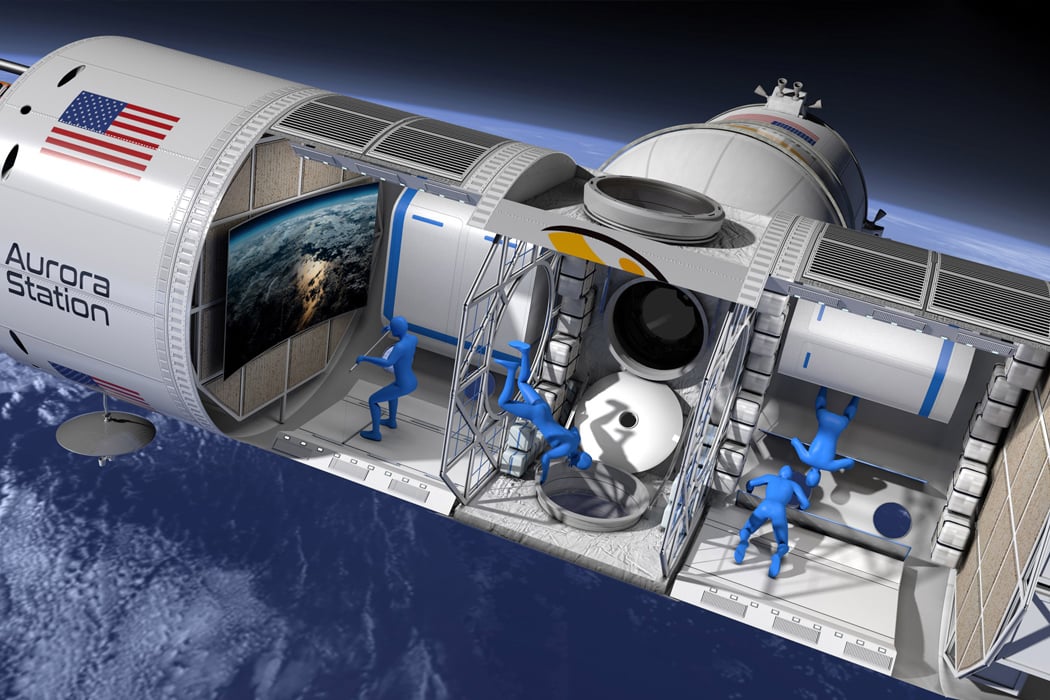
Texas-based startup Orion Span plans to utilize space in a whole new way, by creating a luxury space hotel designed to open in 2022 (I’m sure COVID was not featured in their plans!) Named Aurora Station, the £70 million space hotel is designed to orbit 200 miles above the earth. The hotel plans to hold four guests and two crew members for a total 12-day trip and is priced at about £6.7 million per person. “Upon launch, Aurora Station goes into service immediately, bringing travelers into space quicker and at a lower price point than ever seen before, while still providing an unforgettable experience,” said Frank Bunger, founder of Orion Span. The entire design will be processed by a team led by Frank Eichstadt, who is credited as being the principal architect on the International Space Station’s Enterprise module. “Orion Span has additionally taken what was historically a 24-month training regimen to prepare travelers to visit a space station and streamlined it to three months, at a fraction of the cost,” said Bunger.